DATASTREAM CHARTING
USING STATIC SCATTER CHARTS
ABOUT STATIC SCATTER CHARTS
CREATING A STATIC SCATTER CHART
SETTING DATES IN STATIC SCATTER CHARTS
FORMATTING A STATIC SCATTER CHART
DISPLAYING MULTIPLE SETS OF SCATTER POINTS
REORGANISING THE SERIES ON A STATIC SCATTER CHART
CUSTOMISING INDIVIDUAL POINTS ON A STATIC SCATTER CHART
REMOVING POINTS FROM A STATIC SCATTER CHART
ANNOTATING A STATIC SCATTER CHART
USING SUBSTITUTABLE TEXT ON A STATIC SCATTER CHART
ADDING A LINE OF BEST FIT
DISPLAYING STATISTICAL MEASURES
USING STATIC SCATTER CHARTS WITH TEMPLATES
DISPLAYING YIELD CURVES ON STATIC SCATTER CHARTS
ADJUSTING THE SCREEN LAYOUT
ABOUT STATIC SCATTER CHARTS
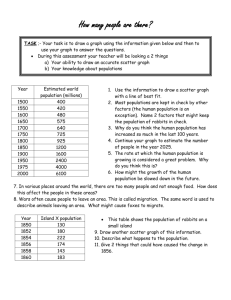
A static scatter chart enables cross-sectional analysis at one point in time of a list or group of entities (sectors,
companies, markets, bonds and so on). Further dates can be added to compare two or more snapshots of the same
entities.
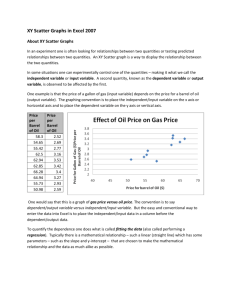
The values for each entity are used to draw points in a coordinate (X, Y) system created by the horizontal (X) and
vertical (Y) axes, for example risk on the horizontal (X) axis and return on the vertical (Y) axis. Each point on the
scatter chart corresponds to a different entity (company, market, bond and so on). SVG users can hover over each
point to see the X and Y coordinate values for each series as well as the date of the point. The values are also shown
in the Data tab.
Datastream Charting New Feature Guide – Static Charts
CREATING A STATIC SCATTER CHART
1. If necessary, click on the New Blank Chart icon on the toolbar.
2. Select the Static Scatter chart layout from the drop-down menu on the toolbar.
3. In the Series area select the series or list you wish to display. If you know the mnemonic(s), type it in the
horizontal (X) axis text box and press Enter. Alternatively, use the flyout at the end of the text box to find a series
or list in Navigator. You can type multiple codes into the text box by separating them with a comma.
The following types of list may be used:
Constituent lists displayed in Navigator (L lists, e.g. LDJINDUS)
User created lists which have been uploaded to the mainframe (L# lists)
UCI lists (X# lists)
Macro-economic series lists (M# lists, e.g. M#USKEY)
A text box will automatically appear for the vertical (Y) axis series. If you want to display two measures for the
same entities such as risk and return for a single list of equities, copy the same series or list mnemonics into the Y
axis text box.
Alternatively, if you are comparing two different sets of economic series, such as current account balance and
government deficit for a selection of countries, enter the current account balance series mnemonics in the X axis
text box and the government deficit series mnemonics on the Y axis text box.
4. If using an expression, select the functions, datatypes and currencies as required in the Expression area. Stored
expressions from the expression picker can also be applied to the series from the function menu.
2
Datastream Charting New Feature Guide – Static Charts
5. Select the required date point(s). For more on dates in static scatter charts see Setting dates in static scatter
charts.
6. Click the Apply Changes button on the chart.
7. The chart will be displayed. The axes will be labelled with any functions or datatypes selected in the expressions
area. You can customise or delete the text of the axis titles.
Top
SETTING DATES IN STATIC SCATTER CHARTS
Static scatter charts display data at a particular date (a Date Point) rather than across a date range. If your chart has
only one Scatter, you can add multiple Date Points.
