Girraween High School
advertisement

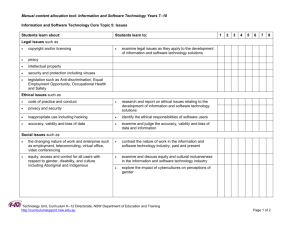
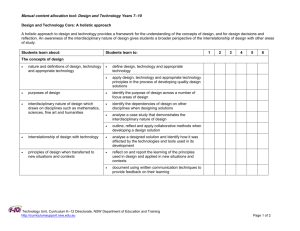
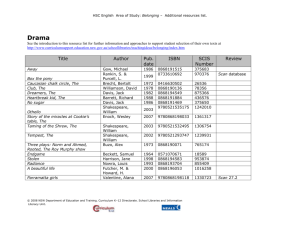
Girraween High School Stage Five English Presentations of Truth unit Focus Stage 5 Outcomes A student: 1 responds to and composes increasingly sophisticated and sustained texts for understanding, interpretation, critical analysis and pleasure 3 selects, uses, describes and explains how different technologies affect and shape meaning 4 selects and uses and describes language forms and features, and structures of texts appropriate to different purposes, audiences and contexts, and explains their effects on meaning 5 transfers understanding of language concepts into new and different contexts 6 experiments with different ways of imaginatively and interpretively transforming experiences, information and ideas into texts 7 thinks critically and interpretively using information, ideas and increasingly complex arguments to respond to and compose texts in a range of contexts 9 demonstrates understanding of the ways texts reflect personal and public worlds 10 Questions, challenges and evaluates cultural assumptions in texts and their effects on meaning Out comes 3 9 Teaching and learning focus Resources 1. Introduction General discussion about: What is the role of a journalist? entertainment sensitivities censorship. Questions and issues raised in ‘Sacked for…’: What impact does this image have on the reader? (initially, only the image is displayed to the class) Could this image have any wide spread impact? Power of an image: discussion about SMH article, ‘When a picture…’ Why was the journalist sacked? Was it warranted? SMH: ‘Sacked for photo Americans were not meant to see’, 23 April 2004 http://www.smh.co m.au/articles/2004 /04/22/108261626 8111.html English Stage 5 October 2005 Page 1 of 11 NSW Department of Education and Training Curriculum K-12 Directorate http://www.curriculumsupport.nsw.edu.au/english Out Teaching and learning focus Resources comes What is the role/duties of a journalist? What are the sensitivities towards families and friends of deceased soldiers? Censorship: who has the right to decide what the public views? Can and should situations alter censorship rules? If cartoon can be accessed: Changing role of the journalist as situations and global climate change Reactive journalism Censorship? Rational or emotive? Does it matter? 4 9 SMH: ‘When a picture packs a punch’, 10 June 2004 http://www.smh.co m.au/articles/2004 /06/09/108674977 4796.html Cartoon by Jenny Coopes ‘The first casualty of war is truth’ 2. Ethics in Journalism Students read the AJA Code of Ethics and discuss the following issues: What are the ethics in this code? How do ethics in journalism apply? Why is there an official guideline? How important is it? What is the language of the code? Are there loopholes? What are the censorship issues? Australian Journalist Association (AJA) Code of Ethics http://www.australi annews.com.au/cod ethics.htm ‘The PG-Rated War’: What is the role of audience in determining the presentation of information? List the external pressures on journalists beyond the code of ethics. When/if ever is it acceptable to ‘bend’ the code of ethics? Time Magazine: ‘The PG-Rated War’ by J Klein, 7 April 2003 ‘The Trouble with Sitting on the Story’ and extract from The Insider What do these texts say about the difficulties faced in reporting ‘the truth’? What price should you pay for the truth? Is part of the truth better than nothing at all? Cultural sensitivities involved in gathering ‘the Time Magazine ‘The Trouble with Sitting on the Story’ by J Poniewozik, 28/4/2003 English Stage 5 October 2005 Page 2 of 11 NSW Department of Education and Training Curriculum K-12 Directorate http://www.curriculumsupport.nsw.edu.au/english Out Teaching and learning focus Resources comes 3 9 10 The Insider, dir Michael Mann, 1999, rated M 3. Presentation of the news 9 truth’ Do you ignore social and cultural beliefs in the pursuit of truth? Is the journalist’s own cultural bias unavoidable? What does the AJA Code of Ethics say