Organizational Life Cycle Assessment
advertisement
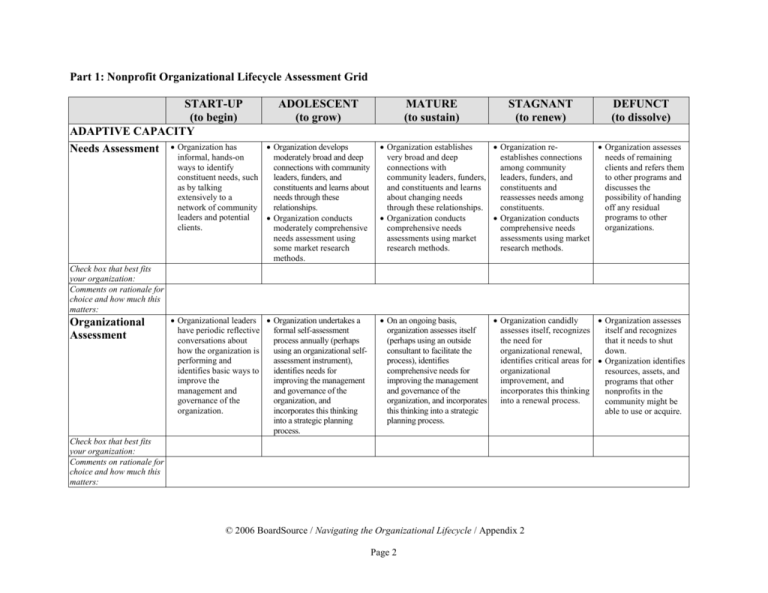
Part 1: Nonprofit Organizational Lifecycle Assessment Grid START-UP (to begin) ADAPTIVE CAPACITY Needs Assessment Organization has ADOLESCENT (to grow) Organization develops informal, hands-on moderately broad and deep ways to identify connections with community constituent needs, such leaders, funders, and as by talking constituents and learns about extensively to a needs through these network of community relationships. leaders and potential Organization conducts clients. moderately comprehensive needs assessment using some market research methods. MATURE (to sustain) STAGNANT (to renew) DEFUNCT (to dissolve) Organization establishes Organization re Organization assesses very broad and deep establishes connections needs of remaining connections with among community clients and refers them community leaders, funders, leaders, funders, and to other programs and and constituents and learns constituents and discusses the about changing needs reassesses needs among possibility of handing through these relationships. constituents. off any residual programs to other Organization conducts Organization conducts organizations. comprehensive needs comprehensive needs assessments using market assessments using market research methods. research methods. Check box that best fits your organization: Comments on rationale for choice and how much this matters: Organizational Assessment Organizational leaders Organization undertakes a have periodic reflective formal self-assessment conversations about process annually (perhaps how the organization is using an organizational selfperforming and assessment instrument), identifies basic ways to identifies needs for improve the improving the management management and and governance of the governance of the organization, and organization. incorporates this thinking into a strategic planning process. On an ongoing basis, Organization candidly Organization assesses organization assesses itself assesses itself, recognizes itself and recognizes (perhaps using an outside the need for that it needs to shut consultant to facilitate the organizational renewal, down. process), identifies identifies critical areas for Organization identifies comprehensive needs for organizational resources, assets, and improving the management improvement, and programs that other and governance of the incorporates this thinking nonprofits in the organization, and incorporates into a renewal process. community might be this thinking into a strategic able to use or acquire. planning process. Check box that best fits your organization: Comments on rationale for choice and how much this matters: © 2006 BoardSource / Navigating the Organizational Lifecycle / Appendix 2 Page 2 START-UP (to begin) ADAPTIVE CAPACITY Program volunteers Program and staff have periodic Evaluation reflective discussions ADOLESCENT (to grow) Program staff develop simple systems for gathering and using data about what seems to be about programmatic working with the outcomes. programs and why, and keep track of anecdotes and stories that relate to outcomes. MATURE (to sustain) STAGNANT (to renew) DEFUNCT (to dissolve) Organization develops formal system for regularly evaluating programs. Program model is documented so that it becomes more transferable. Organization conducts program evaluation and uses the results to inform and revise programs as part of renewal effort. Organization stops investing in program evaluation, documents what it has learned, and shares this information with key constituents. Organization shares evaluation tools and processes with other nonprofits in the community. Staff and board develop formal systems for integrating and using data from needs assessment, organizational assessment, program evaluation, and other sources, and how it relates to organizational improvement. Staff and board revamp Organization reflects and improve systems for on what it has learned integrating and using data and shares this from needs assessment, information with key organizational constituents. assessment, program evaluation, and other sources, and relating it to the organizational renewal effort. Check box that best fits your organization: Comments on rationale for choice and how much this matters: Knowledge Management Staff and board have periodic reflective conversations about what was learned during informal needs assessment, organizational assessment, program evaluation, and other sources, and how it relates to possible organizational improvements. Organization develops simple systems for storing, organizing, disseminating, and using its knowledge. Staff and board develop simple systems for integrating and using data from needs assessment, organizational assessment, program evaluation, and other sources, and how it relates to organizational improvements. Organization develops simple systems for storing, organizing, disseminating, and using its knowledge. Check box that best fits your organization: Comments on rationale for choice and how much this matters: © 2006 BoardSource / Navigating the Organizational Lifecycle / Appendix 2 Page 3 START-UP (to begin) ADAPTIVE CAPACITY Strategic Planning Organizational leaders ADOLESCENT (to grow) MATURE (to sustain) STAGNANT (to renew) Organization articulates Organization creates a Organization affirms or create a strategic a clear