Hurricane Tracking
advertisement

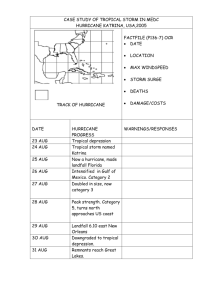
Name: ___________________________Period: ___________ Date: ______________ Group Members: Hurricane Watch (Latitude and Longitude Lab) Introduction: Hurricanes are one of nature’s most powerful disasters! To equal the power of a hurricane one would have to set off about a thousand nuclear devices per second for as long as the hurricane rages. It is very difficult to predict where a hurricane will travel, but this Prediction is very important, especially if you are in its path. In this lab you will be plotting the path of some of the most deadly, devastating, and recent hurricanes. You will be asked to analyze the strength of the hurricanes, compare their speed of travel, and their paths’ of destruction. Storm Surge: "The greatest potential for loss of life related to a hurricane is from the storm surge." - Brian Jarvinen, National Hurricane Center. Storm surge is simply water that is pushed toward the shore by the force of the winds swirling around the storm. This advancing surge combines with the normal tides to create the hurricane storm tide, which can increase the mean water level 15 feet or more. In addition, wind driven waves are superimposed on the storm tide. This rise in water level can cause severe flooding in coastal areas, particularly when the storm tide coincides with the normal high tides. Because much of the United States' densely populated Atlantic and Gulf Coast coastlines lie less than 10 feet above mean sea level, the danger from storm tides is tremendous. Directions: Plot the hurricanes’ paths using their latitude and longitude. Use a different colored pencil to mark the paths of the different hurricanes. Use the Saffir-Simpson scale to determine the category of the hurricane and answer the analysis and conclusion questions. Latitude and longitude are given in degrees and minutes. Remember each degree can be divided into 60 minutes. Saffir-Simpson Scale: The Saffir-Simpson Hurricane Scale is a 1-5 rating based on the hurricane's present intensity. This is used to give an estimate of the potential property damage and flooding expected along the coast from a hurricane landfall. Wind speed is the determining factor in the scale, as storm surge values are highly dependent on the slope of the continental shelf in the landfall region. Category Tropical Storm Wind Speed 1 74-95 mph 2 96-110 mph 3 111-130 mph 4 131-155 mph 5 156 mph + Description 39-73 mph No real damage to buildings. Damage to unanchored mobile homes. Some damage to poorly constructed signs. Also, some coastal flooding and minor pier damage. Some damage to building roofs, doors and windows. Considerable damage to mobile homes. Flooding damages piers and small craft in unprotected moorings may break their moorings. Some trees blown down. Some structural damage to small residences and utility buildings. Large trees blown down. Mobile homes and poorly built signs destroyed. Flooding near the coast destroys smaller structures with larger structures damaged by floating debris. Terrain may be flooded well inland. More extensive curtain wall failures with some complete roof structure failure on small residences. Major erosion of beach areas. Terrain may be flooded well inland. Complete roof failure on many residences and industrial buildings. Some complete building failures with small utility buildings blown over or away. Flooding causes major damage to lower floors of all structures near the shoreline. Massive evacuation likely. 1 Name: ___________________________Period: ___________ Date: ______________ Group Members: Hurricane Andrew (1992): Hurricane Andrew was the most destructive United States hurricane of record. It blasted its way across south Florida on August 24, 1992. NOAA's National Hurricane Center had a peak gust of 164 mph—measured 130 feet above the ground—while a 177 mph gust was measured at a private home. Andrew caused 23 deaths in the United States and three more in the Bahamas. The direct loss of life seems remarkably low considering the destruction caused by this hurricane. The hurricane caused $26.5 billion in damage in the United States, making Andrew the most expensive natural disaster in U.S. history. Plot the following points as an X on your map; connect your points. Label the category of the storm. Note: readings taken every 12 hours # Month Day Year Time N.Lat W.Long MPH 1 Aug 20 1992 00:00 21º, 40' 60º, 40' 46 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 Aug Aug Aug Aug Aug Aug Aug Aug Aug Aug Aug Aug Aug 20 21 21 22 22 23 23 24 24 25 25 26 26 1992 1992 1992 1992 1992 1992 1992 1992 1992 1992 1992 1992 1992 12:00 23º, 10' 62º, 35' 52 00:00 24º, 25' 64º, 10' 58 12:00 25º, 20' 65º, 55' 63 00:00 25º, 50' 68º, 20' 81 12:00 25º, 35' 71º, 05' 104 00:00 25º, 25' 74º, 10' 138 12:00 25º, 25' 77º, 30' 155 00:00 25º, 35' 81º, 10' 127 12:00 26º, 10' 85º, 00' 132 00:00 27º, 10' 88º, 10' 