Expressive Language Skills: Challenges and Strategies
advertisement

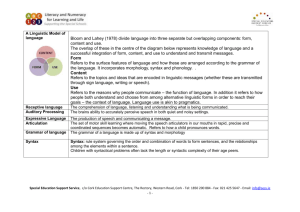
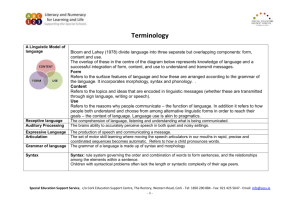
Expressive Language Skills Challenges and Strategies Expressive language skills General Use of vocabulary/word finding Strategies Give the child full attention when they want to speak. Comment on activities while playing alongside the child rather than asking them to talk. Respond to what the child is saying rather than how Be patient, and let the child know you will wait Listen and show interest by maintaining eye contact and using their name Give positive feedback for effort Build on what the child has said, follow their lead Increase opportunities for conversation Take short turns Tell the child if you cannot understand, and ask them to say it in another way Confirm you have understood by paraphrasing, enabling the child to continue Offer help and support Model the correct use of language ( repeat, emphasise, expand) Ask open ended questions Develop self-monitoring skills (ask directly, “did that sound right”; fade to a visual reminder, e.g. a look. Identify key vocabulary for topic Pre teach new vocabulary, find pictures to match key words if possible Use text with picture, it may support some children Teach the vocabulary in context , e.g. prepositions, quantity, adjectives Make semantic connections, describe it, where might you find it, what does it do? What else is like it? heighten knowledge about the structure of the word (phonological awareness) what sound does it start with, is it a long or short word, how many syllables in the word, can you think of another word that starts with the same sound, can you think of a word that rhymes with it. Can you think of other sounds in the word? Support the child in pronouncing new vocabulary correctly Expand on what the child says, Ask the child what they know about the word Have a word wall in the classroom Encourage the child to use the word, e.g. curriculum related vocabulary, time, measure, size shape. Special Education Support Service, c/o Cork Education Support Centre, The Rectory, Western Road, Cork - Tel: 1850 200 884 - Fax: 021 425 5647 - Email: info@sess.ie -1- Word order Sequencing ideas, events Sentence structure Build category trees or word webs/mind maps for curriculum vocabulary Get children to explain the meaning of words that have more than one meaning Revise new vocabulary regularly until established Cue child to find word, phonic cueing, semantic cueing, sign or gesture Cloze procedure, model the sentence and prompt the child to use a similar sentence with different vocabulary Set up a situation which forces the child to make a comment, e.g. asks the child to cut out a picture but do not provide a scissors Forced alternatives, e.g. What colour is the orange? (No response) Is it orange or green? Orange. Barrier games Games to check understanding of meaning, (a) target word with definitions one correct two incorrect. (b) true/false, target word, a number of true/false statements. Teach useful phrases Model the correct structure rather than telling the child they have said it incorrectly. E.g. “bus big school”, “oh you saw a bit bus on the way to school”. Use structured sentences The_____ is________. On a pacing board, using pictures to fill in the gaps, The boy is running. The dog is playing. The girl is dancing. Give explicit structures for supporting narrative skills Prompt with cues, first, then last, use visual cues, or flashcards. Who, what, where, when. Model the use of cues above. Use story sequence cards with two/three pictures, (first then/last) Have the child give instructions with the support of pictures/photographs Take pictures of sequences that are relevant for the child and have them tell the story Use red dots or counters between the pictures to signify connectives, and then, later, expand on connectives, because, so, but. Send the child on messages that involve a sequence Have the child retell familiar stories, use visuals to support Provide sentence frames with examples of how to use more complex language. Pacing boards/gap sheets focused on specific grammatical structures. Model the correct use rather than correct Encourage use of longer sentences, use connectives Special Education Support Service, c/o Cork Education Support Centre, The Rectory, Western Road, Cork - Tel: 1850 200 884 - Fax: 021 425 5647 - Email: info@sess.ie -2- Use of verb tenses Social communication Asking questions Encourage older children to comment on their own sentences, do they have connectives, do they have descriptive words. Barrier games (can provide a script for the child to use to support sentence structure) Colour coding. Subject verb object, use pictures, or words if the child can read e.g. Subject yellow, verb blue, object green, adjectives red. For children with more complex needs Susan Ebbels (2007) suggests shape coding. Model the correct use rather than correct Focus on the target e.g. if the child is working on regular past tense “him walk to the shop” put the emphasis on the target “he walked to the shop” Ask the child to perform certain actions, what did you do, I jumped. This could be modelled by teacher and SNA or during team teaching Have the child instruct peers/doll teacher to jump, write, run Today/Yesterday, irregular verbs, using pictures, Today I am __________, yesterday I. (Pacing cards with the structure written could also be used as a support for this. Listen