To set the Date Point
Set the Date Point in the Dates section of the Series and Dates tab.
A number of options are available:
LATEST
This is the default and is the date of the latest data available among the selected series. So if Series A has data until
February but Series B only has data until January, LATEST will draw a chart of the February value for Series A and
there will be no data to display for Series B.
If you are using a datatype with your series LATEST will return the date of the latest data available for the underlying
series, but it is possible that the datatype you have selected does not have values for that date.
Note: If no values are displayed on the chart for the selected date, switch to the Data tab to check for N/A values and
if necessary try a different date.
COMPARABLE
This setting is the latest date for which all series on the chart have data. So if Series A has data until February but
Series B only has data until January, COMPARABLE will draw a chart of the January values for both series. The
February value for Series A will not be displayed. As soon as Series B is updated with a value for February, the chart
will switch to displaying February values for both series.
COMPARABLE looks for the date of the latest data available for the underlying series, but if you are using datatypes it
is possible that the datatype you have selected does not have values for that date.
3
Datastream Charting New Feature Guide – Static Charts
Relative dates
The usual relative dates can be used. Select from the flyout in the Dates section or type in the required date, for
example -3Y or +6M.
Absolute dates
You can use absolute dates. The format depends on your Internet Explorer language settings. For example UK users
can use DD/MM/YY or MM/YYYY. The chart will display the nearest relevant data, For example, if you request
20/06/2009 for a quarterly series, the chart will display the data for Q2 2009.
Note: You can confirm the date of the displayed values by switching to the Data tab.
Top
FORMATTING A STATIC SCATTER CHART
Click on the hyperlinked scatter number on the Series and Dates tab or the Chart Settings tab (SVG users also have
the option to click on any of the scatter points).
The Scatter editor will appear and you can select the required options as follows:
Customise the legend
If you are using a legend you can customise the text here.
Add a line of best fit
For more on this, see Adding a line of best fit to a static scatter chart below.
Format markers
Click the expand icon
to open the Markers section.
Select from a number of marker styles and set the fill and border colours as well as the size.
Note: to format individual points separately from the rest of the group use the Expand Members option. For more on
this see Customising individual points in a static scatter chart.
Connect the points
Click the checkbox to connect the points in ascending order of X value – for example if plotting benchmark bonds with
Redemption Yield (datatype RY) on the Y axis and Life (datatype L or LF) on the X axis, the points can be connected
to form a basic yield curve. For more on yield curves see Displaying bond yields on static scatter charts.
4
Datastream Charting New Feature Guide – Static Charts
Top
DISPLAYING MULTIPLE SETS OF SCATTER POINTS
You can display multiple sets of points on the same scatter chart and use different markers to style each set of scatter
points.
To compare the same measures for multiple sets of series or lists
For example, you might want to compare a list of Japanese companies with a list of US companies using the same
datatypes.
1. Add the first list or set of series to the X and Y text boxes for Scatter 1.
5
Datastream Charting New Feature Guide – Static Charts
2. Click the link for Add Another Scatter.
3. Add the second list or set of series to the X and Y text boxes for Scatter 2.
4. Format the points as required. See Formatting a static scatter chart.
Note: When multiple scatters are added, only one date point is permitted.
To display the same list or series at different dates
1. Click the link for Add Another Date
2. Select the required date from the flyout or type it in. For more on dates see Setting dates in static scatter charts.
3. e legend will now show the two
4. Format the scatter points as required
Note: When multiple date points are displayed only one set of series i.e. one scatter, is permitted.
Top
REORGANISING THE SERIES ON A STATIC SCATTER CHART
When using economic series to display two indicators for a number of different countries or regions, it is important to
ensure that the series pairs are correctly matched for each country.
For example, if you are creating a scatter chart of unemployment on the X axis and GDP growth on the Y axis for BRIC
economies and the order of the unemployment series in the X axis text box is Brazil, Russia, India, China, then you
must ensure that the order of the GDP growth series in the Y axis text box is also Brazil, Russia, India, China.
To check the order and reorganise the series if necessary click the Reorganise option from the flyout to the left of the
Scatter link.
