Mathematics Pacing Resource Document
advertisement

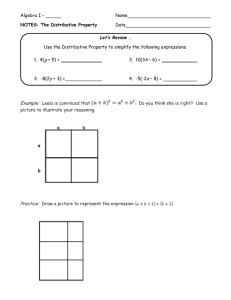
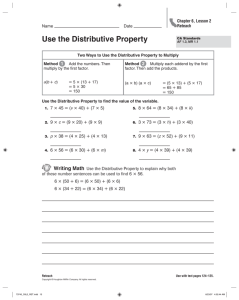
Mathematics Pacing Resource Document 6.NS.7 Standard: 6.NS.7: Find the greatest common factor of two whole numbers less than or equal to 100 and the least common multiple of two whole numbers less than or equal to 12. Use the distributive property to express a sum of two whole numbers from 1 to 100, with a common factor as a multiple of a sum of two whole numbers with no common factor. Teacher Background Information: What is the greatest common factor (GCF) of 24 and 36? How can you use factor lists or the prime factorizations to find the GCF? Solution: 22 3 = 12. Students should be able to explain that both 24 and 36 have 2 factors of 2 and one factor of 3, thus 2 x 2 x 3 is the greatest common factor.) What is the least common multiple (LCM) of 12 and 8? How can you use multiple lists or the prime factorizations to find the LCM? Solution: 23 3 = 24. Students should be able to explain that the least common multiple is the smallest number that is a multiple of 12 and a multiple of 8. To be a multiple of 12, a number must have 2 factors of 2 and one factor of 3 (2 x 2 x 3). To be a multiple of 8, a number must have 3 factors of 2 (2 x 2 x 2). Thus the least common multiple of 12 and 8 must have 3 factors of 2 and one factor of 3 ( 2 x 2 x 2 x 3). Rewrite 84 + 28 by using the distributive property. Have you divided by the largest common factor? How do you know? Given various pairs of addends using whole numbers from 1-100, students should be able to identify if the two numbers have a common factor. If they do, they identify the common factor and use the distributive property to rewrite the expression. They prove that they are correct by simplifying both expressions. o 27 + 36 = 9 (3 + 4) 63 = 9 x 7 63 = 63 o 31 + 80 There are no common factors. I know that because 31 is a prime number, it only has 2 factors, 1 and 31. I know that 31 is not a factor of 80 because 2 x 31 is 62 and 3 x 31 is 93. https://learnzillion.com/lessons/2721-find-the-gcf-of-two-numbers-using-the-distributive-property (GCF using the distributive property) Process Standards to Emphasize with Instruction of 6.NS.7: 6.PS.7: Look for and make use of structure. 6.PS.8: Look for and express regularity in repeated reasoning. Indianapolis Public Schools Curriculum and Instruction Mathematics Pacing Resource Document 6.NS.7 Standard: 6.NS.7: Find the greatest common factor of two whole numbers less than or equal to 100 and the least common multiple of two whole numbers less than or equal to 12. Use the distributive property to express a sum of two whole numbers from 1 to 100, with a common factor as a multiple of a sum of two whole numbers with no common factor. Lesson Plans/Print Activities: Web-based Practice: Indiana Math Connects: Lesson 4-1, 4-5, 12-1 https://www.engageny.org/resource/grade-6-mathematics-module-2topic-d-lesson-16 Students apply knowledge of odd and even numbers to understand factors and multiples. (foundational lesson) https://www.khanacademy.org/math/cc-sixth-grade-math/cc-6thfactors-and-multiples/cc-6th-distributiveproperty/e/distributive_property Khan Academy online practice https://www.engageny.org/resource/grade-6-mathematics-module-2topic-d-lesson-17 Students apply divisibility rules, specifically for 3 and 9, to understand factors and multiples. (foundational lesson) http://www.glencoe.com/sites/common_assets/mathematics/mc1 /cim/chapter_04/M1_06/M1_06_dev_100.html Greatest Common Factor online practice http://glencoe.mheducation.com/sites/0078923379/student_view 0/chapter4/lesson5/personal_tutor.html Personal Tutor http://glencoe.mheducation.com/sites/0078923379/student_view 0/chapter4/lesson5/self-check_quizzes.html Self-Check Quiz http://glencoe.mheducation.com/sites/0078923379/student_view 0/chapter12/lesson1/index.html Distributive Property personal tutor and self-check quizzes https://www.engageny.org/resource/grade-6-mathematics-module-2topic-d-lesson-18 Students find the least common multiple and greatest common factor and apply factors to the Distributive Property. https://www.engageny.org/resource/grade-6-mathematics-module-2topic-d-lesson-19 Students explore and discover that Euclid’s Algorithm is a more efficient means to finding the greatest common factor of larger numbers and determine that Euclid’s Algorithm is based on long division. (extension lesson) Greatest Common Factor & Distributive Property Lesson Plan Indianapolis Public Schools Curriculum and Instruction Mathematics Pacing Resource Document 6.NS.7 Item Bank: 1) What is the greatest common factor of 32 and 56 Answer: C A) 2 B) 16 C) 8 D) 1 2) What is the least common multiple of 3, 4, and 8? A) 16 B) 6 C) 32 D) 24 3) Which number could be used to express 25 + 10 in the following using the distributive property Answer: B 5 ( ___ + 2)? A) 8 B) 5 C) 6 D) 3 4) Kate waters the garden every 3 days and weeds it every 4 days. She does both on April 2nd. Answer: April 14th What is the next date that she will both water and weed her garden? Answer:_______________________ 5) List all of the common factors of 12 and 18? Answer: 1,2,3,6 Use the distributive property to express the sum 12 + 18 using a common factor. Possible answers: 2(6+9) 3(4+6) 6(2+3) _____ ( _____ + _____ ) = _____ Illustrative Math Tasks for 6.NS.7 https://www.illustrativemathematics.org/content-standards/6/NS/B/4/tasks Indianapolis Public Schools Curriculum and Instruction Mathematics Pacing Resource Document 6.NS.7 Item Bank: The least common multiple of 8, 12, and a third number is 120. Which of the following could be the third number? Answer: A A. 15 B. 16 C. 24 D. 32 E. 48 Indianapolis Public Schools Curriculum and Instruction Mathematics Pacing Resource Document 6.NS.7 Item Bank: (Readiness I) Indianapolis Public Schools Curriculum and Instruction Mathematics Pacing Resource Document 6.NS.7 Item Bank: (Readiness II) Indianapolis Public Schools Curriculum and Instruction