and repeat, pictures of verbs, take turns picking up a card “Today I am running” Other person repeats/echoes. Alternative, other person says in the past tense. Praise good listening skills Some skills may need to be taught explicitly encourage them to wait for a gap, or a clear indication from the speaker before joining in. Encourage the child to look at the non-verbal cues that when a person pauses it means you can have a turn Identify what you feel is rude and explain why Discuss the effects of saying the wrong thing to a person Explain about different ways of speaking in different contexts Discuss how tone of voice and posture give clues to emotions barrier games to help a child repair and clarify what was said Develop an ethos of asking for clarification Teach question forms in sequence, 1. Using single words with rising intonation. 2. "Wh" words at the beginning of a sentence What (What with nouns, what with verbs) who, what for, where, when, how, how much, why, whose, which. Play games using the question word through modelling. Special Education Support Service, c/o Cork Education Support Centre, The Rectory, Western Road, Cork - Tel: 1850 200 884 - Fax: 021 425 5647 - Email: info@sess.ie -3- Responding to questions Making requests Who/what? Who is in…? The bag, model, child models, using toys relevant and appropriate to the child, dolls house, garage. Using pictures, who is this?? Turn take, teacher models, or more able child can model. Place pictures face down/ up depending on the level of the child. Use pictures that are relevant/personal to the child first. Where? Dolls house, farm, garage. Hide the object, teacher model, child takes turn, where is the horse, cow, duck? More able children can play games using more difficult question words. What’s in the bag? One child/teacher knows what the item is; the other children have to ask questions to work out what it is. Where is it from, what is it made out of? Who uses it? What is it for? barrier games Give time for children to think and respond to questions Play games using the question word through modelling. Who/what? Who is in…? The bag, model, child models, using toys relevant and appropriate to the child, dolls house, garage. Using pictures, who is this?? Turn take, teacher models, or more able child can model, taking turns to ask and respond. Place pictures face down/ up depending on the level of the child. Use pictures that are relevant/personal to the child first. Where? Dolls house, farm, garage. Hide the object, teacher model, child takes turn, where is the horse, cow, duck? More able children can play games using more difficult question words. What’s in the bag? One child knows what the item is; the other children have to ask questions to work out what it is. Where is it from, what is it made out of? Who uses it? What is it for? Child responds to questions in order to support other children identify the object. Setup a situation which forces the child to make a comment, e.g. asks the child to cut out a picture but does not provide a scissors Model the language Role play Special Education Support Service, c/o Cork Education Support Centre, The Rectory, Western Road, Cork - Tel: 1850 200 884 - Fax: 021 425 5647 - Email: info@sess.ie -4- Receptive Language Skills Challenges and Strategies Receptive language skills Attention Strategies Schedule important and demanding activities early in the day or after an extended break. Keep activities brief or structure them into short blocks, provide a clear beginning and end. Allow for regular breaks, and give the child errands that allow them to move around. Alternate activities between mentally demanding, and less challenging or physical ones. Limit information presented and present one activity or idea at a time. Keep instructions brief or break them down or provide a written copy. When giving instructions get the child's attention by calling their name and making eye contact. Reinforce instructions with written cues or instructions on the whiteboard. Minimize potential distractions - seat child at the front of class and keep their desk free of unnecessary material. Seat the child near the teacher or with children who will be good role models. Provide direct prompts to return to task and positively reinforce on-task behaviour. Simplify and reduce material on worksheets, and the blackboard. Develop and stick to a daily classroom routine. Emphasize the skill or concept over the quantity of work. Gradually increase goals. Ensure that tasks are meaningful to the student and are within the student’s readiness range. Set an alarm for short time segments. From app store (for ipad): “Giant timer” (Benzac) Free. This timer app has clear digits, great sounds and counts down or up. Special Education Support Service, c/o Cork Education Support Centre, The Rectory, Western Road, Cork - Tel: 1850 200 884 - Fax: 021 425 5647 - Email: info@sess.ie -5- Listening Strategies to Control Attention and Concentration Mobilising Attention To control attention, the student must learn to recognise those times when they are about to disconnect so that they can reconnect right away. Certain situation characteristics are effective in mobilising attention, such as discussions and problemsolving groups. Some tactics that can help students stay focused on the subject include taking notes, organising ideas using outlines or note/mind mapping, following along in the text, noting ideas, noting distracting thoughts, purposefully