A dialog will open showing all the pairs of series from the X and Y text boxes.
Use the Move Up and Move Down buttons to change the order of the series as necessary.
Top
6
Datastream Charting New Feature Guide – Static Charts
CUSTOMISING INDIVIDUAL POINTS ON A STATIC SCATTER CHART
1. Click the Expand Members option from the flyout to the left of the Scatter link.
2. Check the checkboxes to select the required entities.
The selected scatters will now be displayed with the same style as the original scatter but with larger markers. Each
scatter can be styled separately by clicking on the relevant scatter link.
You can also annotate the individual scatters or delete them from the chart. For more on deleting points see
Removing points from a static scatter chart.
Alternatively, use the Add Another Scatter link to add each scatter separately. This method can be used if you want
to add the individual point as the first scatter on the chart so that you can refer to it in substitutable text.
For more on this see Using substitutable text on a static scatter chart.
Note: Expand members is not enabled when multiple date points are used.
Top
REMOVING POINTS FROM A STATIC SCATTER CHART
Removing outliers
To remove outliers you can adjust the upper and/or lower limits of your axes so that values outside the specified range
will not be displayed.
In the Chart Settings tab click on the axis links for Left Axis and Bottom Axis to open the required axis editor and set
the upper and/or lower limits.
7
Datastream Charting New Feature Guide – Static Charts
Note: If you have a best fit line on the chart, this will redraw based on the new sample of displayed points. See Adding
a line of best fit to a static scatter chart.
Removing other points
You can suppress the display of individual points within the selected chart range as follows:
3. Click the Expand Members option from the flyout to the left of the Scatter link.
4. Select all the members of the Scatter.
5. Click OK to create individual scatters for all the members.
6. Delete the original Scatter list.
7. Delete the scatter for the point that you want to suppress.
Top
ANNOTATING A STATIC SCATTER CHART
There are a number of ways to annotate the points on a static scatter chart.
To add an annotation to a single series
If the scatter contains a single series, this can be annotated in the usual way. Click the Annotations and Forecasts
tab and select Add Note for the required series.
Alternatively, SVG Users can use Shift and left mouse click to select the point on the chart and open the annotation
editor from here.
To add an annotation to one or more of the points in a list
If the scatter contains more than one series or a list, individual points can still be annotated. Add each individual point
as a separate scatter and annotate as for a single series.
Alternatively, use the Expand Members option to annotate one or more of the points in the scatter as follows:
8
Datastream Charting New Feature Guide – Static Charts
1. Click Expand Members on the flyout menu to the left of the Scatter link.
2. Select the required entities using the checkboxes and click OK.
3. The selected entities will be added as individual scatters, which can then be styled and annotated individually.
To annotate all the points in a list
1. Click Annotate All Points on the flyout menu to the left of the Scatter link.
2. Set the required text and click OK.
Other annotations
Horizontal lines can be applied at the required value on the Y axis.
Vertical lines can be applied at the required value on the X axis.
Text boxes, rectangles and circles can be added at the required position on the chart canvas.
Date based annotations such as recession bands and freehand lines may not be used with static scatter charts.
Top
9
Datastream Charting New Feature Guide – Static Charts
USING SUBSTITUTABLE TEXT ON A STATIC SCATTER CHART
Annotating the scatter points using substitutable text
When adding annotations to the scatter chart, static datatypes can be used in substitutable text to label the points
automatically. The following substitutions may be useful in this context:
{NAME}
Series/company name
{GEOGN}
Geographical classification (country name)
{GEOGC}
2 character Datastream country code
(GGISO}
2 character ISO country code
{INDN}
Industry name (for use with Datastream sector indices)
Some of these are accessible from the flyout menu in the annotation editor:
Using substitutable text in the chart title or chart based annotations
In chart titles and chart based annotations such as text boxes any substitutable text will refer to the first individual
series on the chart.
To ensure that the correct series is referenced, add the series as a separate scatter and make sure that it is the first
scatter on the chart.
