BIOLOGY 105: Study Questions for Exam 2 (Sebastian Kadener)
advertisement
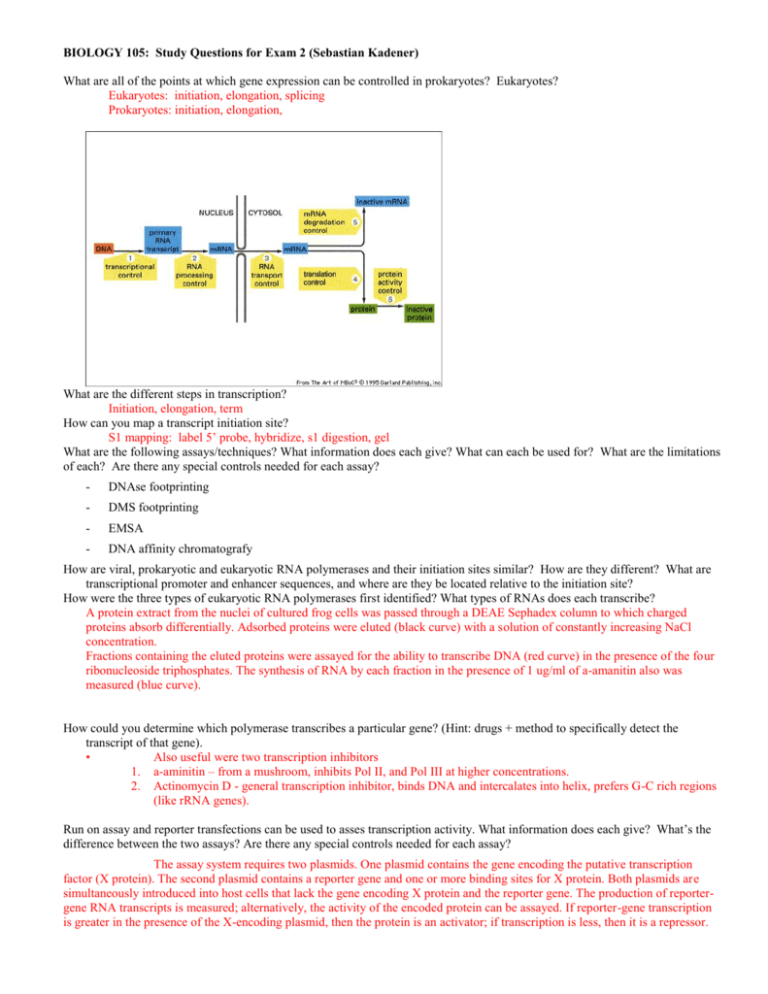
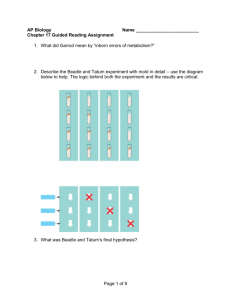
BIOLOGY 105: Study Questions for Exam 2 (Sebastian Kadener) What are all of the points at which gene expression can be controlled in prokaryotes? Eukaryotes? Eukaryotes: initiation, elongation, splicing Prokaryotes: initiation, elongation, What are the different steps in transcription? Initiation, elongation, term How can you map a transcript initiation site? S1 mapping: label 5’ probe, hybridize, s1 digestion, gel What are the following assays/techniques? What information does each give? What can each be used for? What are the limitations of each? Are there any special controls needed for each assay? - DNAse footprinting - DMS footprinting - EMSA - DNA affinity chromatografy How are viral, prokaryotic and eukaryotic RNA polymerases and their initiation sites similar? How are they different? What are transcriptional promoter and enhancer sequences, and where are they be located relative to the initiation site? How were the three types of eukaryotic RNA polymerases first identified? What types of RNAs does each transcribe? A protein extract from the nuclei of cultured frog cells was passed through a DEAE Sephadex column to which charged proteins absorb differentially. Adsorbed proteins were eluted (black curve) with a solution of constantly increasing NaCl concentration. Fractions containing the eluted proteins were assayed for the ability to transcribe DNA (red curve) in the presence of the four ribonucleoside triphosphates. The synthesis of RNA by each fraction in the presence of 1 ug/ml of a-amanitin also was measured (blue curve). How could you determine which polymerase transcribes a particular gene? (Hint: drugs + method to specifically detect the transcript of that gene). • Also useful were two transcription inhibitors 1. a-aminitin – from a mushroom, inhibits Pol II, and Pol III at higher concentrations. 2. Actinomycin D - general transcription inhibitor, binds DNA and intercalates into helix, prefers G-C rich regions (like rRNA genes). Run on assay and reporter transfections can be used to asses transcription activity. What information does each give? What’s the difference between the two assays? Are there any special controls needed for each assay? The assay system requires two plasmids. One plasmid contains the gene encoding the putative transcription factor (X protein). The second plasmid contains a reporter gene and one or more binding sites for X protein. Both plasmids are simultaneously introduced into host cells that lack the gene encoding X protein and the reporter gene. The production of reportergene RNA transcripts is measured; alternatively, the activity of the encoded protein can be assayed. If reporter-gene transcription is greater in the presence of the X-encoding plasmid, then the protein is an activator; if transcription is less, then it is a repressor. By use of plasmids encoding a mutated or rearranged transcription factor, important domains of the protein can be identified. Cisacting DNA sequences can be identified by mutational analysis. Nascent-chain (run-on) assay for transcription rate of a gene. Isolated nuclei are incubated with 32P-labeled ribonucleoside triphosphates for a brief period. During this period RNA polymerase molecules that were transcribing a gene when the nuclei were isolated add 300 – 500 nucleotides to nascent RNA chains. Very little new initiation occurs. By hybridizing the labeled RNA to the cloned DNA for a specific gene (A in this case), the fraction of total RNA produced from that gene (i.e., its relative transcription rate) can be measured. [See J. Weber et al., 1977, Cell 10:611.] What are the GTFs? Proteins other than RNA polymerase involved in transcription How were the Pol II GTFs first identified? Fractionation of nuclear extracts to find GTFs Fractionation scheme, DEAE cellulose What is a TATA-box? TATA box found about 20-25 bp 5’ to the start site for transcription of many (but not all) genes transcribed by RNA polymerase II. How is it recognized? What are TAF's? • TBP bends the DNA about 90 degrees. • TBP alone or with TBP-associated proteins (TAFs) plays an important role in recognizing the core promoter and recruiting RNA polymerase II to the promoter. What are the steps in transcription initiation? What is