disconnecting (look out the window, become aware of my position and breathing, relax) so that I can better reconnect a few moments later. Focusing Attention Encourage students to focus on one aspect of the task at a time. To limit the risk of confusion. Divide the task into smaller units. Between the task sections, use natural break times and opportunities for the student to briefly relax and physically move. Although these breaks are very short (a few minutes), they allow the student to recover their capacity to concentrate. They also help to assimilate and store essential information in my memory long-term, so that I can rapidly recall the main points of the previous work unit. Using Internal Dialogue Negative internal dialogue distracts my attention from the task and weakens resistance to distractions and encourages disconnection. Self-talk about the task; the best way to organize its completion, articulation of my questions and reasoning, either out loud or silently to myself, helps to maintain focus. Self-talk, whether internally or out loud, will often increase understanding. Using Mental Imagery Similarly to internal dialogue, all cerebral activity spontaneously generates a constant flow of images and scenarios. The use of drawings, diagrams, graphs, schemas or models keeps mental imagery focused on the learning task, while facilitating my understanding. Special Education Support Service, c/o Cork Education Support Centre, The Rectory, Western Road, Cork - Tel: 1850 200 884 - Fax: 021 425 5647 - Email: info@sess.ie -6- Listening Strategies Top-down strategies are listener based; the listener taps into background knowledge of the topic, the situation or context, the type of text, and the language. This background knowledge activates a set of expectations that help the listener to interpret what is heard and anticipate what will come next. Top-down strategies include: listening for the main idea predicting drawing inferences summarising Bottom-up strategies are text based; The listener relies on the language in the message, that is, the combination of sounds, words, and grammar that creates meaning. Bottom-up strategies include: listening for specific details recognising/remembering vocabulary words recognising word-order patterns Strategic listeners also use metacognitive strategies to plan, monitor, and evaluate their listening. They plan by deciding which listening strategies will serve best in a particular situation. They monitor their comprehension and the effectiveness of the selected strategies. They evaluate by determining whether they have achieved their listening comprehension goals and whether the combination of listening strategies selected was an effective one. Listening for Meaning To extract meaning from a listening text, students need to follow four basic steps: Figure out the purpose for listening. Activate background knowledge of the topic in order to predict or anticipate content and identify appropriate listening strategies. Attend to the parts of the listening input that are relevant to the identified purpose and ignore the rest. This selectivity enables students to focus on specific items in the input and reduces the amount of information they have to hold in short-term memory in order to recognise it. Select top-down and bottom-up strategies that are appropriate to the listening task and use them flexibly and interactively. Students' comprehension improves and their confidence increases when they use top-down and bottom-up strategies simultaneously to construct meaning. Special Education Support Service, c/o Cork Education Support Centre, The Rectory, Western Road, Cork - Tel: 1850 200 884 - Fax: 021 425 5647 - Email: info@sess.ie -7- Check comprehension while listening and when the listening task is over. Monitoring comprehension helps students detect inconsistencies and comprehension failures, directing them to use alternate strategies. Apps: Auditory workout (Virtual Speech Center Inc.) €17.99. This is suitable for students from four to ten years. It is a research based app that focuses on improving auditory attention/memory/processing of verbal directions. Auditory Processing Direct Intervention-this involves remediation efforts to improve auditory discrimination, integration skills, associative skills and teaching specific language or academic skills. Examples include teaching the person to hear differences in sounds or words, teaching the person to pick out words in the presence of background noise, and teaching the child to use rhythm and tempo cues in speech. Give your student multi-level instructions (with increasing difficulty). E.g. “go to room 2, and ask Ms Harte for some blue paper”. The student will need to listen carefully to your complete instruction, and practice rehearsing the instruction. They may find it helpful to practice visual imagery alongside internal rehearsal. Play a guessing game by giving him clues to an item that you have thought of and see how many clues he needs to guess the item correctly. You could do this while playing “I Spy” or simply by hiding items around the classroom/yard and having him hunt for them. Try playing the “Silly or Not Silly” game by saying a sentence and asking your student to label it “silly” or “not silly.” For example, you could say, “The mop cooked spaghetti and meatballs for the canary.” (Silly - of course!) This can be done in a quick fire round. The student with auditory processing difficulties