10
Datastream Charting New Feature Guide – Static Charts
You can then use {NAME} or other substitutable text in the title or annotation and it will refer to this series. The same
principle can be applied to any calculated values displayed in text box annotations such as {PCHV#(X,YTD)}.
Top
ADDING A LINE OF BEST FIT TO A STATIC SCATTER CHART
You can display a line of best fit through the points on your scatter chart.
1. Click on the hyperlinked scatter number on the Series and Dates tab or the Chart Settings tab (SVG users also
have the option to click on any of the scatter points).
(If you have multiple Date Points on the chart, click on the hyperlinked date point.)
2. The Scatter editor will appear:
In Statistical Calculations select a linear or logarithmic (exponential) line of best fit.
The colour of this line will follow the border colour of your markers.
If required, add one or more lines of standard deviation either side of the line of best fit. The colour of these lines will
follow the Foreground colour.
11
Datastream Charting New Feature Guide – Static Charts
Note 1: The logarithmic line of best fit cannot be applied to a chart with any negative values
Note 2: The line of best fit is calculated and drawn based on the series displayed on the chart and excludes any series
which have been suppressed from the chart, for example outliers which have been excluded by setting upper/lower
limits in the Axis settings,
Top
DISPLAYING STATISTICAL MEASURES FOR A SCATTER CHART
Displaying the equation for a line of best fit
From the flyout menu to the left of the Scatter 1 link select Display Equation.
(If you have multiple Date Points on the chart, click on the flyout menu to the left of the date point.)
A text box will be added to the chart showing the Y = BX + A equation of the line of best fit through the points, where B
is the slope (beta coefficient) and A is the intercept (alpha coefficient).
For more on the line of best fit, see Adding a line of best fit to a scatter chart above.
The text box can be repositioned, formatted and edited in the usual ways.
Displaying other statistics
From the flyout menu to the left of the Scatter 1 link select Display All Statistics.
(If you have multiple Date Points on the chart, click on the flyout menu to the left of the date point.)
A text box will be added to the chart showing the following statistics for the scatter points and line of best fit:
12
Datastream Charting New Feature Guide – Static Charts
Alpha coefficient (intercept)
Beta coefficient (slope)
Correlation coefficient R
R squared
Standard deviation
The text box can be repositioned, formatted and edited in the usual ways.
Top
USING STATIC SCATTER CHARTS WITH TEMPLATES
You can use static scatter charts in templates and click through each member of the scatter to review its position
relative to the rest of the points.
To do this you need to add one member of the scatter as a separate scatter and style and label the point separately
from the rest of the scatter points so it can be identified. For more on this see Customising individual points on a static
scatter chart.
To run the chart with a template:
1. Click the Template tab.
2. Convert the chart to a template.
3. Select the required series or list from Navigator or the Recent Lists flyout. Usually this will be the list you used to
create the scatter chart, but sometimes you might want to see other series set against the context of the scatter
you have created.
4. Click through the template members to see each template chart.
5. Save the template.
Note: To set the chart title or any chart based annotations to display the name of the selected series, add the series as
a separate scatter and make sure that it is the first scatter on the chart. For more on this see Using substitutable text
on a static scatter chart.
Top
DISPLAYING YIELD CURVES ON STATIC SCATTER CHARTS
Static scatter charts can be used to display simple yield curves for a number of markets using linear interpolation to
connect the points on the curve. Swap curves are also available.
To draw a yield curve on a static scatter chart:
1. Select the relevant list of bonds from Navigator or type in the list mnemonic (see details of available lists here).
2. Specify the Life datatype (L) for the X axis. This shows how many years are left until the bond’s redemption date.
13
Datastream Charting New Feature Guide – Static Charts
3. Specify the Redemption Yield datatype (RY) for the Y axis.
Note: if you are using a list which has a default datatype of RY, you do not need to specify any datatype but can
just use X. See below for details of the lists and their default datatypes.
4. Select the date or dates for which you want to display the curve. You can display the same list at multiple dates or
multiple lists at the same date, e.g. curves for different countries.
