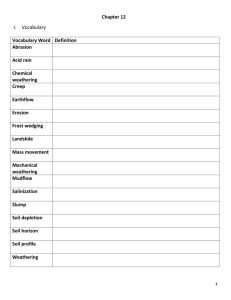
Mrs. Hicks` Chapter 12 Study Guide For each statement or question
advertisement

Mrs. Hicks’ Chapter 12 Study Guide For each statement or question, select the word or expression that best completes the statement or answers the question. ____ 1. Which of the following is an example of erosion? A. Calcite dissolves in carbonic acid. B. Ice wedges forms a pothole in a road. C. A river carries silt to the ocean. D. A car rusts in a junkyard. ____ 2. How do chemical weathering processes differ from mechanical weathering processes? A. Chemical weathering processes break rocks into smaller pieces, but mechanical weathering processes do not. B. Chemical weathering processes affect igneous rocks, but mechanical weathering processes do not. C. Chemical weathering processes involve water, but mechanical weathering processes do not. D. Chemical weathering processes change the composition of rocks, but physical weathering processes do not. ____ 3. Which of the following is an example of mechanical weathering? A. the weathering of feldspar into clay B. the rusting of automobiles C. the cracking of concrete sidewalks D. the decay of dead plants ____ 4. Which property of water makes frost wedging possible? A. Water expands as it freezes. B. Water freezes at 0°C. C. Water is involved in all chemical weathering. D. Water molecules have covalent bonds. ____ 5. Sharp-cornered boulders on bare mountaintops are likely to be the result of A. frost wedging B. exfoliation C. lichen growth D. wetting and drying ____ 6. Which mineral dissolves most rapidly in carbonic acid? A. feldspar B. augite C. quartz D. calcite ____ 7. Which conglomerate would be most resistant to all weathering processes? A. feldspar pebbles with calcite cement B. quartz pebbles with calcite cement C. feldspar pebbles with silica cement D. quartz pebbles with silica cement ____ 8. Which of the following, if released in large amounts into the atmosphere, can cause acid rain to form? A. carbon dioxide B. sulfur dioxide C. nitrogen compounds D. all of the above ____ 9. A residual soil A. shows little weathering B. is found only in the top layer of a soil profile C. has the underlying bedrock as its parent material D. forms only in desert climates ____ 10. Soils erosion can be reduced by A. planting trees along the edges of fields B. rotating the crops planted in a particular field C. building dams in streams D. all of the above ____ 11. Which type of soil would you expect to find in a region that is hot and rainy year-round? A. temperate forest soil B. temperate grassland soil C. tropical forest soil D. tropical grassland soil ____ 12. Which of the following best describes a mudflow? A. Weathered material saturated with water flows downhill. B. Soil moves slowly downhill. C. Blocks of land tilt and move downhill. D. Water carrying clay and silt moves rapidly downhill. ____ 13. Which of the following causes mass movements? A. gravity B. wind C. water D. upward expansion ____ 14. Which of the following is not an agent of erosion? A. ice B. water C. talus D. wind ____ 15. Which of the following is an example of soil depletion? A. Water used to irrigate a field deposits minerals in the soil as it evaporates. B. Planting and harvesting corn year after year removes nutrients from the soil in a field. C. Winds carry topsoil away from a field. D. Fertilizers wash into lakes and streams, stimulating aquatic plant growth. 16. Use the soil profile shown. Label the A-, B-, and C-horizons. Identify the layer with the greatest humus content and the layer where clay and soluble minerals accumulate. ____ 17. In which of the following types of climates is chemical weathering likely to occur most rapidly? A. warm and humid B. warm and dry C. cool and humid D. cool and dry ____ 18. Which of the following is a problem associated with using artificial fertilizers? A. The soil becomes depleted of nutrients. B. The soil erodes more quickly because of the fertilizers. C. The fertilizers enter lakes and streams, upsetting the ecological balance in these environments. D. The fertilizers cause mineral salts to build up in the soil. Answer each question in the space provided. Use complete sentences in your answer. 19. Describe two techniques farmers can use to prevent soil erosion. Explain how these techniques are effective. 20. In what way is the mechanical weathering process of wetting and drying like the chemical weathering process of hydrolysis? How are the two processes different?