theory of change. detailed updated theory of revises a theory of thinking piece with a change. change. Organization creates a 2-year horizon that strategic plan with a 3-5 Organization creates a Organization creates a explains how it will year horizon that has clear strategic plan with a 3-5turnaround plan that has start up the goals and annual objectives, year horizon that has clear clear goals and objectives organization. and develops annual goals and annual objectives, and creates an annual Organization has a operating plans and program and develops annual operating plan based on it. simple plan for plans based on it. operating plans and program Organization has a plan generating revenues plans based on it. Organization has a plan for for restoring the from at least one major generating revenues from at Organization has a plan for confidence of dedicated funding source. least two or three main securing diverse and stable funders and enlisting the sources to enable the revenue sources, possibly support of new ones so organization to grow. including business plans for that the organization earned income and stabilizes financially. fundraising campaigns for capital projects. Organization considers developing or creates a plan to develop a cash reserve or endowment. Check box that best fits your organization: Comments on rationale for choice and how much this matters: © 2006 BoardSource / Navigating the Organizational Lifecycle / Appendix 2 Page 4 DEFUNCT (to dissolve) Organization creates a plan to dissolve itself in a responsible and orderly manner. START-UP (to begin) ADAPTIVE CAPACITY Organization forms Collaborations relationships with other and Partnerships groups and begins ADOLESCENT (to grow) Organization develops connections with other organizations and forges informally cooperating more formal collaborations with some of them, with some of them, such as such as by sharing by coordinating program information and delivery and sharing making cross-referrals. resources. MATURE (to sustain) STAGNANT (to renew) DEFUNCT (to dissolve) Organization develops strong connections with other organizations and considers developing or does develop such formal collaborations as joint ventures or shared backoffice space and functions. Organization maintains relationships with other organizations, develops new relationships, and considers collaborations and partnerships as a part of its renewal effort. Organization ends any collaborations with other organizations and considers handing off some programs to other groups and referring clients to them. Organization meets with other nonprofit leaders and funders to discuss ways to address client needs in an ongoing manner. Check box that best fits your organization: Comments on rationale for choice and how much this matters: © 2006 BoardSource / Navigating the Organizational Lifecycle / Appendix 2 Page 5 START-UP (to begin) LEADERSHIP CAPACITY Organization Board establishes a small Development homogenous board. ADOLESCENT (to grow) Organization expands the size of the board. Board’s role is formalized Board develops a clear and there are job purpose and vision that descriptions for board is understood by itself, members. staff, and volunteers. Board articulates a clear Board plays a hands-on mission, vision, and set of role in overseeing and values and they are well managing the understood by board, staff, organization. and volunteers. Board conducts an Board clarifies its role in informal performance relation to chief executive, review of the chief increases its planning executive. function, and develops a deliberate decision-making process. Board conducts a formal annual evaluation of the chief executive and talks about a succession plan. Board discusses how it is performing and how it needs to improve. MATURE (to sustain) Organization has a formal nominating process and adds people to the board who represent the community that the organization serves and have skills that the organization requires, such as program, financial, and legal expertise. Organization affirms or revises its mission, vision, and values, and they are well understood by board, staff, and volunteers. Board clarifies its role in relation to the chief executive, reduces its operational role, and increases its policy and fundraising function. Board has committees, work groups, or task forces and, possibly, advisory councils. Board conducts a formal annual evaluation of the chief executive and creates a succession plan. Board formally assesses itself and creates a board development plan. STAGNANT (to renew) Organization retires some Board ensures that veteran board members the organization’s who are not engaged and dissolution process adds new board members is responsible and who support the renewal orderly. effort. Board dissolves itself. Organization affirms or revises its mission, vision, and values, and they are well understood by board, staff, and volunteers. The board plays a handson role during the renewal effort and ensures the financial viability of the organization. The board reviews the performance of the chief executive and, if necessary, terminates the person and hires a new one to lead the renewal effort. Check box that best fits your organization: Comments on rationale for choice and how much this matters: © 2006 BoardSource / Navigating the Organizational Lifecycle / Appendix 2 Page 6 DEFUNCT (to dissolve) START-UP (to