the PIC? How is it assembled? • Bacterial transcription • Closed complex: holoenzyme+promoter • Open complex (DNA melting, not need ATP) • Abortive transcripton • Productive initiation – Transcribe past +9 – Sigma dissociates • Elongation • • • • • • Eukaryotic transcription Preinitiation complex (PIC) assembly PIC activation (DNA melting, needs ATP) Abortive transcription Productive initiation – CTD phosphorylated – Promoter clearance Elongation A Model for assembly of Mediator-Holo RNA Polymerase II onto the DNA template RNA PolII M F activator TAF B TBP H E M M elongation What is the CTD? What is the SRB/mediator complex? • Srb proteins – Yeast strains with truncations in the CTD of the large subunit of RNA polymerase B are cold-sensitive – SRB genes: when mutated, suppress the phenotype of CTD deletions – Extragenic suppressors: implicated in RNA polymerase function How is the structure of a transcription factor? • Many have modular structure: 1. DNA-binding domain 2. Transcription activating domain • Proteins can have > 1 of each, and they can be in different positions in • Many also have a dimerization domain protein. In what other ways can proteins function to regulate transcription without interacting directly with the PIC? INITIATION VS ELONGATION What’s an insulator? Function? Properties? How does it work? Boundary or insulator elements have two characteristic effects on gene expression: 1. They confer position independent transcription to transgenes stably integrated in a chromosome. 2. They buffer a promoter from activation by enhancers when located between the two. Chromatin model (Barrier): insulators blocks the spreading of active and inactive chromatin structures. B) Decoy model: insulators form non-productive interactions with enhancers, preventing them from interacting with their target promoter What characteristic of TFIIH make the protein important for transcriptional initiation and elongation? Why? • TFIIH 1. Required for promoter clearance 2. Complex protein with 9 subunits 3. Has DNA helicase/ATPase activity (RAD25 gene) for melting DNA at transcription bubble 1. Also has Kinase activity: phosphorylates the carboxyl terminal domain (CTD) of the large subunit of RNAP What are the different types of elongation factors? How they work? TFIIF: Increases the efficiency of transcriptional initiation by significantly reducing the frequency at which RNA Pol II aborts transcription during synthesis of the first few nt. Also stimulates then elongation ELL: Important for elongation. Deletion of this gene provokes big changes in the transcription of long genes, but has no effect on shorter ones. ELONGIN: Involved in transcriptional elongation. Is a component of the proteasome. What are the two types of transcription termination in bacteria and how does they differ? – Rho dependent – Rho independent How RNA pol II transcribe through nucleosomes? What’s the elongator complex? What’s the FACT? Sequential histone acetylation by transcription factor-targeted histone acetyltransferases and by a transcription-coupled histone acetyltransferase. Polymerase II association with the promoter precedes binding of the elongator, which requires phosphorylation of the polymerase II CTD. FACT enables the displacement of the histone H2A/H2B dimer from the nucleosome octamer, leaving a "hexasome" on the DNA. The histone chaperone activity of FACT might help to redeposit the dimer after passage of RNAPII, thus resetting chromatin structure How ChIP can be used to see changes in the chromatin template? How can be used to measure RNA pol II processivity (compare with run on assays)? Chromatin Immunoprecipitation In vivo formaldeyde crosslinking RNA DNA Pol II Cell lysis Pol II Pol II sonication HeLa cells immunoprecipitation Reverse crosslinking and analyses by PCR What’s the difference between RNA pol II pausing and arrest? Pausing: brief stop and then continue Arrest: stop, disassociation, then start over. What types of modifications are done to the RNA pol II transcripts? Capping, poly A What’s capping? Structure? When does it happen? What are the enzymes in charge of it? Capping occurs co-transcriptionally shortly after initiation • guanylyltransferase (nuclear) transfers G residue to 5’ end • methyltransferases (nuclear and cytoplasmic) add methyl groups to 5’ terminal G and at two 2’ ribose positions on the next two nucleotides How does