must be taught and encouraged to use strategies to cope with and compensate for deficit areas. For example, homework instructions could be taped, the person could be taught how to ask for repetition of things not heard or understood, and the use of visual cues to complement what is heard can be taught. Special Education Support Service, c/o Cork Education Support Centre, The Rectory, Western Road, Cork - Tel: 1850 200 884 - Fax: 021 425 5647 - Email: info@sess.ie -8- Apps: Auditory Processing Studio (Virtual Speech Center Inc) €26.99. This app was created by a speech and language pathologist for children aged seven and upwards who experience auditory processing difficulties. It incorporates a bottom up approach which focuses on the improvement of auditory processing through auditory discrimination and phonological awareness activities. It allows for the introduction of background noise to help children practice skills in a noisy environment. Sequencing Skills Prior to listening to a story being read aloud, remind students that they will be working on their sequencing skills. Depending on your lesson, you might say, "As we read, let's think about what happens during the beginning, middle, and end of the story," or "After we finish reading, we're going to try to retell the story." As you read, pause frequently to ask students to identify the events in the story and to encourage them to think about when the beginning gives way to the middle and the middle transitions to the end. Once you have read the story, make lists with students about the events that occurred, trying to arrange them sequentially. Sentence strips or pictures work well for this type of activity, since events can be represented by either pictures or words and then put in the correct order. Let students use these lists or pictures as reminders as they retell the story by acting it out with puppets, for instance. Independent sequencing Begin by reminding students that they will be working on their sequencing skills (encourage their metacognition by having them think about the skill they are going to work on). One strategy that may be helpful is to give students pieces of paper and pencils to use as they read. Students can write page numbers and a few words (for older students) to remind them of important events in the story. For instance, a student who is reading Goldilocks and the Three Bears in order to retell it may jot down: Goldilocks comes in--She eats the porridge--She breaks the chair--She falls asleep--The bears come home This list doesn't tell the whole story, but it does provide the key elements, in order, and would serve as a good outline for someone wanting to retell it themselves. If this procedure is new to students, model it before asking them to do it on their own, using a read aloud story and recording your own ideas in a think aloud style to show students how to do this on their own. Once students have completed reading, give them opportunities to write about their stories' sequences in a reading journal, to discuss their stories with partners, or to retell them to family members for homework. Special Education Support Service, c/o Cork Education Support Centre, The Rectory, Western Road, Cork - Tel: 1850 200 884 - Fax: 021 425 5647 - Email: info@sess.ie -9- Understanding Vocabulary Apps: 1. ’Speech with Milo’ sequencing (Doonan Speech Therapy) €2.69. This app is suitable for students from four to seven years. It introduces the skills of sequencing on a ‘first-next-last’ basis of increasing difficulty. Skills of retell, increasing utterance length and the development of more complex sentences. 2. Also ‘Sequencing Lickity Split’ (Lickity Split Learning) €30.99. This app is focuses on the improvement of visual and auditory sequencing. It aims to do this by building the student’s memory capacity for auditory sequences of at least seven numbers. This allows for data for up to five users to be stored and updated. Use recording device (dictaphone/phone etc.), make a recording of words. Say the word, define it, and then use it in a sentence. (Select words that the student will find interesting.) Encourage regular use of this mode. (If they are studying for a spelling test, spellings can be revised this way.) “Word of the Week/Day” Each student selects a word taking turns each time. As the words are selected and used, they are posted somewhere visible to stimulate continued usage. “Ten Questions” One group member thinks of something, which the other players must guess with no more than ten questions. The first question always is “Is it animal, vegetable, or mineral? Then, question by question, the field is narrowed to likely possibilities. After the first questions, the following questions must be asked so that they can be answered by “yes” or “no.” For some students, “Ten Questions” might be too demanding, so make it “Twenty Questions” One of the values of the extension is that additional reasoning and logic can be expressed. Stretch the game as much as possible. You can show, for example, the process of moving from broad-based questions to more discrete ones. In this way, students will team to ask questions such as, “Is it located in the Northern Hemisphere?” “Is it in the Western Hemisphere?” “Is it in the United States?” “Is it land based?” and so on. This becomes an exercise not only in vocabulary development but also in geography. Encourage the use of a diary. Play games with homonyms – words that sound