Course 2: Mastering pedagogy in the online environment
advertisement
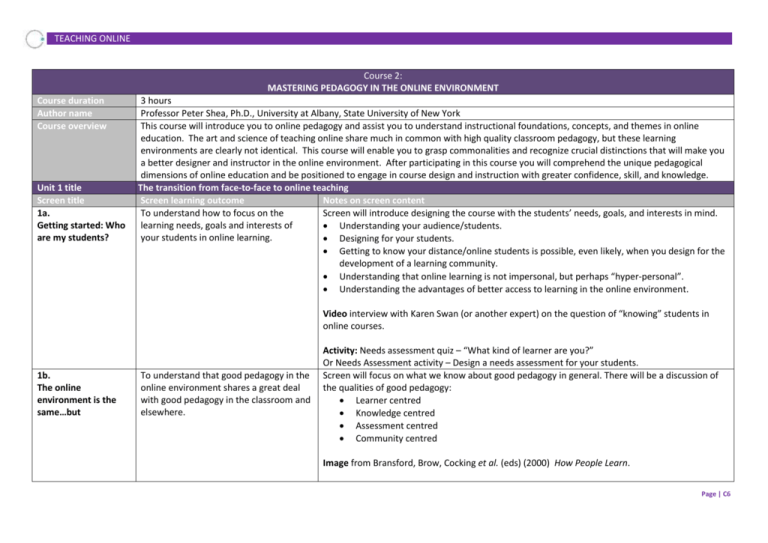
TEACHING ONLINE Course 2: MASTERING PEDAGOGY IN THE ONLINE ENVIRONMENT Course duration Author name Course overview Unit 1 title Screen title 1a. Getting started: Who are my students? 3 hours Professor Peter Shea, Ph.D., University at Albany, State University of New York This course will introduce you to online pedagogy and assist you to understand instructional foundations, concepts, and themes in online education. The art and science of teaching online share much in common with high quality classroom pedagogy, but these learning environments are clearly not identical. This course will enable you to grasp commonalities and recognize crucial distinctions that will make you a better designer and instructor in the online environment. After participating in this course you will comprehend the unique pedagogical dimensions of online education and be positioned to engage in course design and instruction with greater confidence, skill, and knowledge. The transition from face-to-face to online teaching Screen learning outcome Notes on screen content To understand how to focus on the Screen will introduce designing the course with the students’ needs, goals, and interests in mind. learning needs, goals and interests of Understanding your audience/students. your students in online learning. Designing for your students. Getting to know your distance/online students is possible, even likely, when you design for the development of a learning community. Understanding that online learning is not impersonal, but perhaps “hyper-personal”. Understanding the advantages of better access to learning in the online environment. Video interview with Karen Swan (or another expert) on the question of “knowing” students in online courses. 1b. The online environment is the same…but To understand that good pedagogy in the online environment shares a great deal with good pedagogy in the classroom and elsewhere. Activity: Needs assessment quiz – “What kind of learner are you?” Or Needs Assessment activity – Design a needs assessment for your students. Screen will focus on what we know about good pedagogy in general. There will be a discussion of the qualities of good pedagogy: Learner centred Knowledge centred Assessment centred Community centred Image from Bransford, Brow, Cocking et al. (eds) (2000) How People Learn. Page | C6 TEACHING ONLINE 1c. …The online environment is also different 1d. Transformation, not duplication To understand that the pedagogy of online learning has some distinctive qualities: Teaching Presence Social Presence Cognitive Presence Learning Presence To understand that classroom-based materials must be transformed for online environments. Orientation and Syllabus Modular Design Office Hours Activity: Finding the right balance – Which “centre” is crucial to support student learning in your own course(s) and why? Can we sacrifice one in favour of another? How? Why? This screen will explain the Community of Inquiry (CoI) model. Presentational activity Overlays CoI on ‘How People Learn’ framework. Activity: Self-assessment quiz on CoI. [Further information on the CoI model can be found in Course 4: ‘Being a successful online instructor’.] Discussion and examples of the need for greater explicitness and redundancy. Need for more complete orientation and syllabus with examples. Need for complete schedule with due dates and ranges for asynchronous discussion. Need for setting expectations etc. Examples of various elements of the orientation and syllabus section. Activity: Presentation of two syllabi highlighting the flow needed for an asynchronous online course and the added detail required to compensate for the lack of face-to-face negotiation of meaning 1e. Instructional design 101: Start with the end and work back To be introduced to the role of instructional design for pedagogy in the online environment. 1f. Some dos and don’ts for online teachers To understand common mistakes in online teaching and how to avoid them. Application: Participants will work on their own course syllabus Participants will learn how to create a plan that will be solid yet allow for increased flexibility. Modular design of courses. Consistency with variety. Working back from overarching goals and objectives to design supporting learning activities. Goal-setting template and activity. [This screen will be linked with learning from Course 3: ‘Designing and Developing your course’.] Discussion and examples of activities that do and do not work well and why: The Course and a Half Lack of Structure Mistakes in Group Work Page | C7 TEACHING ONLINE Others Video interviews with instructors on one learning activity that worked and one learning activity that they would not do again. 