Notes Chapter 6 Lesson 1 Physical Features Affecting
advertisement
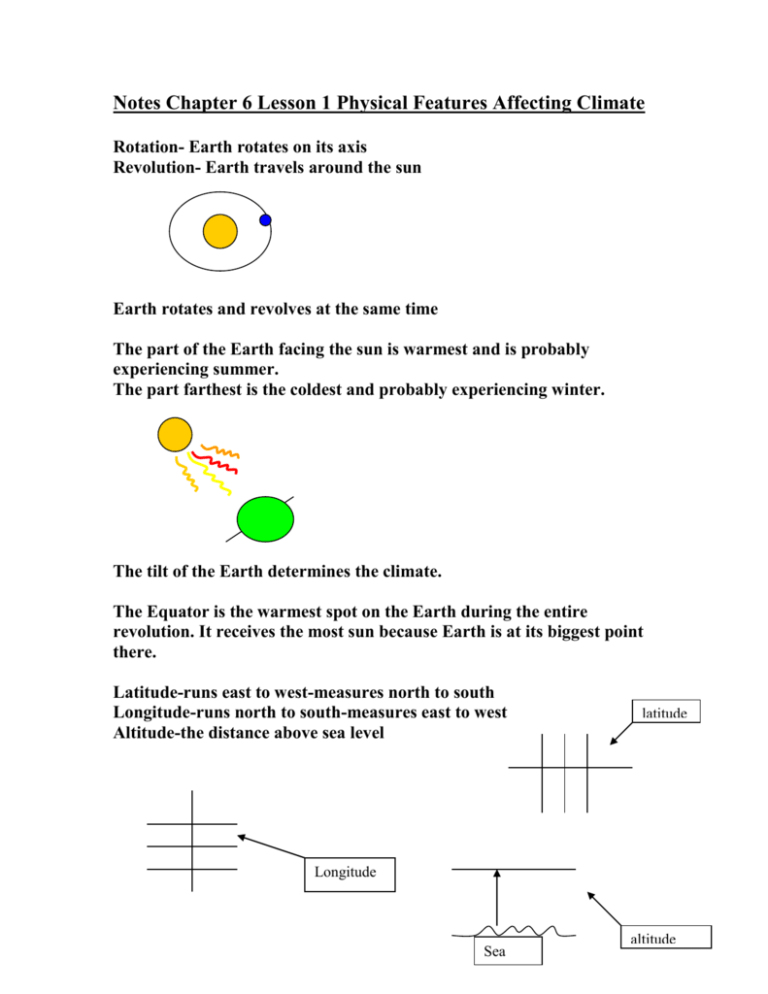
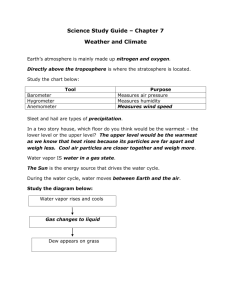
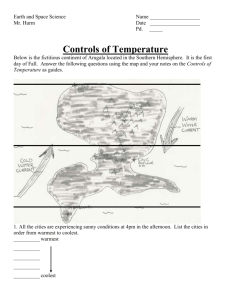
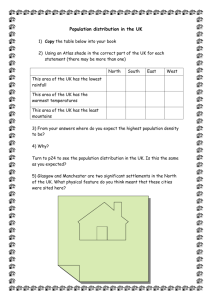
Notes Chapter 6 Lesson 1 Physical Features Affecting Climate Rotation- Earth rotates on its axis Revolution- Earth travels around the sun Earth rotates and revolves at the same time The part of the Earth facing the sun is warmest and is probably experiencing summer. The part farthest is the coldest and probably experiencing winter. The tilt of the Earth determines the climate. The Equator is the warmest spot on the Earth during the entire revolution. It receives the most sun because Earth is at its biggest point there. Latitude-runs east to west-measures north to south Longitude-runs north to south-measures east to west Altitude-the distance above sea level latitude Longitude Sea altitude Heat capacity- the ability to hold heat The ocean holds heat longer because it has high heat capacity meaning that it warms up faster and cools down slower. The land is does not hold heat long because it has low heat capacity meaning that it warms up slower and cools down faster. Water and air from/near the equator is the warmest water and air. Water and air from/near the poles it the coldest air and water. Topography is how the land is shaped. Clouds are warmer Areas with trees are cold Mountain ranges are cold Areas without trees can be cold Clouds are warm because they reflect some of the rays from the sun-day Clouds are also warm because they hold in the Earths heat-night Notes Chapter 6 Lesson 2 Climates of the World 5 climates: Polar Temperate Tropical Boreal Desert Polar- cold- at the poles- ice (no rain or snow)- considered a desert Because there is no water Temperate- life-sun- trees- animals- warm humid summers- cold humid Winters Tropical- heat, humid, high water Boreal- Canada –Siberia –transition of the polar/temperate –small Summers Desert- little water –near the equator and poles and temperate zones