alike but are spelled differently and mean something different, as in “sun” and “son.” For example, on a display board, post train rain- or “reign-rain” or” prayprey” or “flower -flour.” Ask students to add to the list. Special Education Support Service, c/o Cork Education Support Centre, The Rectory, Western Road, Cork - Tel: 1850 200 884 - Fax: 021 425 5647 - Email: info@sess.ie - 10 - Play ‘Top Score’ game which can be played even if your child is having difficulty with reading. You might use a comic book, the comic strips or sports pages in your local newspaper, or a magazine article- To play the game, the child must know that some words start with a consonant followed by a vowel-for example, “say, look, go, pay,” etc. that other words begin with two consonants (called a blend) such as “grow, plate, tray, brush,” etc. Tell the student they will earn a point for every word he underlines that starts with a blend. A guessing word-finding game can be fun. “I’m thinking of a word that starts with “br” that is something you use to paint a house.” (Brush) “I’m thinking of a word that starts with “tr” that is something we do to the bushes when they get too large.” (Trim) “My father owns ” Example: “My father owns a shop, and in it he sells something that begins with the letter B. ” This is a simple word finding activity. If the child does not know the alphabet, letter sounds can be used. Revolving blend- is another game in which someone gives a common blend-for example, “tr”–and, in sequence around the table or room, everyone must think of a word that begins with that blend-”train, truck, truffle, try, tray, trumpet, truce.” et cetera. When the list is exhausted, the last person begins another blend, such as “st”–”stay, start, stick, stuck, star,” etc. Word origins or facts about words can also be explored as a research project. For example, the word “salary” had its origin in “salarium,” which is Latin for salt. Roman soldiers received their pay in salt. Students could have similar activities for homework. Apps: 1. Grammar and vocabulary language development, educational games for kids in preschool and kindergarten (Tribal Nova). Free. This is an app for children up to six years where students practice language and grammatical concepts primarily through sentence building. 2. Improve English with Synonyms (Dev IT Solutions PVT Ltd.) Free. This app helps students with the matching and analysis of synonyms with a focus on speed and accuracy. 3. Improve English with Antonyms (Dev IT Solutions PVT Ltd.) Free. This app helps students with the matching and analysis of antonyms with a focus on speed and accuracy. 4. Vocabulary Builder Grades 5-6 (Greg Levy) €1.79. A vocabulary ‘flashcard’ system that targets: multiple meaning words, synonyms, antonyms, adjectives, nouns and verbs. Special Education Support Service, c/o Cork Education Support Centre, The Rectory, Western Road, Cork - Tel: 1850 200 884 - Fax: 021 425 5647 - Email: info@sess.ie - 11 - Conceptual Language Grammatical Concepts Receptive language therapy often focuses on expanding a child’s vocabulary base and assisting them in being able to compare and contrast attributes of an item for the purpose of accurate categorisation. Encourage students to continually compare and contrast how words and concepts are related. Each new concept or word they learn should be compared to a child’s prior knowledge about the world. For example, if a child learns about kites, they compare their prior knowledge related to toys, wind, and the sky. The child thinks about the attributes of a kite and classifies the item into various categories such as, “things that fly,” or “outside toys.” Think of different ways to explain new concepts e.g. looking at the concept of "wet": use water to wet things and talk about things that are wet and dry; look at pictures of things that are "wet"; if it rains talk about the concept of being "wet"; make up sentences and stories about being wet/dry etc. Apps: 1. Let’s Do Basic Concepts (Kids Can Talk, LLC €5.49). This app concentrates on spatial concepts and associated language. It builds skill through listening and receptive identification of twenty two concepts by following commands. 2. Autism iHelp – Language Concepts (John Talavera) €1.79. While this app has a function for vocabulary development it also has a function to categorize items shown by denoting “what does not belong”. 3. Comparative Adjectives (GrasshopperApps.com) Free. This app enables students to compare and describe the difference between two objects, e.g. bigger/youngest/heavier. Grammar is in its most simple terms the system and rules of language. These aspects need to be explicitly taught (verbs/nouns/pronouns/adjective/adverb/preposition etc.) Explicit teaching would involve giving a definition of that particular term, and allow students become familiar with the structure. A progression of this would be to engage students in activities with identifying these concepts, and/or generating sentences with these concepts contained therein. Give students parts of a sentence on individual large sheets of paper. Have them discuss and formulate the sentence while holding up the pieces of paper. Model incorrect sentences, have students proofread, discuss in pairs, and correct. Use checklists to enable students to edit/proofread their own work with a grammatical focus. Apps: 1. Grammar and vocabulary language development, educational games for kids in preschool and kindergarten (Tribal Nova). Free. This is an app for children up to six years where students practice language and grammatical concepts primarily through sentence building. Special Education Support Service, c/o Cork Education Support Centre, The Rectory, Western Road, Cork - Tel: 1850 200 884 - Fax: 021 425 5647 - Email: info@sess.ie - 12 - Inferential Language 2. Advanced Grammar in Use Tests (Cambridge University Press) €4.99. A ‘challenge’ based app to practice grammar skills across fourteen grammatical areas. 