S. No
advertisement

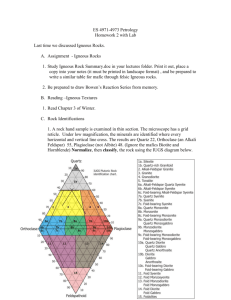
S. No Igneous Rock families 1 Defination: 2 Mineralogy Granite – Rhyolite family Granite Rhyolite Granodiorite Plutonic , hypabyssal, holocrystaliline, Phaneritic Extrusive, hypabyssal, holocrystalline to hypocrystalline, aphanetic Is intrusive, Holocrystalline, phaneritic Quartz Potash feldspar Sodic Plagioclase 1-Calc-alkali granite: - Potash feldspar (Perthitic orthoclase or microcline. - Biotite ± muscovite (mafic min.). - Oligoclase or rarely andesine. - H.B(green to brownish), - Diopside or augite. - Qtz is interstitial 2- Alkaligranite: - Strongly Perthitic (orth.,or micro. - Allbite or Na oligocllase. - Iron rich Biotite. - Hastingsite,riebeckite. - Aegirineaugite,aegirine. - Quartz. Accessory minerals Granodiorite- Quartz Latite - Magnetite,ilmenite, hematite, pyrite, apatite, monazite, zircon, allanite, sphene, tourmaline, fluorite, and garnet. 10-40% 30- 60% 35-10% Potash Felds. 20 – 40 % Sodic Plagio. 25 – 45 % Quartz 10 - 35 % Mafics (Bio, H.B) 10 – 30% 1- Potassic Rhyolite: - Grano diorite Plagioclase - Alkali feldspar equal o exceed K'Sanidine untwined or feldspar. twinned Carlsbad - But if k-feldspar is rare twinning" then the rock is called - Plagioclase if present is TONLITE Oligoclase> - Potash felds. Is - Green biotite as orthoclase & microcline, phenocrysts andmatrix - Plagioclase is Oligoclase flakes or less andesine. - Brown or green H.B. - Browm biotite and green 2- Sodic Rhyolite: HB. - Same as above but, - Pyroxene ( Diopside or Amphibole minerals augite) are riebeckite, - The arfvdsedsonite, orthoclase/plagiocalse hastingsite. ratio the rock will be - Pyroxenes are not named: common in Rhyolite. - 13¼ /66 tonalite - 33 /66 Quartz mononite - In Holocrystalline type: Tridymite Qtz, Titanian, magnetite, cordierite, sphene, zircon, apatite, garnet. Apatite, magenetite, ilmenite, sphene, and garnet. Quartz- Latite (Dellenite and Rhyodacite) Is extrusive, hypabyssal, aphanitic matrix holocrystalllline to vitreous (porphyritic Potash feldspar 20 – 30 % Sodic Plagio. 30 – 50c% Quartz 10 – 35 % Mafics 10 – 20 % Sanidine (is the usual kfelds.) appear as phynocrysts. Calcic andesine to Oligoclase Brown bio, & H.B as phynpcrysts. Sphene Quartz (Tridymite) Apatite, magenetite, ilmenite, sphene, zircon, 3 Texture & microstructure - Euhedral-granullar,fine to coarse grained, - Granophyritic rime, plagioclase embayed with orthoclase, - Graphitic texture. - Cataclastics effect(undulatort qtz, feldspar bent cleavageand mica plate) - Aplite texture: fine grained , leucogranites - Pegmatitic textur couse grain dykes - Rapakivi texture (large oval shalle of orthoclase surrounded by oligocllase 4 Occurrence Granites occur in: - Batholiths, stocks, Hypabyssal bodies ( minor intrusion sill & dikes) - Porphyritic and great - Equigranular, medium - Porphyritic with variety of matrix grained Holocrystalline, textures are presented: - Subhedral to anhedral cryptocrystalline, 1- Holocrystalline: granular texture vitreous - Microgranular, - Myrmekite texture - Flow structures - Trachytic - Granophyric - Spherulitic - Cryptocrystalline (devitrified. 2- Hypcrystalline: - Hyalopilitic (microcrystalline with interstitial glass), - Vitreous wt. cryptocrystalline patches. - Vitreous wt. microlites. - Vitreous wi. Spherulites. 3- Rhyolite Vitrophyres - Crystalites. - Banded, streaked, fluidal. Rhyolite occurs as Granodiorites occur in: Rhyodacite occurs as - Flow Batholiths, stocks, - Flow - Volcanic type is Hypabyssal bodies ( minor - Volcanic rocks & also hypabyssal intrusive intrusion sill & dikes) as dikes and sills. dikes and sills. Associted with Rhyolite - Ass0cited with dacite and trachyte and andesite and basalt basalt S. No 1 2 3 4 S. No 1 2 3 4 Igneous Rock families Syenite – Trachyte family Syenite Tonlite – Dacite family Trachyte Defination: Mineralogy Accessory minerals Texture & microstructure Occurrence Igneous Rock families Defination: Mineralogy Accessory minerals Texture & microstructure Occurrence Syenite – Trachyte family Syenite Tonlite – Dacite family Trachyte