8.1 Exploring Integer Multiplication
advertisement

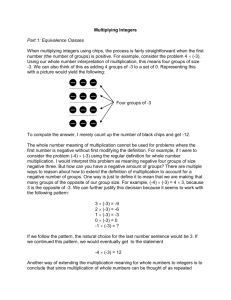
Exploring Integer Multiplication Focus on… After this lesson, you will be able to... φ multiply integers using integer chips The Columbia Icefield is the largest mass of ice in North America below The Columbia Icefield is a major source of fresh water. Melt water from the icefield feeds rivers that flow to the Arctic Ocean, the Pacific Ocean, and Hudson’s Bay. the Arctic Circle. The icefield lies across the Alberta–British Columbia border in the Rockies. Six large glaciers flow from the icefield. One of them, the Athabasca Glacier, is a popular tourist destination in Jasper National Park. The Athabasca Glacier has been melting for over a century. The front edge or “snout” of the glacier has been receding at an average of approximately 12 m per year. At that rate, how far would it recede in four years? How can you use integer chips to multiply two integers? • red and blue integer chips Literacy Link Representing Integers Integer chips are coloured disks that represent integers. In this book, one red chip represents +1, and one blue chip represents -1. +1 286 −1 1. Multiplication can be expressed as a repeated addition. (+3) × (+2) = (+2) + (+2) + (+2) a) Use red integer chips to model the addition (+2) + (+2) + (+2). b) Copy and complete the multiplication statement (+3) × (+2) = . Express (+4) × (+3) as a repeated addition. b) Use red integer chips to model the addition. c) Copy and complete the multiplication statement (+4) × (+3) = . 2. a) Express (+3) × (-5) as a repeated addition. b) Use blue integer chips to model the addition. c) Copy and complete the multiplication statement (+3) × (-5) = . 3. a) MHR • Chapter 8 08_ML8_Chapter08_6th.indd 286 4/9/08 4:23:55 PM 4. 5. Use integer chips to model each multiplication. Copy and complete each multiplication statement. a) (+3) × (+5) = b) (+2) × (+3) = c) (+4) × (-3) = d) (+3) × (-4) = Can you use the same method as in #1 to #4 to complete the multiplication (-2) × (+3) or the multiplication (-3) × (-4)? Explain. 6. a) The diagrams show how to model the multiplications from #5 by using zero pairs. Describe each model. (-2) × (+3) Use enough zero pairs so that there are two groups of three red chips available to remove. Literacy Understanding Multiplication The product of 4 and 2 is 8, because 4 × 2 = 8. The multiplication statement 4 × 2 = 8 means that 4 groups of 2 make 8. You can also think of 4 × 2 as the repeated addition 2 + 2 + 2 + 2. Literacy (-3) × (-4) Link Link Modelling With Zero Pairs A zero pair is a pair of integer chips, with one chip representing +1 and one chip representing -1. +1 −1 A zero pair represents zero because (+1) + (-1) = 0. Any whole number of zero pairs represents zero. b) 7. Copy and complete each multiplication statement. (-2) × (+3) = (-3) × (-4) = Use integer chips to model each multiplication. Copy and complete each multiplication statement. a) (-4) × (-3) = b) (-5) × (+2) = c) (-2) × (+4) = d) (-1) × (-4) = Reflect on Your Findings 8. How can you use integer chips to multiply two integers? In your description, state when you use zero pairs. How do you determine the number of zero pairs to use? 8.1 Exploring Integer Multiplication • MHR 08_ML8_Chapter08_6th.indd 287 287 4/9/08 4:23:57 PM Example 1: Multiply Using Integer Chips Determine each product using integer chips. Copy and complete each multiplication statement. a) (+5) × (+2) b) (+6) × (-2) c) (-3) × (+2) d) (-2) × (-4) Solution Strategies a) Model It There are 10 red chips. Strategies (+5) × (+2) = (+2) + (+2) + (+2) + (+2) + (+2) Insert 5 groups with 2 red chips in each group. What other strategy could you use? The product is +10. The multiplication statement is (+5) × (+2) = +10. b) There are 12 blue chips. (+6) × (-2) = (-2) + (-2) + (-2) + (-2) + (-2) + (-2) Insert 6 groups with 2 blue chips in each group. The product is -12. The multiplication statement is (+6) × (-2) = -12. c) The negative sign in -3 shows that you need to remove 3 groups. Each group will contain 2 red chips. So, you need to remove a total of 6 red chips. Start with 6 zero pairs, so that there are enough red chips to remove. Now remove the red chips. There are 6 blue chips. The product is -6. The multiplication statement is (-3) × (+2) = -6. 