Ch 14 Study Guide – Rocks: Mineral Mixtures
advertisement
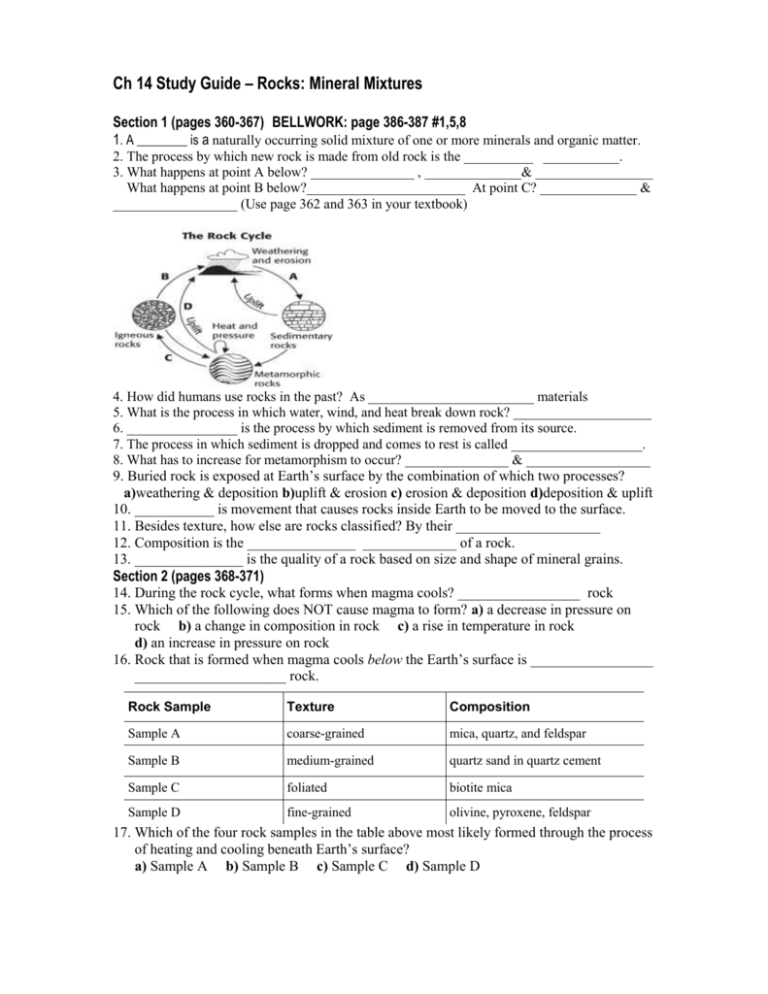
Ch 14 Study Guide – Rocks: Mineral Mixtures Section 1 (pages 360-367) BELLWORK: page 386-387 #1,5,8 1. A ________ is a naturally occurring solid mixture of one or more minerals and organic matter. 2. The process by which new rock is made from old rock is the __________ ___________. 3. What happens at point A below? _______________ , ______________& _________________ What happens at point B below?_______________________ At point C? ______________ & __________________ (Use page 362 and 363 in your textbook) 4. How did humans use rocks in the past? As ________________________ materials 5. What is the process in which water, wind, and heat break down rock? ____________________ 6. ________________ is the process by which sediment is removed from its source. 7. The process in which sediment is dropped and comes to rest is called ___________________. 8. What has to increase for metamorphism to occur? _______________ & __________________ 9. Buried rock is exposed at Earth’s surface by the combination of which two processes? a)weathering & deposition b)uplift & erosion c) erosion & deposition d)deposition & uplift 10. ___________ is movement that causes rocks inside Earth to be moved to the surface. 11. Besides texture, how else are rocks classified? By their ____________________ 12. Composition is the _______________ _____________ of a rock. 13. _______________ is the quality of a rock based on size and shape of mineral grains. Section 2 (pages 368-371) 14. During the rock cycle, what forms when magma cools? _________________ rock 15. Which of the following does NOT cause magma to form? a) a decrease in pressure on rock b) a change in composition in rock c) a rise in temperature in rock d) an increase in pressure on rock 16. Rock that is formed when magma cools below the Earth’s surface is _________________ _____________________ rock. Rock Sample Texture Composition Sample A coarse-grained mica, quartz, and feldspar Sample B medium-grained quartz sand in quartz cement Sample C foliated biotite mica Sample D fine-grained olivine, pyroxene, feldspar 17. Which of the four rock samples in the table above most likely formed through the process of heating and cooling beneath Earth’s surface? a) Sample A b) Sample B c) Sample C d) Sample D 18. Rock that cools at the Earth’s surface is _________________ igneous rock. 19. When magma cools quickly, what kind of texture does rock have? ___________-grained. 20. Volcanic activity on Earth’s surface would most likely result in the formation of which of the following types of rock? a)intrusive igneous b) chemical sedimentary c) clastic sedimentary d) extrusive igneous *Now answer # 3 on page 371, using figure 1 on page 368 Section 3 (pages 372-375) BELLWORK: page 386-387 # 9 & 10 21. Erosion causes rock and mineral fragments called _____________________ to move from one place to another. 22. Sedimentary rock is formed through the process of ___________________________. 23. Layers found in sedimentary rocks are known as ___________. 24. Fragments of rock cemented together by a mineral are _______________ sedimentary. 25. ______________ sedimentary rock forms from solutions of dissolved minerals. 26. ______________ sedimentary rocks are made of skeletons and shells of sea animals, and one example is ___________. 27. What are the main categories of sedimentary rock? _________, ___________, ________ 28. __________________ is the process in which the layers found in sedimentary rock form. 29. Stratification would occur as the result of which of the following processes? a) the cooling and solidification of magma b) the partial or complete melting of rock c) the deposition of sediments in a body of water d) the deformation of rock by heat & pressure *Now answer # 4 on page 375 in your Section Reviews section of your science notebook. Section 4 (pages 376-381) BELLWORK: page 386-387 # 2,6,7 30. When temperature and pressure change, what can happen to the minerals in rocks during metamorphism? They _____________ into minerals that are more ______________. 31. What kind of metamorphic rock has its mineral grains arranged in planes or bands? a) extrusive b) nonfoliated c) foliated d) intrusive 32. In ___________________ metamorphic rock, mineral grains are NOT arranged in bands. 33. A rock that forms from the melting and cooling of rock is made of ______________. 34. As a consequence of recrystallization, ______________ ________________ rock forms. 35. During metamorphism, limestone changes to become a metamorphic rock called marble. What happens to the calcite in the limestone during this process? a) They recrystallize and grow larger b) They separate to form bonds c) They change in chemical composition c) They become quartz crystals 36. The process in which rocks change shape is called _____________________. *Now answer # 2 on page 381, using figure 6 on page 380 ANSWER KEY 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. 22. 23. 24. 25. 26. 27. 28. 29. 30. 31. 32. 33. 34. 35. 36. rock rock cycle (A) deposition, compaction, & cementation; (B) solidification; (C) melting & cooling construction weathering Erosion deposition temperature (or heat) & pressure B uplift composition chemical makeup texture igneous D intrusive igneous A extrusive fine (small) D sediment cementation strata clastic Chemical Organic, coal clastic, chemical, organic Stratification C change, stable C nonfoliated crystals nonfoliated metamorphic A deformation





