Exemptions update - July 2013
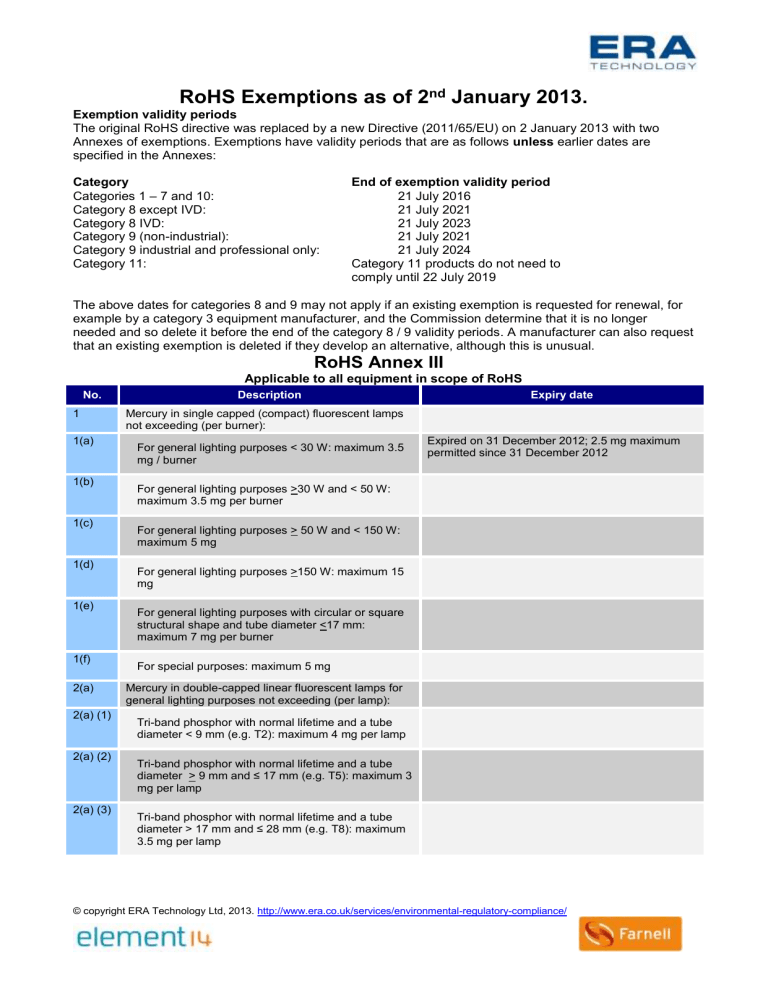
RoHS Exemptions as of 2
nd
January 2013.
Exemption validity periods
The original RoHS directive was replaced by a new Directive (2011/65/EU) on 2 January 2013 with two
Annexes of exemptions. Exemptions have validity periods that are as follows unless earlier dates are specified in the Annexes:
Category
Categories 1 – 7 and 10:
Category 8 except IVD:
Category 8 IVD:
Category 9 (non-industrial):
Category 9 industrial and professional only:
End of exemption validity period
21 July 2016
21 July 2021
21 July 2023
21 July 2021
21 July 2024
Category 11: Category 11 products do not need to comply until 22 July 2019
The above dates for categories 8 and 9 may not apply if an existing exemption is requested for renewal, for example by a category 3 equipment manufacturer, and the Commission determine that it is no longer needed and so delete it before the end of the category 8 / 9 validity periods. A manufacturer can also request that an existing exemption is deleted if they develop an alternative, although this is unusual.
RoHS Annex III
Applicable to all equipment in scope of RoHS
No. Description Expiry date
1 Mercury in single capped (compact) fluorescent lamps not exceeding (per burner):
1(a)
For general lighting purposes < 30 W: maximum 3.5 mg / burner
Expired on 31 December 2012; 2.5 mg maximum permitted since 31 December 2012
1(b)
For general lighting purposes >30 W and < 50 W: maximum 3.5 mg per burner
1(c)
For general lighting purposes > 50 W and < 150 W: maximum 5 mg
1(d)
1(e)
For general lighting purposes with circular or square structural shape and tube diameter <17 mm: maximum 7 mg per burner
1(f)
2(a)
2(a) (1)
For special purposes: maximum 5 mg
Mercury in double-capped linear fluorescent lamps for general lighting purposes not exceeding (per lamp):
Tri-band phosphor with normal lifetime and a tube diameter < 9 mm (e.g. T2): maximum 4 mg per lamp
2(a) (2)
For general lighting purposes >150 W: maximum 15 mg
2(a) (3)
Tri-band phosphor with normal lifetime and a tube diameter >
9 mm and ≤ 17 mm (e.g. T5): maximum 3 mg per lamp
Tri-band phosphor with normal lifetime and a tube diameter > 17 mm and ≤ 28 mm (e.g. T8): maximum
3.5 mg per lamp
© copyright ERA Technology Ltd, 2013. http://www.era.co.uk/services/environmental-regulatory-compliance/
No.