begin) LEADERSHIP CAPACITY Volunteer or staff Executive person founds Leadership organization or board Development hires staff leader. Staff leader is entrepreneurial and adept at establishing and growing the organization. ADOLESCENT (to grow) MATURE (to sustain) Chief executive’s role is The chief executive and distinct in relation to the board have distinct roles board. and they hold each other accountable. Chief executive disconnects personal and organizational Chief executive is adept at needs as the organization managing a large staff and ages and expands. complex finances and sustaining the organization. Chief executive has the ability to manage the Chief executive forms a growth of the organization. strong senior management team, including possibly a chief operating officer. STAGNANT (to renew) DEFUNCT (to dissolve) Chief executive is adept Chief executive at managing a turnaround completes his or her process. duties and leaves the organization. Check box that best fits your organization: Comments on rationale for choice and how much this matters: Leadership Transitions Board hires chief executive. Board appoints board chair. Board ensures that chief executive has the ability to manage the growth of the organization, and, if necessary, hires a new chief executive who is more able to do so. Succession plans exist for staff and board leadership. Board ensures that chief Board determines if chief Chief executive leaves executive has the ability to executive is able to renew job and board dissolves sustain the organization and, the organization and, if itself in an orderly if necessary, hires a new necessary, hires a new manner. chief executive who is more chief executive who is able to do so. more able to do so. Succession plans exist for executive and staff leadership. Check box that best fits your organization: Comments on rationale for choice and how much this matters: © 2006 BoardSource / Navigating the Organizational Lifecycle / Appendix 2 Page 7 START-UP (to begin) MANAGEMENT CAPACITY Human-Resource Organization has a small number of Development and volunteers or staff and Management there is little or no ADOLESCENT (to grow) MATURE (to sustain) STAGNANT (to renew) Organizational leaders Organization hires Organizational leaders develop recruitment and additional staff, including revise staff job hiring plan, write job program specialists and descriptions and descriptions for volunteers professional managers, and restructure staff to reflect organizational and staff, recruit and hire creates a more centralized plan to renew the hierarchy. them, and establish a simple and hierarchical organization. organizational hierarchy. organizational structure that Organizational leaders has a clear division of labor establish roles for staff Staff orientation and and reporting relationships. and volunteers and training becomes more recruit and hire people. formal and annual staff Organization has a formal evaluations are established. staff orientation, training, Volunteers and staff and evaluation process. are informally oriented, Staff decision-making trained, and evaluated. process becomes more Well-developed personnel formal. policies exist. Staff decision-making process is informal. Simple personnel policies are established. There are few or no formal personnel policies. DEFUNCT (to dissolve) Organizational leaders terminate staff respectfully. Check box that best fits your organization: Comments on rationale for choice and how much this matters: Internal Communications Organization communicates informally among staff, such as by having sporadic conversations and meetings. Organization develops more Organization has formal Organizational leaders formal methods for methods for communicating freely share information communicating, such as by among staff, such as by with all staff about the holding regular staff having a management organizational renewal meetings and documenting reporting system, staff efforts. and disseminating what is meetings at the discussed at them. departmental and organizational levels, and a regular staff newsletter. Check box that best fits your organization: Comments on rationale for choice and how much this matters: © 2006 BoardSource / Navigating the Organizational Lifecycle / Appendix 2 Page 8 Organizational leaders clearly communicate with staff about dissolution plans. START-UP (to begin) MANAGEMENT CAPACITY Organizational leaders Financial create a basic annual Management budget and meet ADOLESCENT (to grow) MATURE (to sustain) Organizational leaders create a multiyear budget and meet regularly to regularly to discuss discuss how to allocate how to allocate financial resources, manage financial resources. cash flow, and live within its means. Organization Organization develops an establishes a basic accounting system, accrual accounting system which may be cashand creates quarterly based, and creates financial reports (which annual financial show budget vs. actual statements that are figures) and an annual audited internally and financial statement that is approved by the board. audited by an outside Certified Public Accountant Organization has and approved by the board. adequate human resources, such as a Organization has adequate part-time bookkeeper, human resources, such as a to handle the financial full-time financial manager, management function. to handle the financial management function. STAGNANT (to