Food Chains and Food Webs

Ecosystems
1.
Energy flows ______ through _____ an ecosystem, while chemicals ____ cycle ____ within it.
2.
Food chains generally start with an autotrophic organism called a ______ producer _______ that obtains its energy from _____ photosynthesis ___.
3.
The first heterotrophic organism in a food chain obtains ___ chemical ___ energy by feeding on the producers and is called first order or primary ____ consumer ____.
4.
The second heterotroph in a food chain is called a _____ secondary ____ ______ consumer ____.
5.
Organisms that feed on dead organsims or the waste products of other organisms are called
__ decomposers __.
6.
Energy enters an ecosystem as __ sunlight __, is converted to ___ chemical ____ energy by producers, and leaves the ecosystem as __ heat __.
7.
Arrange the organisms in each group below into a food chain and tell which of the above terms refers to each.
A) Man, corn, pig
Corn (producer) pig (primary consumer) man (secondary consumer)
B) Grasshopper, lizard, goldenrod, hawk
Goldenrod (producer) grasshopper (primary consumer) lizard (secondary consumer) hawk
(tertiary consumer)
C) Child, peanut butter sandwich, mosquito
Peanut butter sandwich (producer) child (primary consumer) mosquito (secondary consumer)
D) Water plant, raccoon, mosquito larvae, small fish
Water plant (producer) mosquito larvae (primary consumer) small fish (secondary consumer)
raccoon (tertiary consumer)
E) Flea, algae, snail, fox, snake, fish
Algae (producer) snail (primary consumer) fish (secondary consumer) snake (tertiary consumer) fox (4 th order consumer) flea (5 th order consumer)
8.
For each of the food chains in #5 tell which organisms would have the most total energy and which would have the least total energy.
In each case, the producers have the most energy while the highest order consumer has the least.
9.
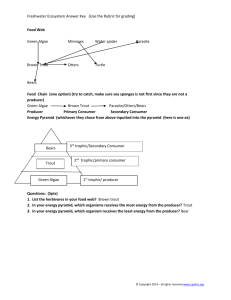
Refer to the food web pictured below and use it to answer questions A- F.
Blue herons
Mosquitoes
Bats
Trout
Grasshoppers
Swamp grass
Frogs
Geese
Mosquito larvae
Algae
Ducks
Water plants Cattails
A) For each of the organisms described in the chart below, give its trophic level:
Organism Trophic Level
A beaver Primary consumer
Beavers
Poplar trees
A frog that eats a mosquito Tertiary consumer
A frog that eats a mosquito larva
A water plant
Secondary consumer
Producer
A blue heron that ate a trout that ate algae
A blue heron that ate a trout that ate a grasshopper
A duck that eats a water plant
A bat
A goose that eats a grasshopper
Secondary consumer
Tertiary consumer
Primary consumer
Tertiary consumer
Secondary consumer
B) Place each of the organisms from the food web into the correct box in the energy pyramid below. (If an organism eats at two different trophic levels, place it in the correct box for is lowest trophic level.)
TERTIARY
CONSUMERS
Blue herons
Bats
SECONDARY
CONSUMERS
Frogs
Mosquitoes
PRIMARY CONSUMERS
Grasshopper
Geese
Ducks
Mosquito larvae
Beavers
Trout
PRODUCERS
Swamp grass
Algae
Water plants
Cattails
Poplar trees
10.
List the three general steps involved in chemical cycling.
Producers incorporate chemicals from the nonliving environment into organic compounds.
Consumers feed on the producers, incorporating some of the chemicals into their bodies and releasing the rest back into the environment in waste products.
Decomposers break down dead organisms and wastes, releasing raw materials for the producers.
11.
What two processes in living organisms are primarily responsible for cycling carbon and oxygen atoms in the carbon/oxygen cycle?
Photosynthesis and cellular respiration
12.
Fill in the blanks in the picture of the carbon oxygen cycle below:
PRODUCERS
(Name a process)
Photosynthesis
CO
2
+
Water
Organic compounds +
O
2
(Name a process)
Cellular
Respiration
PRODUCERS
CONSUMERS
DECOMPOSERS