processing of Pol I and Pol III transcripts differ from processing of Pol II transcripts? What are the snoRNA? Synthesis of rRNA occurs within nucleolus. The nucleolus is a nuclear suborganelle produced at sites of rRNA genes through the action of nucleolar organizer associated with the rRNA gene locus (requires only a single rRNA gene for nucleolus formation). Nucleoli are the sites for synthesis, modification, processing, and assembly of rRNA into ribosomes. Nucleoli may form containing rRNA genes derived from multiple different chromosomes in humans. Small nucleolar RNA (snoRNA) has many modifying functions including methylation and pseudouridylation of pre-rRNA. • The exact purpose of these modifications are still unknown except to say that they somehow guide the rRNA subunits to form a functional ribosome. What are the ribozymes? RNA can act as an Enzyme and catalyse Reactions Including Its own replication What are hnRNA and pre-mRNA? How are they related to mRNA? What is an R-loop experiment and how did it lead to the discovery of introns? • Discovered using R-loop Analysis – Cloned genomic DNAs of a few highly expressed nuclear genes (e.g., hemoglobin, ovalbumin), and certain Adenoviral genes were hybridized to RNA fractions and visualized by EM – Loops form from RNA annealing to the template strand and displacing coding strand of DNA How is the exon-intron structure of a typical eukaryotic gene? What are lariats? What are the two steps of pre-mRNA splicing? What are self-splicing introns? How do their chemical mechanisms compare to pre-mRNA splicing? How are tRNA introns related to other intron types? How is splicing studied? What are the spliceosomes? What are the snurps? Composition? Splicing cycle? Urine rich RNA + protein = snurps What do the results of Abelson and coworkers suggest about how spliceosome assembly occurs in vivo? (preassembled Vs. cycle). How are the exon/intron boundaries recognized? By what means were "splicing factors" discovered historically? How are new spliceosome-associated proteins being discovered today? What are DExD/H-box proteins and why are they required at so many steps in the pre-mRNA splicing pathway? Spliceosome Assembly, Rearrangement, and Disassembly Requires ATP, Numerous DExD/H box Proteins What other steps in RNA metabolism require DExD/H-box proteins? What is trans splicing? How was discovered? • Intermolecular splicing of pre-mRNAs • First discovered in African trypanosomes, a disease-causing (African Sleeping Sickness) parasitic protozoan • The mRNAs had 35 nt not encoded in the main gene – called the spliced leader sequence • Spliced leader sequence (SL) is encoded separately, and there about 200 copies in the genome • SL transcript also contains ~100 nt that resembles the 5’ end of a NmRNA intron What is polyadenylation and what are the main steps in the polyadenylation pathway? What does it happen when there are mutations in the splice sites? Less or no splicing What is alternative splicing? When happens? How are usually the flanking sites of an alternative spliced exon? How often happens in metazoans? Describe the different types of alternative splicing? How can be the alternative exon regulated? How does negative and positive regulation of alternative splicing contribute to Drosophila sex determination? What are the individual roles of U2AF, Sxl and Tra in this process? How does transcription termination work in eukaryotes? What are the necessary steps in transcription termination? • What are splicing enhancers? What does mutation of a splicing enhancer often lead to? What are SR proteins? How they work? What two different type of activities they have? In humans: the SR proteins SC35 and SF2 commit splicing on globin pre-mRNA – SR proteins have domains rich in serine and arginine – – In yeast: the branchpoint bridging protein (BBP) binds to the U1 snurp at the 5’ end of the intron and near the 3’ end of the intron Helps define the intron prior to splicing What is the evidence that splicing can occur co-transcriptionally? Melissa’s paper What is the evidence that the Pol II CTD is required for both splicing and polyA addition? How does the Pol II CTD mediate this coordination? What is the RNA factory model? How can a transcriptional promoter affect the alternative splicing pattern of the downstream gene? What is the evidence for this? What is editing? Definition? Types?