renew) DEFUNCT (to dissolve) Organizational leaders Organizational leaders Organizational leaders create a multiyear budget assess the financial distribute any and discuss how to allocate situation frequently, remaining assets and financial resources and live strengthen financial fulfill any outstanding within its means. controls, and ensure that financial obligations. the organization is living Organization maintains a within its means. well-developed accrual Organization continues to accounting system, creates quarterly financial reports maintain a wellthat include projections, and developed accrual produces an annual financial accounting system and statement that is audited by creates quarterly financial an outside Certified Public reports and annual Accountant and approved audited financial the board. statements. Organization creates Organization has monthly cash flow adequate human projections and manages its resources to handle the cash flow well. financial management function during the If necessary, organization renewal effort and may has ability to manage a need to hire a new staff capital budget, cash reserve, person to handle the and/or an endowment. financial management Organization has adequate function and/or replace human resources, such as a the outside auditor. chief financial officer or comptroller, to handle the financial management function. Check box that best fits your organization: Comments on rationale for choice and how much this matters: © 2006 BoardSource / Navigating the Organizational Lifecycle / Appendix 2 Page 9 START-UP (to begin) TECHNICAL CAPACITY Organization Service Delivery establishes basic skills Skills to effectively provide simple programs that meet the needs that it identifies. ADOLESCENT (to grow) MATURE (to sustain) STAGNANT (to renew) DEFUNCT (to dissolve) Organization has skills to expand responsive and credible programs that respond to changing needs and maintain their quality. Organization has skills to refine comprehensive programs based on changing needs. Organization has skills to establish and implement simple systems for program evaluation. Organization has skills to Organization has skills to Organization has skills evaluate programs regularly, evaluate programs to to document outcomes systematically, and inform decisions about and lessons learned, formally, and document the program revisions. and communicate this program model. information to stakeholders. Organization has skills Organization has skills to revise programs to be to responsibly end responsive to needs as programs and refer part of organizational clients elsewhere. renewal effort. Check box that best fits your organization: Comments on rationale for choice and how much this matters: Evaluation Skills Organization has fundamental skills to have reflective conversations about program outcomes and informally evaluate programs. Check box that best fits your organization: Comments on rationale for choice and how much this matters: Outreach and Advocacy Skills Organization builds basic skills to develop strong connections with constituents and effectively perform outreach and advocacy. Organization builds strong Organization maintains and Organization has skills to Organization has skills skills to develop and further improves skills to effectively maintain and to responsibly end maintain solid connections develop strong connections develop strong outreach and advocacy with constituents and with constituents and connections with efforts. effectively perform outreach effectively perform outreach constituents, and revise and advocacy. and advocacy. outreach and advocacy efforts as part of organizational renewal effort. Check box that best fits your organization: Comments on rationale for choice and how much this matters: © 2006 BoardSource / Navigating the Organizational Lifecycle / Appendix 2 Page 10 START-UP (to begin) TECHNICAL CAPACITY Organization has Marketing and adequate ability to Communication market its programs Skills and services and communicate about its activities in simple ways, such as through word-of-mouth and written program descriptions. ADOLESCENT (to grow) MATURE (to sustain) STAGNANT (to renew) DEFUNCT (to dissolve) Organization has ability to market its programs and services and communicate about its activities in moderately advanced ways, such as by creating simple brochures. Organization has ability to market its programs and services and communicate about its activities in advanced ways, such as through a Web site, newsletter, and annual report. Organization has ability to market its revised programs and services and communicate honestly and clearly with constituents about the renewal effort. Organization has ability to communicate with stakeholders about its accomplishments and dissolution. Check box that best fits your organization: Comments on rationale for choice and how much this matters: Legal Skills Organization has legal skills necessary for the organization, such as for creating bylaws and articles of incorporation and obtaining tax-exempt status. Organization has legal skills Organization has advanced Organization has legal Organization has necessary for the legal skills necessary for the skills necessary for the access to basic legal organization, such as for organization, such as for organization, such as for skills necessary for the employment, leases, and joint ventures, trademark renegotiating