5. Select the ‘Connect All Points’ option in the Scatter editor to draw the curve between the bonds. The colour and
style of the curve follows the styling of the marker borders.
6. If you wish to add further bonds to the curve, add the comma separated codes to the Series text box. For
example, you could extend the short end of the US curve by adding some constant maturity T-Bill rates, as shown
below. You can add the series in any order, as the Life datatype will ensure they are plotted in the correct position
on the curve.
7. If you wish to display only part of the curve, set the X axis upper and/or lower limits to exclude some of the points.
Note: You can also access the yield curve sample charts in the Datastream folder of the Chart Library and use these
as a starting point for your own chart. Look for the ‘Yield Curves’ folder or search for charts with Chart Name
containing ‘Yield Curve’ in the Datastream folder.
14
Datastream Charting New Feature Guide – Static Charts
Datastream benchmark yield curves
The Datastream benchmark lists are derived from the Datastream government bond indices and cover a wide range of
markets. The constituents of the lists have been stored historically, so you can be sure of seeing the correct curve for
the time period you select.
To find the list mnemonics you can search for ‘DS benchmark list’ in the Constituent Lists category in Navigator or click
here to check details of which curves are available.
For example, to display a yield curve of benchmark bonds for the United States, use the list mnemonic LDSUSBMK.
These curves contain bonds with maturities over 2 years. You can add series at the shorter end of the curve as
outlined above.
The default datatype is Price Index (PI). Use Life (L) on the X axis and Redemption Yield (RY) on the Y axis to plot the
curve.
Note: RY shows yields compounded according to the conventions of each market, e.g. semi-annually for the US,
annually for France. If you are comparing markets with different conventions you can use the Annualised Redemption
Yield datatype (RA) to see annualised yields for all markets.
Thomson Reuters yield curves
These lists provide rates for government bonds and treasury bills sourced from matrix prices.
The default datatype is Redemption Yield (RY). Use Life (L) on the X axis and the default X on the Y axis to plot the
curve.
To find the list mnemonics you can search for ‘TR benchmark list’ in the Constituent Lists category in Navigator or click
here to check details of which curves are available.
Swap curves
These lists cover a wide array of markets with maturities starting at 1 year.
The default datatype is Interest Rate (IR). Use Life (L) on the X axis and the default X on the Y axis to plot the curve.
Datatypes for bid (IB) and offer (IO) rates can also be used on the Y axis if preferred.
To find the list mnemonics you can search for ‘TR swap list’ in the Constituent Lists category in Navigator or click here
to check details of which curves are available.
Note: you may need to have an additional entitlement added to your Datastream ID to access these swap rates. If you
see N/A values on the Data tab, please contact your customer services representative and ask for the ICAP
entitlement to be added.
Using different types of list on the same chart
Care is needed when using swap lists alongside benchmark lists or Datastream benchmark lists in conjunction with
Thomson Reuters benchmark lists, as it is necessary to determine a datatype which will work with all the requested
data.
You can display swap curves (default datatype IR) alongside Thomson Reuters benchmark curves (default
datatype RY) by specifying no datatype for the Y axis. Each will then use the default and all values will be
displayed correctly.
You can display Thomson Reuters benchmark curves (default datatype RY) alongside Datastream benchmark
curves (default datatype PI) by specifying the RY datatype for Y axis.
You cannot display Datastream benchmark lists and swap lists on the same scatter chart as they have no
relevant datatype in common.
Top
15
Datastream Charting New Feature Guide – Static Charts
ADJUSTING THE SCREEN LAYOUT
The splitter between the chart and the settings can be moved to allow more room to view either the chart or the
settings. You can drag it to the left or to the right or click the arrows to maximise the chart or the settings.
To reset to the default position, click the default icon on the splitter.
Top
______________________________________________________________________________________________
© 2011 Thomson Reuters. All rights reserved.
Republication or redistribution of Thomson Reuters
content, including by framing or similar means, is
prohibited without the prior written consent of Thomson
Reuters. 'Thomson Reuters' and the Thomson Reuters
logo are registered trademarks and trademarks of
Thomson Reuters and its affiliated companies.
16