2(a) (4)
Description
Tri-band phosphor with normal lifetime and a tube diameter > 28 mm (e.g. T12): maximum 5 mg per lamp
2(a) (5)
4(b)
4(b)-I
4(b)-II
4(b)-III
4(c)
4(c)-I
2(b)
2(b) (1)
2(b) (2)
2(b) (3)
2(b) (4)
3
3(a)
3(b)
3(c)
Mercury in other fluorescent lamps not exceeding (per lamp):
Expired on 13 April 2012
Linear halophosphate lamps with tube diameter > 28 mm (e.g. T10 and T12): maximum 10 mg per lamp
Non-linear halophosphate lamps (all diameters): maximum 15 mg per lamp
Non-linear tri-band phosphor lamps with tube diameter > 17 mm (e.g. T9): maximum 15mg per lamp
Lamps for other general lighting and special purposes
(e.g. induction lamps): maximum 15 mg per lamp
Will expire on 13 April 2016
Mercury in cold cathode fluorescent lamps and external electrode fluorescent lamps (CCFL and EEFL) for special purposes not exceeding (per lamp):
Short length (< 500 mm): maximum 3.5 mg per lamp
Medium length (> 500 mm and < 1,500 mm): maximum 5 mg per lamp
Long length (> 1,500 mm): maximum 13 mg per lamp
4(a)
Tri-band phosphor with long lifetime(> 25,000 h): maximum 5 mg per lamp
Mercury in other low pressure discharge lamps (per lamp): maximum 15 mg per lamp
Mercury in High Pressure Sodium (vapour) lamps for general lighting purposes not exceeding (per burner) in lamps with improved colour rendering index Ra > 60:
P < 155 W: maximum 30 mg may be used per burner
155 W < P < 405 W: maximum 40 mg may be used per burner
P > 405 W: : maximum 40 mg may be used per burner
Mercury in other High Pressure Sodium (vapour) lamps for general lighting purposes not exceeding (per burner):
P < 155 W: : maximum 25 mg may be used per burner
4(c)-II
155 W < P < 405W: : maximum 30 mg may be used per burner
Expiry date
Expired on 31 December 2012; 3.5 mg maximum permitted since 31 December 2012
© copyright ERA Technology Ltd, 2013. http://www.era.co.uk/services/environmental-regulatory-compliance/
No.
4(c)-III
Description Expiry date
P > 405 W: : maximum 40 mg may be used per burner
4(d) Will expire on 13 April 2015
Mercury in High Pressure Mercury (vapour) lamps
(HPMV)
4(e)
Mercury in metal halide lamps (MH)
4(f)
5(a)
5(b)
6(a)
6(b)
6(c)
7(a)
7(b)
Mercury in other discharge lamps for special purposes not specifically mentioned in this Annex
Lead in glass of cathode ray tubes
Lead in glass of fluorescent tubes not exceeding 0.2% by weight
Lead as an alloying element in steel for machining purposes and in galvanized steel containing up to
0.35% lead by weight
Lead as an alloying element in aluminium containing up to 0.4% lead by weight
Copper alloy containing up to 4% lead by weight
Lead in high melting temperature type solders (i.e. leadbased alloys containing 85% by weight or more lead)
Lead in solders for servers, storage and storage array systems, network infrastructure equipment for switching, signalling, transmission, and network management for telecommunications
7(c)-I
Electrical and electronic components containing lead in a glass or ceramic other than dielectric ceramic in capacitors, e.g. piezoelectronic devices, or in a glass or ceramic matrix compound
7(c)-II
Lead in dielectric ceramic in capacitors for a rated voltage of 125 V AC or 250 V DC or higher
7(c)-III
Lead in dielectric ceramic in capacitors for a rated voltage of less than 125 V AC or 250 V DC
Expired on 1 January 2013 but may be used only in spare parts for EEE placed on the market before 1
January 2013
7 (c)-IV
Lead in PZT based dielectric ceramic materials for capacitors being part of integrated circuits or discrete semiconductors’
8(a)
8(b)
Cadmium and its compounds in one shot pellet type thermal cut-offs
Expired on 1 January 2012 but may be used only in spare parts for EEE placed on the market before 1
January 2012
Cadmium and its compounds in electrical contacts
9
Hexavalent chromium as an anticorrosion agent of the carbon steel cooling system in absorption refrigerators up to 0.75 % by weight in the cooling solution
© copyright ERA Technology Ltd, 2013. http://www.era.co.uk/services/environmental-regulatory-compliance/
No.