debt with organization, such as insurance. and licensing issues, and creditors, restructuring, or for terminating leases construction contracts. terminating contracts. and bankruptcy. Check box that best fits your organization: Comments on rationale for choice and how much this matters: © 2006 BoardSource / Navigating the Organizational Lifecycle / Appendix 2 Page 11 START-UP (to begin) TECHNICAL CAPACITY Fundraising Skills Organization has skills to secure contributed revenue from at least one main source. ADOLESCENT (to grow) MATURE (to sustain) STAGNANT (to renew) DEFUNCT (to dissolve) Organization has skills to secure contributed revenues from several main sources. Organization has skills to secure contributed revenues from diverse sources and, if necessary, effectively conduct a capital campaign for a capital project, cash reserve, or endowment. Organization has skills to reassure current funders and maintain their support, and enlist new ones to support the renewal effort. Organization has skills to responsibly end relationships with funders and donors. Organization has skills to broker relationships between other nonprofits working with the same clients and their funders in order to meet the ongoing needs of their clients. Organization has skills to generate a moderate to high amount of earned income. Organization has ability Organization has to maintain or increase ability to responsibly any earned income during end relationships with renewal effort. customers who generated earned income. Check box that best fits your organization: Comments on rationale for choice and how much this matters: Earned-Income Generation Skills Organization has skills Organization has skills to to begin planning generate a limited amount possible earned-income of earned income. activities. Check box that best fits your organization: Comments on rationale for choice and how much this matters: © 2006 BoardSource / Navigating the Organizational Lifecycle / Appendix 2 Page 12 START-UP (to begin) TECHNICAL CAPACITY Accounting Skills Organization has accounting and financial management skills needed to set up payroll, create and manage an annual budget, establish and implement a simple accounting system, and create annual financial statements. ADOLESCENT (to grow) MATURE (to sustain) STAGNANT (to renew) DEFUNCT (to dissolve) Organization has accounting Organization has accounting Organization has Organization has and financial management and financial management accounting and financial accounting and skills to create and manage skills to create and manage management skills to financial management a multiyear budget, manage a multiyear budget, manage strengthen financial skills to distribute any cash flow, implement a cash flow, implement an controls, manage a remaining assets and moderately advanced advanced accrual multiyear budget, manage fulfill any outstanding accrual accounting system, accounting system, create cash flow, implement an financial obligations. and create quarterly quarterly financial reports advanced accrual financial reports and annual and annual audited financial accounting system, create audited financial statements. statements, and, if quarterly financial reports necessary, manage a capital and annual audited budget, cash reserve, and/or financial statements, and endowment. anything else required to support the organizational renewal effort. Check box that best fits your organization: Comments on rationale for choice and how much this matters: Facilities Management Skills Organization has fundamental skills to manage, operate, and maintain its facilities, such as borrowing, subleasing, leasing, and maintaining office and program space. Organization has skills to manage, operate, and maintain its facilities, such as by leasing and maintaining additional space for expanding programs. Organization has advanced Organization has skills to Organization has basic skills to manage, operate, manage, operate, and skills to manage its and maintain its facility, maintain its facilities, facilities, such as by such as by purchasing, such as by consolidating terminating leases and building, upgrading, leasing, space, selling property, or selling property. and managing additional subletting. program and office space. Check box that best fits your organization: Comments on rationale for choice and how much this matters: © 2006 BoardSource / Navigating the Organizational Lifecycle / Appendix 2 Page 13 START-UP (to begin) TECHNICAL CAPACITY Technology Skills Organization has basic skills to use and manage technology, such as telephone, fax, and computer hardware and software. ADOLESCENT (to grow) MATURE (to sustain) STAGNANT (to renew) DEFUNCT (to dissolve) Organization has moderately advanced skills to use and manage technology, such as telephone, fax, a networked computer system, and basic applications. Organization has advanced skills to use and manage technology, including telephone, fax, a networked computer system, and a wide array of sophisticated applications. Organization has skills to use and manage technology to support the organization’s renewal efforts. Organization has skills to shut down and end any technological systems that the organization has used. Check box that best fits your organization: Comments on rationale for choice and how much this matters: © 2006 BoardSource / Navigating the Organizational Lifecycle / Appendix 2 Page 14