1g. Unit review Unit 2 title Screen title 2a. The promises of online learning 2b. Interaction in all its forms Scenario activity: Participants are presented with a series of scenarios of ‘common mistakes’; they select their preferred course of action and are given feedback on their choices. This screen will review and check understanding of key concepts covered in the preceding screens. How learning takes place in the online environment Screen learning outcome Notes on screen content To gain an understanding of the Screen will focus on the motivating visions as well as mechanisms for promoting learning across ‘promises’ of presentation, intelligent distance education modalities, including online learning. tutoring, and epistemic engagement. Presentation. Intelligent tutoring. Epistemic engagement. To be able to promote epistemic engagement through various forms of interaction. Video case study: MOOCs as case studies that unwittingly reflect the promises of online learning. Screen will focus on promoting epistemic engagement (will be defined in previous section) through various forms of interaction. Student-Content Student-Instructor Student-Student Student-Interface Student-Agent Vicarious Interaction Activity: Examples of activities that promote or support each form of interaction 2c. Formative feedback To understand that feedback is the most powerful tool in online and traditional settings. Brief review of research on feedback and examples of forms of feedback that support learning. Formative feedback activities Multiple Drafts of papers Revisions of Projects Other Staged Learning Activities Page | C8 TEACHING ONLINE 2d. Collaboration and knowledge construction 2e. Learning “presence”: Online regulated learning To understand the rationale for collaboration and the conceptual foundations for community-centric learning environments. To understand the rationale, conceptual foundations, and ways to promote online learner self-regulation. Reflective Journals Video of various experts responding to the question “Why is feedback so important?” Screen will contain a brief review of the rationale for collaboration. Activity: Presentational activity explaining the concepts of: Community and Learning Roots of Collaborative Learning Cooperative Learning Case studies of successful collaborative learning activities. Brief review of self and co-regulation of learning and its special relevance to online environments. Self-regulated Learning Self Efficacy Online Learning Demands Activity: Examples of self-tests for self-regulation in the online environment. 2f. Unit review Unit 3 title Screen title 3a. The non-traditional student 3b. The professional student Pod: Cross reference to Course 6, ‘Studying online’ – a course for students. This screen will review and check understanding of key concepts covered in the preceding screens. The learner: Understanding learner characteristics Screen learning outcome Notes on screen content To understand in more detail some of the Case study of non-traditional student with: demographics that shape non-traditional kids student needs. low paying job other stressors and how this can affect performance in online learning. To understand how to adapt for the learner characteristics of a ‘professional student’. Activity: Top Tips for Working with the Non-Traditional Student. Case study of professional student with drive, self-organization, and conflicting responsibilities and how such students may contribute to or struggle with online learning. Activity: Top Tips for working with Professionals. Page | C9 TEACHING ONLINE 3c. The adult student To understand the importance of andragogy with an adult population. 3d. Clueless: The dependent student 3e. “Expert”: the dominant student 3f. Unit review Unit 4 title Screen title 4a. Designer To learn how to support students who may be less self-regulated. 4b. Coach 4c. Sage 4d. Self-regulation aid To build up strategies for coping with students who attempt to dominate in the online environment. Case study of adult student with reference to Knowles and concept of andragogy – need for choice in learning activities. Activity: Top Tips for working with Adult Students. Case study and discussion of Dzuiban and Moskal’s work on less successful student types. Activity: Top Tips for working with Dependent Students. Case study of dominant students and strategies for managing this student type. Activity: Top Tips for working with Dominant Students. This screen will review and check understanding of key concepts covered in the preceding screens. The instructor: The changing role of the instructor Screen learning outcome Notes on screen content To understand the instructor’s role as a Activity: Feature comparison –comparison of the two roles ‘instructor’ and ‘designer’. designer of learning activities. Activity: Diagnostic exercise to assess how comfortable the participant is with the different aspects of these roles. Activity identifies areas for improvement and offers supporting feedback with links to resources. To help you to identify the skills and Activity: Comic graphic novel branching scenario – The coaching metaphor of online instruction. capabilities within the learner, and how Participant is presented with a series of scenarios and choses the ‘correct’ course of action to get to enable them to use them to the best of the best out of their student. their ability. Video: Interview with expert practitioners giving tips on when and how to be a good coach. To understand your role in direct Developing materials for the provision of direct instruction that are appropriate to the online instruction and how to incorporate it into environment: your course. Mini-lectures Stand alone video Stand alone PPT Narrated Prezi To understand how to support students in need of additional self-regulation. Video case study: The Khan Academy approach to online instruction. Present/Depiction of Cycle of: Planning Page | C10 TEACHING ONLINE 4e. Motivational guide 4f. Unit review Unit 5 title Screen title 5a. Learners 5b. Instructional Designer 5c. Multimedia Designer/Educational Technologist 5d. Help Desk staff To understand the role of motivation – intrinsic and extrinsic – and how to use motivation to enhance learner success. Monitoring and Strategy use Reflection Case study: “The Undermining Effects of External Rewards on Intrinsic Motivation”. Activity: Game – motivate the student. Select the most appropriate motivational elements