9(b)
11(a)
11(b)
12
13(a)
13(b)
14
15
16
17
18(b)
21
23
24
25
29
Description Expiry date
Lead in bearing shells and bushes for refrigerantcontaining compressors for heating, ventilation, air conditioning and refrigeration (HVACR) applications
Lead used in C-press compliant pin connector systems
Lead used in other than C-press compliant pin connector systems
May only be used in spare parts for EEE placed on the market before 24 September 2010
Expired on 1 January 2013 but may be used only in spare parts for EEE placed on the market before 1
January 2013
May only be used in spare parts for EEE placed on the market before 24 September 2010
Lead as a coating material for the thermal conduction module C-ring
Lead in white glasses used for optical applications
Cadmium and lead in filter glasses and glasses used for reflectance standards
Lead in solders consisting of more than two elements for the connection between the pins and the package of microprocessors with a lead content of more than 80% and less than 85% by weight
These may only be used in spare parts for EEE placed on the market before 1 January 2011
Lead in solders to complete a viable electrical connection between semiconductor die and carrier within integrated circuit flip chip packages
Lead in linear incandescent lamps with silicate coated tubes
Lead halide as radiant agent in high intensity discharge
(HID) lamps used for professional reprography applications
Lead as activator in the fluorescent powder (1% lead by weight or less) of discharge lamps when used as sun tanning lamps containing phosphors such as BSP
(BaSi
2
O
5
:Pb)
Will expire on 1 September 2013
Lead and cadmium in printing inks for the application of enamels on glasses, such as borosilicate and soda lime glasses
Lead in finishes of fine pitch components other than connectors with a pitch of 0.65 mm and less
May only be used in spare parts for EEE placed on the market before 24 September 2010
Lead in solders for the soldering to machined through hole discoidal and planar array ceramic multilayer capacitors
Lead oxide in surface conduction electron emitter displays (SED) used in structural elements, notably in the seal frit and frit ring
Lead bound in crystal glass as defined in Annex I
(Categories 1, 2, 3 and 4) of Council Directive
69/493/EEC
© copyright ERA Technology Ltd, 2013. http://www.era.co.uk/services/environmental-regulatory-compliance/
No.
30
31
32
33
34
37
38
39
40
Description
Cadmium alloys as electrical/mechanical solder joints to electrical conductors located directly on the voice coil in transducers used in high-powered loudspeakers with sound pressure levels of 100 dB (A) and more
Lead in soldering materials in mercury free flat fluorescent lamps (which e.g. are used for liquid crystal displays, design or industrial lighting)
Lead oxide in seal frit used for making window assemblies for Argon and Krypton laser tubes
Lead in solders for the soldering of thin copper wires of
100 μm diameter and less in power transformers
Lead in cermet-based trimmer potentiometer elements
Lead in the plating layer of high voltage diodes on the basis of a zinc borate glass body
Cadmium and cadmium oxide in thick film pastes used on aluminium bonded beryllium oxide
Expiry date
Will expire on 1 July 2014
Cadmium in colour converting II-
VI LEDs (< 10 μg Cd per mm 2 of light-emitting area) for use in solid state illumination or display systems
Will expire on 31 December 2013
Cadmium in photo-resistors for analogue opto-couplers applied in professional audio equipment
1
No.
