DOCUMENTION OF THE NURSING PROCESS
advertisement

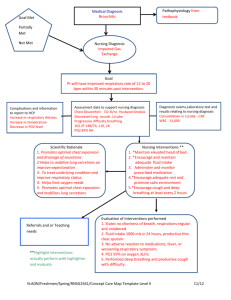
LAGUARDIA COMMUNITY COLLEGE CITY UNIVERSITY OF NEW YORK DEPARTMENT OF NATURAL & APPLIED SCIENCE PRACTICAL NURSING PROGRAM DOCUMENTION OF THE NURSING PROCESS CLIENT’S INTIALS: STUDENT NAME: MANOLITO GULLA___________________ DATE: ____11/11/06____________ MEDICAL DIAGNOSIS: _PNEUMONIA_______________________ INSTRUCTOR VALERIE TAYLOR-HASLIP, MSN,FNP CLIENT CARE OBJECTIVE (S):TO RELIEVE CLIENT’S SYMPTOMS THROUGH APPROPRIATE ANTIBIOTIC THERAPY AND ADMINISTRATION OF OXYGEN. _______ _______ ASSESSMENT (SUBJECTIVE/OBJECTIVE) Data Collection 2-day history of chest pain, weakness, and fever At risk for pneumonia Long history of alcohol abuse CLIENT’S PROBLEM (S)/NEED(S) (USE NURSING DIAGNOSIS STATEMENTS) Ineffective Airway Clearance related to tracheobronchial infection as evidenced by great respiratory distress, difficulty in breathing and extreme anxiety. Risk for ineffective gas exchange related to lung pathology. CLIENT SHORT TERM GOAL/OUTCOME (PLANNING) Client will maintain patent airway as evidenced by easy and unlabored respirations. NURSING INTERVENTION (APPROACH)/ (ACTION) SCIENTIFIC RATIONALE FOR NURSING INTERVENTION Elevate HOB to put client in an orthopneic position. Proper positioning makes the client more comfortable and helps to make breathing easier. Instruct and assist client to turn, cough, and deep breathe every 2 hours. TCDB assists in the loosening and expectoration of mucous. Promote optimum level of activity Activity leads to the best possible lung expansion. Monitor for increasingly labored respirations. If client exhibits increasing difficulty in breathing, give oxygen by mask or cannula. Place pillow lengthwise under the back. This encourages fuller chest expansion. Place a blanket around the shoulders if the client has chills. A blanket provides comfort and warmth, minimizing energy expenditure. Keep the client’s bed dry. Wet bed linens can chill the client. Heavy smoker for 50+ years In great respiratory distress Difficulty in breathing Risk for activity intolerance related to reduced lung capacity. Extremely anxious LAGUARDIA COMMUNITY COLLEGE CITY UNIVERSITY OF NEW YORK DEPARTMENT OF NATURAL & APPLIED SCIENCE PRACTICAL NURSING PROGRAM DOCUMENTION OF THE NURSING PROCESS ( Con’t) ASSESSMENT (SUBJECTIVE/OBJECTIVE) Data Collection CLIENT’S PROBLEM (S)/NEED(S) (USE NURSING DIAGNOSIS STATEMENTS) CLIENT SHORT TERM GOAL/OUTCOME (PLANNING) NURSING INTERVENTION (APPROACH) (ACTION) SCIENTIFIC RATIONALE FOR NURSING INTERVENTION Assess the client’s vital signs at least every 4 hours. Frequent monitoring is necessary to allow for prompt detection and early intervention if problems arise. Maintain the IV site or heparin lock. The client is probably receiving antibiotics. Encourage the client to cough and to expectorate secretions while splinting the chest. Keep the lungs as free of secretions as possible. Splinting the chest helps to relieve the discomfort of coughing. Encourage deep breathing. Aerosolized treatments or incentive spirometry may be prescribed. The lungs must be expanded as much as possible. Measure intake and output and daily weights, if ordered. Client may have edema. He may need TPN to maintain hydration and nutrition. Give small amounts of fluids frequently. Fluids help to encourage hydration. Provide frequent mouth care; put water soluble lubricant on the client’s lips. Client has probably been breathing through the mouth and made it dry. Encourage client to move about. Movement causes lung expansion. Keep the client’s surroundings quiet. Rest promotes healing.