to get the best out of the student. This screen will review and check understanding of key concepts covered in the preceding screens. The different roles of those who contribute to a successful learning experience Screen learning outcome Notes on screen content To understand common: Activity: Quiz on the question “What does it mean to be “Learner Centred?” Needs Goals Contributions etc. of learners. To understand the role of an instructional Description of the role of the instructional designer and how you can work with them. designer in helping to: Video vignette from instructional designers and how they view their work. Plan Design Pod: ‘Your context’- institutions upload their own contact information for instructional design Evaluate services on campus. This pod will be set as a default with links to ID resources open to all. online courses. To understand the role of a multimedia designer in designing: Illustrations Animation Simulations etc. in a course. To understand how the help desk can be used to support learners. Pod: Portfolio activity – Seek out an instructional designer at your institution and discuss with them your needs and ideas for your online course. Description of the role of the multimedia designer. Video vignette of how they view/do their work. Activity: How to write a brief for a multimedia designer. Activity: Interactive image of call centre staff and clear description of the importance of Help Desk in making online teaching sustainable. Pod: ‘Your context’ – institutions upload their own contact information for IT help desk services on campus. Page | C11 TEACHING ONLINE 5e. Disability support services staff 5f. Advisors and others 5g. Unit review Unit 6 title Screen title 6a. Introduction to different pedagogical approaches To understand how the disability services staff can be used to ensure that your course follows universal accessibility standards. To understand the many other roles that may be a part of the online learning environment: Advisors Librarians Counsellors etc. Description of the role of the disability support services staff. Video: Case study of a practitioner who followed steps to design a course with inbuilt universal accessibility. Advice. Common pitfalls. Points to consider. Pod: ‘Your context’ – institutions upload their own contact information for disability support services on campus. Activity: The role of Digital age advisors, librarians, counsellors. Pod: ‘Your context’ – institutions upload their own contact information for library/resource support services on campus. This screen will review and check understanding of key concepts covered in the preceding screens. Common pedagogical approaches Screen learning outcome Participants will be given an overview of the different pedagogical models that are covered in this unit. 6b. Blended learning To understand how to adapt your pedagogical approach for a ‘Blended Learning’ course. 6c. Problem-based learning design To understand and be able to design a ‘problem-based learning’ program. Notes on screen content Activity: Descriptions of each of the models. Similarities and differences between the different curriculum models. Participants will be set up to be able to evaluate which curriculum suits their own course adaptation needs. Podcast: A discussion of key pedagogical approaches in online learning. Blended learning: Planning Organizing Managing Defining the objectives of a facilitator Introducing students to a Blended Learning approach How to ‘Flip the Classroom’ Case study of advantages and disadvantages of Blended Learning. Problem Based Learning Design (students learn through problem solving): Planning Organizing Page | C12 TEACHING ONLINE 6d. Assessment-based learning design To understand and be able to design an ‘assessment-based learning’ program. Managing Defining the objectives of a facilitator Introducing Students to the PBL Program Changing the assessment to suit the PBL curriculum Case study of advantages and disadvantages of PBL. Activity: Planning your own PBL curriculum. Assessment-based learning design (students learn): Planning Organizing Managing Defining the objectives of a facilitator Introducing Students to the Assessment Based Learning Program Changing the assessment to suit the Assessment Based Learning curriculum Case study of advantages and disadvantages of Assessment Based Learning. 6e. Inquiry-based learning design 6f. Discussion-based/ eclectic approaches To understand and be able to design an ‘inquiry-based learning’ program Activity: When is it appropriate to use assessment-based learning and when is another approach more effective? Inquiry-based learning: Planning Organizing Managing Defining the objectives of a facilitator Introducing Students to Inquiry Based Learning Changing the assessment to suit the Inquiry Based curriculum Case study of advantages and disadvantages of Inquiry Based Learning. Activity: Planning your own Inquiry Based Learning program. To understand and be able to use Discussion-based/eclectic approaches to learning: discussion or other eclectic approaches in Planning your online program. Organizing Managing Defining the objectives of a facilitator Page | C13 TEACHING ONLINE 6g. Unit review Introducing Students to Inquiry Based Learning Changing the assessment to suit the Discussion-Based curriculum Case study of advantages and disadvantages of Discussion Based/Eclectic Approaches. Activity: Designing good discussion-based activities. This screen will review and check understanding of key concepts covered in the preceding screens. Application: Considering and planning your own pedagogical approach Page | C14