3. Grammaropolis (Grammaropolis LLC) Free. This app uses parts of speech as animated characters with personalities based on the roles they play in a sentence. Some downloads are free, others are at a cost to download. The student must simply read between the lines and make inferences about things not directly stated. Inferential language also involves interpreting figurative language, drawing conclusions, predicting outcomes, determining the mood, and judging the author’s point of view. When making inferences, explicitly model the process (through ‘thinking talk’) of using prior knowledge and logical guessing to guide students to make connections between what is in the text and what they can assume based on what they already know. Pause from time to time to ask questions about the text. Identify difficult words and ask students to use context clues to figure out their meaning. In this way, students must infer the meaning of the difficult word from the context. Ask students to make inferences about the setting of the text. Have students identify the setting (time and place), and ask them what they already know about that place and time period. Have students add details about the setting that are not written in the text. In this way, students apply their prior knowledge to infer details about the setting. Ask students to make inferences about the characters or people in the text. Ask students to explain why they think the character did something. Allow different students to offer multiple interpretations of the character's actions. Write an inferential question about the text on the board and have students copy it at the top of a journal page. Have students fold the journal page in half vertically, using the folded line as a divider. Have them write on the left side, "What the Text Says," and have them write on the right side, "What I Know." Have students look for sentences in the text that they think answer the question. Have them copy these sentences under the heading, "What the Text Says." Ask students to think about details or facts from their prior knowledge that they think answer the question. Have students record these under the heading, "What I Know." Have students create a new heading at the bottom of the page that says, "My Answer: What I Infer." Have students think about the sentences they copied from the text and the facts they already knew. Have them write an answer to the question that combines both under the new heading. Their answer should be in complete sentences. Special Education Support Service, c/o Cork Education Support Centre, The Rectory, Western Road, Cork - Tel: 1850 200 884 - Fax: 021 425 5647 - Email: info@sess.ie - 13 - Explicitly teach figurative language and idioms/metaphors etc. Display these around the classroom and have students add their own. Apps: 1. Kidioms (Ventura Educational Systems) €1.79. This app uses an interactive notebook to present an idiom, its meaning and an example showing the idiom in context. Each page has an accompanying graphic. There is also a ‘match up’ game. There are also Kidioms 2 & 3. 2. Painless Reading Comprehension Challenge (Barron’s Educational Series Inc Mobile) Free. This app tests knowledge and skill, with multi choice for meanings and phrases. Reasoning Skills In developing these skills, place an emphasis on higher order skills; these being those skills that encourage the ability to reason. This group or hierarchy of skills involves recalling information, basic concept formation, critical thinking, and creative idea formation. (Formerly viewed as the tools of mathematics, these skills are now recognised as crucial to competence across the curriculum) Teach these skills explicitly in a bottom up way from recalling information, to the more difficult area of creative thinking. Activities may be modified, simplified, lengthened, or deleted to meet the needs of the intellectual diversity found in most classrooms. Let students witness what high quality reasoning is like through modelling, and the use of a thought bubble symbol to denote you are ‘thinking out loud’. Use visuals to support the kind of thinking strategy/skill you are currently using: e.g. making connections/putting in context/making inferences/relating to my experience/problem solving. Use interactive discussion to facilitate concept development. Use current media stories (where appropriate) to encourage students to make connections with events/problems that occur in real life. Apps: 1. If…Then...Fun Deck (Super Duper Publications) €2.69. Suitable for younger students where they complete statements to enhance critical thinking. 2. Blooms Taxonomy (Maggie Fossum) €0.89. This app breaks down cognitive levels into separate sections to encourage and develop students’ higher level thinking skills. Special Education Support Service, c/o Cork Education Support Centre, The Rectory, Western Road, Cork - Tel: 1850 200 884 - Fax: 021 425 5647 - Email: info@sess.ie - 14 -