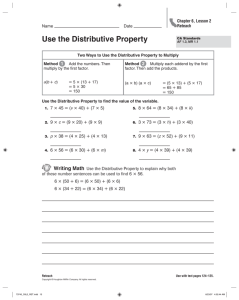
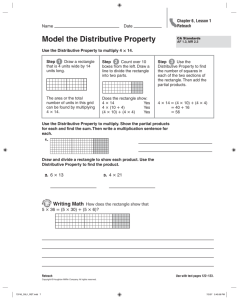
The Distributive Property (Pages 98–102)
advertisement
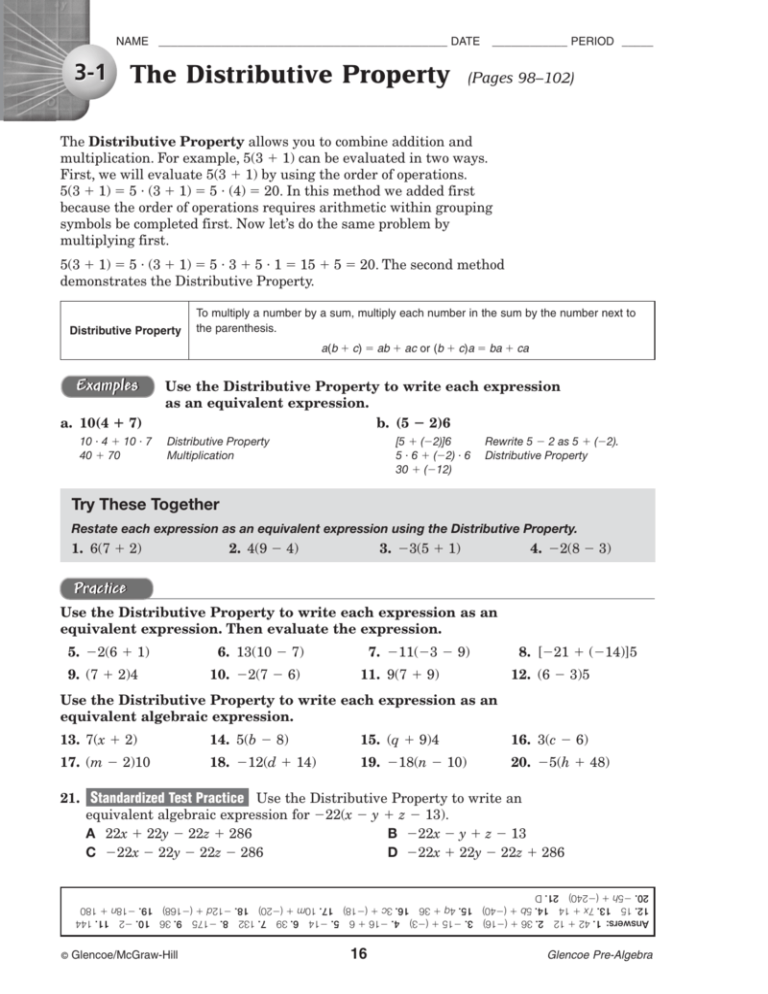
NAME ______________________________________________ DATE 3-1 The Distributive Property ____________ PERIOD _____ (Pages 98–102) The Distributive Property allows you to combine addition and multiplication. For example, 5(3 1) can be evaluated in two ways. First, we will evaluate 5(3 1) by using the order of operations. 5(3 1) 5 (3 1) 5 (4) 20. In this method we added first because the order of operations requires arithmetic within grouping symbols be completed first. Now let’s do the same problem by multiplying first. 5(3 1) 5 (3 1) 5 3 5 1 15 5 20. The second method demonstrates the Distributive Property. Distributive Property To multiply a number by a sum, multiply each number in the sum by the number next to the parenthesis. a(b c) ab ac or (b c)a ba ca Examples a. 10(4 7) 10 4 10 7 40 70 Use the Distributive Property to write each expression as an equivalent expression. b. (5 2)6 [5 (2)]6 5 6 (2) 6 30 (12) Distributive Property Multiplication Rewrite 5 2 as 5 (2). Distributive Property Try These Together Restate each expression as an equivalent expression using the Distributive Property. 1. 6(7 2) 2. 4(9 4) 3. 3(5 1) 4. 2(8 3) Practice Use the Distributive Property to write each expression as an equivalent expression. Then evaluate the expression. 5. 2(6 1) 9. (7 2)4 6. 13(10 7) 10. 2(7 6) 7. 11(3 9) 11. 9(7 9) 8. [21 (14)]5 12. (6 3)5 Use the Distributive Property to write each expression as an equivalent algebraic expression. 13. 7(x 2) 14. 5(b 8) 15. (q 9)4 16. 3(c 6) 17. (m 2)10 18. 12(d 14) 19. 18(n 10) 20. 5(h 48) 21. Standardized Test Practice Use the Distributive Property to write an equivalent algebraic expression for 22(x y z 13). A 22x 22y 22z 286 B 22x y z 13 C 22x 22y 22z 286 D 22x 22y 22z 286 Answers: 1. 42 12 2. 36 (16) 3. 15 (3) 4. 16 6 5. 14 6. 39 7. 132 8. 175 9. 36 10. 2 11. 144 12. 15 13. 7x 14 14. 5b (40) 15. 4q 36 16. 3c (18) 17. 10m (20) 18. 12d (168) 19. 18n 180 20. 5h (240) 21. D © Glencoe/McGraw-Hill 16 Glencoe Pre-Algebra