288 MHR • Chapter 8 08_ML8_Chapter08_6th.indd 288 4/9/08 4:23:58 PM d) The negative sign in -2 shows that you need to remove 2 groups. Each group will contain 4 blue chips. So, you need to remove a total of 8 blue chips. Start with 8 zero pairs, so that there are enough blue chips to remove. Now remove the blue chips. There are 8 red chips. The product is +8. The multiplication statement is (-2) × (-4) = +8. Determine each product using integer chips. Use diagrams to show your thinking. a) (+4) × (+2) b) (+5) × (-2) c) (-4) × (+2) d) (-6) × (-1) Example 2: Apply Integer Multiplication For 5 h, the temperature in Flin Flon fell by 3 °C each hour. What was the total change in temperature? Solution Use the multiplication of two integers to represent the situation. Represent the time of 5 h by the integer +5. Represent the 3 °C decrease in each hour by the integer -3. The total change in temperature can be represented by the expression (+5) × (-3). Multiply (+5) × (-3) using integer chips. The number of hours times the change per hour gives the total change. The product is -15. The total change in temperature was a decrease of 15 °C. For 4 h, the temperature in Victoria fell by 2 °C each hour. What was the total change in temperature? Flin Flon lies along the Manitoba– Saskatchewan border. The town is named after a fictional character called Professor Josiah Flintabbatey Flonatin. He was the hero of a science fiction novel called The Sunless City. In this novel, Josiah explored a bottomless lake in a submarine and discovered a tunnel lined with gold. Flin Flon was named after him because of the large mineral deposits discovered there. 8.1 Exploring Integer Multiplication • MHR 08_ML8_Chapter08_6th.indd 289 289 4/9/08 4:24:00 PM • To model the multiplication of an integer by a positive integer, you can insert integer chips of the appropriate colour. (+2) × (-3) = -6 • To model the multiplication of an integer by a negative integer, you can remove integer chips of the appropriate colour from zero pairs. (-2) × (-3) = +6 1. David said that he could model the multiplication (+3) × (-7) using 3 red chips and 7 blue chips. a) Do you agree with David? Explain. b) What chips would you use to model (+3) × (-7)? Explain. 2. To model (-3) × (-5), Raini places 15 zero pairs on her desk. a) Why did she use 15 zero pairs? b) What should she do next? 3. a) b) 4. 290 Paolo models (-2) × (+3) as shown in the diagram. He determines the correct product, -6. Explain why his method works. Could Paolo model the product if he started with 4 zero pairs? Explain. Jasmine said that she did not need any integer chips to multiply 0 × (+2) or to multiply (-3) × 0. Explain her thinking. MHR • Chapter 8 08_ML8_Chapter08_6th.indd 290 4/9/08 4:24:01 PM 10. What multiplication statement does each set of diagrams represent? a) For help with #5 to #14, refer to Example 1 on pages 288–289. 5. Write each repeated addition as a multiplication. a) (+1) + (+1) + (+1) + (+1) + (+1) b) (-6) + (-6) 6. Write each expression as a multiplication. a) (+7) + (+7) + (+7) b) (-4) + (-4) + (-4) + (-4) 7. Write each multiplication as a repeated addition. a) (+3) × (+8) b) (+5) × (-6) 8. Write each expression as a repeated addition. a) (+7) × (+2) b) (+4) × (-9) 9. What multiplication statement does each set of diagrams represent? b) 11. What multiplication statement does each set of diagrams represent? a) a) b) b) 8.1 Exploring Integer Multiplication • MHR 08_ML8_Chapter08_6th.indd 291 291 4/9/08 4:24:02 PM 12. What multiplication statement does each set of diagrams represent? 15. An aircraft descends at 3 m/s for 12 s. Use the multiplication of two integers to represent the situation. How far does the aircraft descend? 16. A building has 10 storeys above ground and 3 storeys below ground. Each storey has a height of 4 m. a) What is the total height of the building above ground? b) What is the total depth of the building below ground? 17. An oil rig is drilling a well at 2 m/min. How deep is the well after the first 8 min? 18. Does doubling an integer always result in an integer of greater value? Explain. 19. In a magic square, the numbers in each row, column, and diagonal have the same sum. This is called the magic sum. a) What is the magic +2 +3 -2 sum for this magic square? a) b) 13. Copy and complete each multiplication statement. a) (+4) × (+6) b) (+7) × (-2) c) (-1) × (+5) d) (-8) × (-2) -3 +1 +5 +4 -1 0 Multiply each integer in the square by -2. Is the result another magic square? If so, what is the new magic sum? c) Create a magic square with a magic sum of -12. b) For help with #14 to #17, refer to Example 2 on page 289. 14. 292 Use the multiplication of two integers to represent each situation. Then determine the product and explain its meaning. a) The temperature increased for 6 h at 2 °C per hour. b) Ayesha repaid some money she owed in 4 instalments of $8 each. 20. Arrange the following numbers of +1s and -1s in the small squares on a threeby-three grid so that each row, column, and diagonal has a product of -1. a) six +1s, three -1s b) four +1s, five -1s MHR • Chapter 8 08_ML8_Chapter08_6th.indd 292 4/9/08 4:24:02 PM