review answers
advertisement

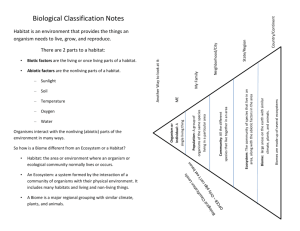
Name___________________________ Mrs. Terhune Ecology Chapter Review (Test Thursday 10/4) 1. A living thing is known as a _____biotic____ factor. 2. A non-living think is known as a(n) _____abiotic______ factor. Give an example - soil, weather, sunlight, water 3. What makes an organism living? - This is from last chapter and will not be on the Test 4. Define the following terms: a. Population: a group of similar species b. Community: a group of different species c. Ecosystem: the biotic and abiotic factors in an area What is the difference between a habitat and a niche? - a habitat is where an organism lives and a niche is the role within their habitat 6. The area in which certain types of plants or animals can be found living in close proximity to each other is called a a. habitat b. community c. niche d. kingdom 6. Nitrogen, oxygen, and carbon dioxide are among the most biologically important atmospheric gases. What are these called? a. abiotic factors b. biotic factors c. biospheric factors d. habitat factors 7. The giant noctule bat preys mostly upon insects during the summer months, and on migrating songbirds during the autmn and spring. It attacks the birds at night from several hundred meters in the air. During the day the bat roosts in trees. What do these sentences describe? a. community b. habitat c. biome d. niche 8. Define the following terms and give an example: a. Producer (Autotroph): organism that makes its own food using photosynthesis b. Consumer (Heterotroph): organism that must eat in order to obtain energy c. Herbivore: plant eater d. Omnivore: eating plants and animals e. Decomposer: an organism who breaks down organic matter and recycles the nutrients back into the soil 9. What is the difference between a food chain and a food web? Which one is more stable and why? Draw your own food web and discuss what would happen if you add and remove organisms. - A food chain is a linear depiction of energy flow in an ecosystem and a food web illustrates the complex feeding relationships 10. What is a trophic level? - energy level within a food web or energy pyramid 12. Put the following organisms into an energy pyramid Grass->Rabbit->Fox->Hawk a. How much energy is transferred from one trophic level to the next? 10% energy is transferred, 90% is lost in the form of heat b. Which organism has the most available energy and why? - the producers because they get their energy from the sun c. What happens to energy as you move throughout a food chain? - energy decreases each time by 90% d. Which level contains the most biomass? - the producers as they have the most available energy to them 13. What is the difference between energy transfer and a nutrient cycle? - In energy transfer, energy is lost to the environment as heat. In a nutrient cycle like carbon, nitrogen, phosphorous, nutrients are cycled through the biosphere, not lost 14. In your own words explain the carbon cycle. - carbon enters the atmosphere through processes like decomposition, fires, burning of fossil fuels, and respiration. Plants take in carbon as carbon dioxide during photosynthesis. Animals obtain carbon by consuming plants. What sorts of human activities impact the carbon cycle in a negative manner?- burning of fossil fuels. 15. How do humans impact the water cycle? Why do we care - Pollution of water sources by runoff of chemicals such as fertilizers and the burning of fossil fuels produces sulfuric dioxide which combines with water to form sulfuric acid, which is acid rain. We care because this is the water available to us to survive. 17. Define the following (include what it is, what leads to it): a. Global Warming: now known as climate change, it is due to an increase in Earth’s greenhouse gases such as carbon dioxide and methane. Too much heat gets trapped, therefore warming earth too much. In addition, cows release methane when they fart! Adding to the greenhouse gases b. Ozone Depletion: this is a layer of gas that protects Earth from harmful UV rays, depleted when CFC’s are used 18. What are the causes of biodiversity loss? Explain them. - deforestation and habitat loss - hunting/poaching - introduction of invasive species - removal of keystone species Why do we care about biodiversity? - aesthetic purposes - stability of food web - medicines and food products What sorts of effects do invasive species have on an ecosystem? - They do not have any natural predators and are not resistant to natural diseases so they overpopulate areas and outcompete native species Why might ecologists choose to protect a keystone species? - Because they have a profound effect on the ecosystem, like the grey wolf in Yellowstone where it controls the elk population, therefore the willows were able to regrow and create habitat and food for other organism 19. What is the difference between renewable and nonrenewable resources. Give an example of each. - renewable are resources that can be replaced: trees, food, water - nonrenewable are resources that can not be replaced: oil, coal, gas 20. Why are our resources being depleted? - an increase in the human population, exponential growth 21. What is carrying capacity? What kinds of factors will determine how much/quickly a population can grow? - Carrying capacity is the maximum number of organisms that a population can support. Limiting factors determine how quickly a population can grow- food, water, shelter, oxygen, carbon dioxide