Name: Period: ______ Date:______ “The Moving Man
advertisement

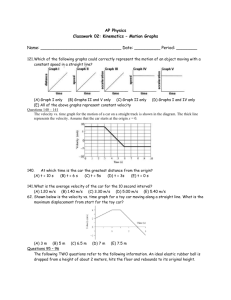
Name: __________________________________ Period: ___________ Date:____________ “The Moving Man” – Interpreting Motion Graphs [Lab 5] Points: __________ / 50 Part 1 – Constant Velocity 1. Through a web browser, navigate to http://phet.colorado.edu. Click "Play with Sims," then "Physics," then "Motion," then choose the "Moving Man" simulation. Click "Run now" to start the simulation. 2. Click on Charts at the top left and Click on the red ‘Minus’ button on the top right corner of the bottom graph to remove the acceleration graph from your view. 3. By manipulating the man’s position and velocity, running the simulation and observing the resulting graphs, make some general conclusions about motion graphs based on the questions below. Based on observations of the simulation: a) The position graph line is on the positive side when: f) The velocity graph line is on the positive side when: b) The position graph line is on the negative side when: g) The velocity graph line is on the negative side when: c) The position graph line has a positive slope when: h) The velocity graph line is on zero when: d) The position graph line has a negative slope when: i) The slope of the line on the position graph is steep when: e) The position graph line has a slope of zero when: j) The line on the velocity graph is closer to zero when: 4. On the graph to the right, draw an example of The Moving Man moving forward starting at 0 meters with a velocity of 2m/s for 4 seconds. a. How far would he move? How do you know based on the graph? b. How far would he move if he went twice as fast? 5. Draw an example of The Moving Man moving backward from zero at a velocity of -5m/s. 6. What could be happening to The Moving Man according to this graph? 7. Click on the Clear button at the bottom. Make sure the program is paused. Set the initial values to: Position: - 10.0 m Velocity: + 4 m/s Draw what you think both graphs will look like in the picture. How long do you think it will take for the Moving Man to get to the other side? Explain your reasoning. 8. Now, click on the play button. What happened? Draw the results here: Were you correct? What might be a surprising result? 9. Click on the Clear button at the bottom. Make sure the program is paused. Set the initial values to: Position: 8.0 m Velocity: - 2 m/s Draw what you think both graphs will look like in the picture. How long do you think it will take for the Moving Man to get to the other side? Explain your reasoning. 10. Now, click on the play button. What happened? Draw the results here: Were you correct? What might be a surprising result? 11. Describe the motion that created this graph by identifying the object’s: a) Starting Position: b) Direction: c) Velocity: d) Time interval: e) Displacement: Part 2 – Constant Acceleration 1. Clear all, and click on the green ‘plus sign’ button on the bottom right corner of the simulation to bring the acceleration graph into view. 2. By manipulating the man’s position and velocity, running the simulation and observing the resulting graphs, make some general conclusions about motion graphs based on the questions below. This works better if you type numbers into the box instead of moving the man with your mouse. For each question, answer with both a sentence and a graph of velocity vs. time. You must adjust the values for starting position, velocity and acceleration based on each question. By observing the motion of the man and the shape of the graphs produced, make general statements about motion according to each question. 3. How do you know from the graphs if the object moves with constant velocity? Explanation: Graph of Motion (velocity vs. time graph) 4. How do you know from the graphs if the object is moving forward or backwards? Explanation: Graph of Motion (velocity vs. time graph) 5. What happens when you have a positive velocity and a negative acceleration? Explanation: Graph of Motion (velocity vs. time graph) 6. What happens when you have a negative velocity and a positive acceleration? Explanation: Graph of Motion (velocity vs. time graph) 7. There are two ways to get positive acceleration. What are they? (Describe how the man moves in each example.) 8. There are two ways to get negative acceleration. What are they? (Describe how the man moves in each example.)