132 12:00 28º, 30' 90º, 30' 138 00:00 30º, 00' 91º, 40' 92 12:00 31º, 30' 91º, 00' 40 Category 2 Name: ___________________________Period: ___________ Date: ______________ Group Members: Hurricane Jeanne (2004): Jeanne hit Florida after Charley, Frances, and Ivan. In six weeks these storms shut down much of the state and prompted recovery plans on a scale never before seen in the nation. Jeanne was blamed for at least six deaths in Florida. The storm had already cut a deadly path through the Caribbean, where floods in Haiti, the Dominican Republic and Puerto Rico killed over 3,000 people. Haiti suffered the heaviest toll. Two days of torrential rains caused massive flooding and mudslides in the northern region, killing close to 3,000 people. Plot the following points as an X on your map; connect your points with a different colored line. Label the category of the storm. Note: readings taken every 6 hours # 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 Month Sept Sept Sept Sept Sept Sept Sept Sept Sept Sept Sept Sept Sept Sept Sept Sept Sept Sept Sept Sept Sept Sept Sept Day 20 20 21 21 21 21 22 22 22 22 23 23 23 23 24 24 24 24 25 25 25 25 26 Year 2004 2004 2004 2004 2004 2004 2004 2004 2004 2004 2004 2004 2004 2004 2004 2004 2004 2004 2004 2004 2004 2004 2004 Time 5:00PM 11:00PM 5:00AM 11:00AM 5:00PM 11:00PM 5:00AM 11:00AM 5:00PM 11:00PM 5:00AM 11:00AM 5:00PM 11:00PM 5:00AM 11:00AM 5:00PM 11:00PM 5:00AM 11:00AM 5:00PM 11:00PM 5:00AM N.Lat 27º, 25’ 27º, 25’ 27º, 40’ 27º, 30’ 27º, 20’ 27º, 00’ 26º, 40’ 26º, 20’ 26º, 05’ 25º, 40’ 25º, 30’ 25º, 40’ 25º, 55’ 26º, 05’ 26º, 05’ 26º, 15’ 26º, 25’ 26º, 30’ 26º, 30’ 26º, 35’ 27º, 10’ 27º, 15’ 27º, 25’ W.Long 71º, 15’ 70º, 35’ 70º, 00’ 69º, 20’ 68º, 50’ 68º, 45’ 68º, 40’ 68º, 30’ 69º, 00’ 69º, 20’ 69º, 30’ 69º, 40’ 70º, 20’ 70º, 45’ 71º, 35’ 72º, 25’ 73º, 30’ 74º, 55’ 76º, 10’ 77º, 35’ 78º, 40’ 80º, 00’ 81º, 10’ MPH 80 80 85 85 85 85 85 90 90 90 90 95 95 95 90 90 90 90 95 105 115 110 95 Category 3 Name: ___________________________Period: ___________ Date: ______________ Group Members: Hurricane Ernesto (2006): Remnants of this storm brought many of our Labor Day plans to a halt. Wind speeds of over 50mph brought many trees and and limbs down causing massive power outages all along the South Shore of Long Island. Beach erosion hit Robert Moses State Park most severely, affecting nearly the entire beachfront. Sunken Meadow Park on the North Shore lost two to four feet of dunes. The wind pushed the sand up to the point where a lake, two to three feet deep, was created on Jones Beach near the West Bathhouse. At least six died in North Carolina and Virginia as the storm made its way up the Eastern Seaboard. Plot the following points as an X on your map; connect your points with a third color. Note: readings taken every 12 hours. # 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 Month Aug Aug Aug Aug Aug Aug Aug Aug Aug Aug Aug Aug Aug Aug Sept Sept Sept Sept Sept Day 25 25 26 26 27 27 28 28 29 29 30 30 31 31 1 1 2 2 3 Year 2006 2006 2006 2006 2006 2006 2006 2006 2006 2006 2006 2006 2006 2006 2006 2006 2006 2006 2006 Time 03:00AM 03:00PM 03:00AM 03:00PM 03:00AM 03:00PM 03:00AM 03:00PM 03:00AM 03:00PM 03:00AM 03:00PM 03:00AM 03:00PM 03:00AM 03:00PM 03:00AM 03:00PM 03:00AM N.Lat 13º 12’ 13º 30’ 14º 48’ 15º 06’ 16º 48’ 17º 36’ 18º 36’ 20º 18’ 21º 42’ 23º 18’ 24º 54’ 26º 24’ 28º 42’ 31º 18’ 33º 54’ 36º 24’ 37º 30’ 38º 42’ 40º 42’ W.Long 63º 54’ 66º 24’ 69º 06’ 71º 12’ 72º 42’ 73º 42’ 74º 42’ 75º 42’ 78º 48’ 79º 30’ 80º 30’ 80º 54’ 80º 36’ 79º 36’ 78º 12’ 77º 36’ 76º 48’ 76º 48’ 76º 54’ MPH 35 35 45 50 60 75 50 40 40 45 45 35 35 60 70 35 40 50 35 Category Analysis: 1. Mark the 30ºN Latitude line on your map. State the general direction that the storms moved below this line. ________________________ What direction did the storms move above this line? ____________________ 2. Go to page 14 of the ESRT. What is a likely reason for the general paths of the storms? _________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________________ 4 Name: ___________________________Period: ___________ Date: ______________ Group Members: 3. Cuba is 1,140km across. Create a scale for your map. Show your work. 4. Speed is distance divided by time. What was the average speed (not wind speed) of Hurricane Andrew between points #5 and #11. Show your work. 5. What was the average speed of Ernesto between points #9 and #19 Show your work. 6. Where are the storms when they had their strongest winds? ________________________________________ 7. What happens to the wind speeds and intensity of the storm as they move over land? __________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________________ 8. Based on what you already know about seasons and hurricanes, make an inference about why most Hurricanes form in the months of July, August, and September._________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________________ 5