Unit 2: Rational Number Operations—Multiplication and Division
advertisement

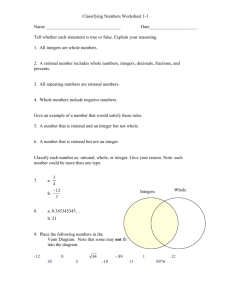
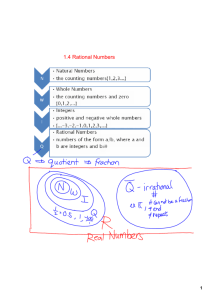
2015-2016 Curriculum Blueprint Grade: 7 Course: M/J Grade 7 Math Unit 2: Rational Number Operations—Multiplication and Division Learning Goal Students will understand operations to multiply and divide rational numbers in order to analyze and solve real world problems. Link to Learning Scale Multiplication & Division of Rational Numbers Essential Question(s) How do operations with integers compare to operations with whole numbers? What kinds of numbers make up the set of rational numbers? Does the order in which you perform a mathematical operation matter? How can you tell when it is best to use a fraction or a decimal? Approximate Time: 10 Days Unit Overview The purpose of this unit is to provide students an opportunity to reinforce and extend their understanding of multiplication and division with rational numbers. Problems addressed in this unit will focus on multiplication and division, but may also incorporate addition and subtraction. By the end of this unit, students should be comfortable applying all four operations to positive and negative fractions and decimals. When addressing 7.NS.1.2a note that students already know the distributive property from earlier grades. It was first introduced in grade 3. In grade 6, students applied the distributive property to generate equivalent expressions involving both numbers and variables. In this unit, 7.EE.2.3 will focus on problem situations involving all four operations with rational numbers. Work with 7.NS.1.3 should focus on all four operations with positive and negative rational numbers. As with unit 4, looking for and making use of structure (MP.7) aids students’ understanding of multiplication and division of positive and negative rational numbers. Students also engage in MP.1 and MP.6 as they solve the multi--‐step problems presented in this unit. Focus Standards Bullets are the deconstructed standards These should be used to develop concise learning statements/daily objectives/scales. Standards below are not intended to be followed in the order they are listed. See unit sequence for intended order. Vertical Progression: http://www.turnonccmath.net/ K-8 Learning Trajectories (This could be used to determine remediation needs or enrichment opportunities) 6th Grade: Students gained an understanding of rational numbers: quantities can be shown using + or – as having opposite directions or values points on a number line show distance and direction Grade 7 Test Item Specifications opposite signs of numbers indicate locations on opposite sides of 0 on the number line MAFS.7.NS.1.2(DOK 2): the opposite of an opposite is the number itself Apply and extend previous understandings of multiplication and division and of fractions to the absolute value of a rational number is its distance from 0 on the number line multiply and divide rational numbers. the absolute value is the magnitude for a positive or negative quantity locating and comparing a. Understand that multiplication is extended from fractions to rational numbers by locations on a coordinate grid by using negative and positive numbers. requiring that operations continue to satisfy the properties of operations, 8th Grade: Students work with irrational numbers by comparing the size of irrational numbers using particularly the distributive property, leading to products such as (–1)(–1) = 1 and rational approximations. the rules for multiplying signed numbers. b. Interpret products of rational numbers by describing real- world contexts. Lesson Sequence Essential Vocabulary c. Understand that integers can be divided, provided that the divisor is not zero, and Be selective in choosing problems aligned to the Absolute Value every quotient of integers (with non-zero divisor) is a rational number. If p and q are standards within each lesson. The unit sequence below is Integers integers, then –(p/q) = (–p)/q = p/(–q). Interpret quotients of rational numbers by the recommended order to follow. Repeating Decimal describing real-world contexts. Terminating Decimal Multiplication of Integers d. Apply properties of operations as strategies to multiply and divide rational Rational Numbers Holt 2-4 numbers. Order of Operations Engage NY Module 2: Lesson 10/11 – e. Convert a rational number to a decimal using long division; know that the decimal Associative Property (page 103) form of a rational number terminates in 0s or eventually repeats. Commutative Property Division of Integers Recognize that the process for multiplying fractions can be used to multiply Distributive Property Holt 2-4 rational numbers including integers. Engage NY Module 2: Lesson 12 – (page 119) Know and describe the rules when multiplying signed numbers. Higher Order Questions/Stems Converting Between Fractions and Decimals Explain why integers can be divided except when the divisor is 0. Holt 2-11 Describe why the quotient is always a rational number. Grade 7 FSA Reference Sheet – pg.5. 2015-2016 Curriculum Blueprint Grade: 7 Course: M/J Grade 7 Math Unit 2: Rational Number Operations—Multiplication and Division Know and describe the rules when dividing signed numbers, integers. Engage NY Module 2: Lesson 13/14 – (page 128) Multiplication & Division of Rational Numbers Recognize that –(p/q) = (-p)/q = p/(-q) Holt 3-4, 3-5, 3-10, 3-11 Identify how properties of operations can be used to multiply and divide rational numbers. Engage NY Module 2: Lesson 15 – (page 145) Convert a rational number to a decimal using long division. MARS Task: Division – Explores the decimal form of a rational number that repeats, including Explain that the decimal form of a rational number terminates (stops) in zeroes or translation of this number to a sensible answer. repeats. Applying Properties of Operations Apply the properties of operations, particularly distributive property to multiply rational numbers. Holt 1-3 Interpret the products of rational numbers by describing real-world contexts. Engage NY Module 2: Lesson 16 – (page 152) Interpret the quotient of rational numbers by describing real-world contexts. Supplemental Resources Apply properties of operations as strategies to multiply and divide rational 7th Grade Flip Book – A user-friendly resource for numbers. understanding the specifications of the Common Core Standards. Mathematical Practice Standards Link to Mathematical Practice Standards Rubric Mid-Module Assessment and Rubric – This assessment MAFS.K12.MP.1.1: Make sense of problems and persevere in solving them. may be used at the end of the unit and will assess MAFS.K12.MP.6.1: Attend to precision. 7.NS.1.1 and 7.NS.1.2. MAFS.K12.MP.7.1: Look for and make use of structure. MARS Task: Division – Task that explores the decimal form of a rational number that repeats, including translation of this number to a sensible answer. On this page, you will find the task, rubric, and student examples. Georgia Unit 1: Operations with Rational Numbers Tasks aligned to operations with rational numbers involving multiplication and division: o Multiplying Rational Number – page 55 o Patterns of Multiplication and Division – page 60 o The Repeater vs. The Terminator – page 85 o A Poster – page 93 o Whodunit? The undoing of (-7) – page 98 Illustrative Mathematics – 7th grade tasks developed under the direction of writers of the CCSS at the University of Arizona. Learnzillion.com – Lessons and Videos aligned to CCSS to watch and use for planning purposes (Personalized Learning Opportunity). Teaching Channel Video Two minute video with a focus on Improving Participation with Talk Moves (Personalized Learning Opportunity). Approximate Time: 10 Days Why does the decimal form of a rational number either terminate in zeros or repeat? Why can integers not be divided by 0? Why is the quotient always a rational number? How can properties of operations be used to multiply and divide rational numbers? How do we determine if the product of two signed numbers will be positive or negative? Why does the product of two negative values result in a positive value? Writing Connections Write to explain why the product of two negative values results in a positive value. If I have a negative quotient, what must be true about the signs of the dividend and/or divisor? What must be true if the quotient is positive? Explain your process. Justify your answer. Writing Template Tasks These template tasks are designed from the Mathematical Practice Standards. When filled in, these templates become teaching tasks that create opportunities for teaching literacy skills in mathematics. Link to Problem Solving Rubric Link to Webb’s DOK Guide