least common multiple (LCM) least common denominator (LCD
advertisement

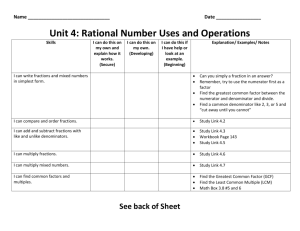
Vocab Lesson 8–2 Lesson 8–5 common factor common multiple 12: 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 12 4: 4, 8, 12, 16, 20, 24, 28, 32, 36 . . . 6: 6, 12, 18, 24, 30, 36, 42 . . . 30: 1, 2, 3, 5, 6, 10, 15, 30 common multiples of 4 and 6: 12, 24, 36 common factors of 12 and 30: 1, 2, 3, 6 Lesson 8–1 Lesson 8–3 denominator equivalent fractions _58 = 5 ÷ 8 8 =_ 4 _ 7 14 Lesson 8–1 Lesson 8–2 fraction 1 3 greatest common factor (GCF) 1 3 12: 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 12 _3 30: 1, 2, 3, 5, 6, 10, 15, 30 Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. 2 greatest common factor: 6 Lesson 8–6 Lesson 8–5 least common denominator (LCD) 2×2 =_ 4 _2 = _ × 6 3 3 2 1×1 =_ 1 _1 = _ 6 6×1 0544_0548_Gr5_S_C08MVC_116196.indd least common multiple (LCM) 4: 4, 8, 12, 16, 20, 24, 28, 32, 36 . . . 6: 6, 12, 18, 24, 30, 36, 42 . . . 6 is the LCD least common multiple of 4 and 6: 12 6 545 10/19/11 Program: GMH CCM Component: SE Vendor: Quad Graphics Grade: 5 PDF Pass 1:29 PM Ideas for Use • Design a crossword puzzle. Use the definition for each word as the clues. A whole number that is a multiple of two or more numbers. A number that is a factor of two or more numbers. Use a thesaurus to write a synonym and an antonym for common. When are factors useful? Fractions that have the same value. The bottom number in a fraction. It represents the total number of equal parts. Give an example of two fractions that are equivalent. Write a tip to help you remember which number is the denominator in a fraction. The greatest of the common factors of two or more numbers. A number that represents equal parts of a whole or parts of a set. Find the greatest common factor of 24 and 36. Show your work. Explain how fractions represent division. The least multiple, other than 0, common to sets of multiples. The least common multiple of the denominators of two fractions. How can finding the LCM of two numbers be helpful in a real-world situation? Explain why finding the LCD is important in working with fractions. 0544_0548_Gr5_S_C08MVC_116196.indd 546 Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. • Develop categories for the words. Sort them by category. Ask another student to guess each category. 9/27/11 11:43 AM Program: GMH CCM Component: SE Vendor: Quad Graphics Grade: 5 PDF Pass Vocab Lesson 8–5 Lesson 8–1 multiple 7, 1×7 14, 2×7 21, 3×7 28, 4×7 35, 5×7 42,... 6×7 numerator _58 = 5 ÷ 8 Lesson 8–3 simplest form = Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. 8÷ 4 =2 12 ÷ 4 = 3 0544_0548_Gr5_S_C08MVC_116196.indd 547 10/19/11 Program: GMH CCM Component: SE Vendor: Quad Graphics Grade: 5 PDF Pass 1:30 PM Ideas for Use • Write a tally mark on each card every time you read the word in this chapter or use it in your writing. Challenge yourself to use at least 3 or 4 tally marks for each card. • Write the names of lessons you would like to review on the front of each blank card. Write a few study tips on the back of each card. The top number in a fraction. It tells how many of the equal parts are being used. A multiple of a number is the product of that number and any whole number. The Latin root numer means “number.” Write two words that contain this root. Explain why 32 is a multiple of 8. What is another multiple of 8? A fraction in which the GCF of the numerator and the denominator is 1. Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Form is a word that can also be used as a verb. Write a sentence using it as a verb. 0544_0548_Gr5_S_C08MVC_116196.indd 548 9/27/11 11:44 AM Program: GMH CCM Component: SE Vendor: Quad Graphics Grade: 5 PDF Pass







![fihkmxg fhgbmh kbs:zyh m>k:i]nmb<: =: i](http://s2.studylib.net/store/data/018817581_1-87f1bd80b992dd286d6f144592ad96d5-300x300.png)