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
RoHS Annex IV
Applicable to equipment in RoHS categories 8 and 9 only
Description Expiry date
Equipment utilising or detecting ionising radiation
Lead, cadmium and mercury in detectors for ionising radiation
Lead bearings in X-ray tubes.
Lead in electromagnetic radiation amplification devices: micro-channel plate and capillary plate.
Lead in glass frit of X-ray tubes and image intensifiers and lead in glass frit binder for assembly of gas lasers and for vacuum tubes that convert electromagnetic radiation into electrons.
Lead in shielding for ionising radiation.
Lead in X-ray test objects.
Lead stearate X-ray diffraction crystals.
Radioactive cadmium isotope source for portable X-ray fluorescence spectrometers.
© copyright ERA Technology Ltd, 2013. http://www.era.co.uk/services/environmental-regulatory-compliance/
1a
1b
1c
1d
9
No.
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
Description
Sensors, detectors and electrodes
Lead and cadmium in ion selective electrodes including glass of pH electrodes.
Lead anodes in electrochemical oxygen sensors.
Lead, cadmium and mercury in infra-red light detectors.
Mercury in reference electrodes: low chloride mercury chloride, mercury sulphate and mercury oxide.
Others
Cadmium in helium-cadmium lasers.
Lead and cadmium in atomic absorption spectroscopy lamps.
Lead in alloys as a superconductor and thermal conductor in MRI.
Lead and cadmium in metallic bonds to superconducting materials in MRI and SQUID detectors.
Lead in counterweights.
Lead in single crystal piezoelectric materials for ultrasonic transducers.
Lead in solders for bonding to ultrasonic transducers.
Mercury in very high accuracy capacitance and loss measurement bridges and in high frequency RF switches and relays in monitoring and control instruments not exceeding 20 mg of mercury per switch or relay.
Lead in solders in portable emergency defibrillators.
Lead in solders of high performance infrared imaging modules to detect in the range 8-
14 μm.
Lead in Liquid crystal on silicon (LCoS) displays.
Expiry date
20
Cadmium in X-ray measurement filters.
RoHS FAQ – Exemptions
Guidance on the RoHS recast has been published and this includes several questions relating to exemptions. These are summarised here.
Q9.1
“What is the difference between RoHS1 and RoHS2?”.
Answer: There are changes to the requirements for manufacturers who apply for exemptions.
Information in exemption requests must be as a minimum that in Annex V.
RoHS1 had 4 – yearly reviews of exemptions whereas exemptions now are valid for periods of up to
5 or 7 years.
© copyright ERA Technology Ltd, 2013. http://www.era.co.uk/services/environmental-regulatory-compliance/
There are deadlines and transitional arrangements for exemption renewal requests
The criteria for justification of exemptions have slightly altered with “reliability” being added as acceptable criteria. Availability and socio-economic impact will be considered when determining expiry dates but are not themselves acceptable criteria for granting exemptions.
The original exemptions of RoHS1 are listed in Annex III whereas additional exemptions that may be utilised by categories 8 and 9 only are listed in Annex IV.
Q9.2
“Are exemptions applicant specific?”
Answer: No, granted exemptions may be used by anyone
Q9.3
“Is it possible to check if an exemption has been applied for?”
Answer: Yes but only after a stakeholder consultation has been published which takes at least 4 weeks after submission of the request to the Commission and can be much longer. Consultations are announced at http://ec.europa.eu/environment/waste/rohs_eee/events_rohs1_en.htm
Q9.4
“How will recent exemptions that were granted under RoHS1 apply to RoHS2?”
Answer: The Commission has amended the RoHS2 Annex III. This applies to exemptions 7 c-IV and 40, both of which are included in the above list
Q9.5
“Does the exclusion granted by Article 4(4)(f) apply to all expired exemptions, irrespective of whether or not the text in Annex III or IV explicitly confirms this point?
”
Answer: Some exemptions in Annex III specifically state that they may be utilised for spare parts used to repair equipment that was placed on the market before the exemption had expired. Article 4.4 (f) states that that all exemptions can be used after they expire, for spare parts that are used to repair equipment that was placed on the market before the exemption had expired, not only where this is specifically stated in Annex III.
© copyright ERA Technology Ltd, 2013. http://www.era.co.uk/services/environmental-regulatory-compliance/