about cultural bias? Cutting Edge: How is television news presented? Operation How does presentation form, style and Saddam, meaning affect meaning? America’s List the differences and similarities of Propaganda commercial versus government owned Battle (Part I), channels in their news production. SBS, 29 July 2003 What are the impact or results of budgets in the production of news? Refer back to Time Magazine How is local, national and global news presented? ‘The Trouble with List the targeted audience of various television Sitting on the news bulletins. Story’ by J Comment on reliability and bias in news. Poniewozik, Is the news a reflection of a nation’s position? 28/4/2003 What different cultural perspectives are obvious The Insider, dir in the presentation of television news? How is material selected (footage, length, etc)? Michael Mann, List the general editing techniques. 1999, rated M, extract 4. Personalities behind the news How can the personality of a journalist have an impact on the presentation of information? Should it? How does the AJA Code of Ethics address this? What are the pressures on a journalist? What outside factors are involved in the presentation of information to the public? What is the role of the host in television news? What is the importance of status in reporting the news? Refer back to Time Magazine ‘The Trouble with Sitting on the Story’ by J Poniewozik, 28/4/2003 Shattered Glass, dir Billy Ray, 2003, rated M, extract English Stage 5 October 2005 Page 3 of 11 NSW Department of Education and Training Curriculum K-12 Directorate http://www.curriculumsupport.nsw.edu.au/english Out Teaching and learning focus Resources comes Comment on how different channels appeal to their targeted audience? Role play task: Choose different styles of presentation of the same news item and have class members identify purpose, targeted audience and context, etc 3 5 9 5. Truth in television news General questions for the following texts: What are the major differences between print and television news? Comment on the impact of language choice and usage in presentation of the ‘truth’ in the news Is there an entertainment factor evident? What are the differences between ‘entertainment’ and ‘info-tainment’ (purposes, language choices, audience, style? What are the different sources of media (local, national, global), and their effects on the presentation of information and the truth? Whose version of the ‘truth’ is it? Targeting Media: What is the role of television news in informing society? What is its purpose? List the structure and language features of news items. Media Watch and Cutting Edge: Comment on the audience appeal. List examples of emotive language. What editing techniques have been used and what effect do they have on the meaning? Frontline, (ABC TV), R Sitch: ‘Playing the Ego Card’ episode, 1994 http://www.workin gdog.com/frontline Note: The Frontline episodes in this unit are prescribed HSC 2004-2007 Advanced English text. Targeting Media: Television and Film, A Lopez, 2000 Worksheets: o Structure of the news o Conflict on the news o Facts versus opinion Media Watch, ABC TV, http://www.abc.net .au/mediawatch/ (Littlemore, Video Education Australia) Cutting Edge: Operation Saddam, America’s Propaganda Battle (Part 1), SBS, 29 July 2003 English Stage 5 October 2005 Page 4 of 11 NSW Department of Education and Training Curriculum K-12 Directorate http://www.curriculumsupport.nsw.edu.au/english Out Teaching and learning focus Resources 6. Selection of news items and footage comes 3 5 6 7 General discussion on: targeted audience of news on different channels impact of ratings differing styles of presentation personalities in the news elements of television news (setting, structure etc.) priorities and agendas sort of footage: type of shots, length, etc used and effects in the positioning of the viewer. Targeting Media and pre-taped news: elements of television news styles of presentation role of the audience role of the ratings agendas. Targeting Media worksheet o Selection on the news Pre-taped news programs from same night: (Channels 7, 10 and ABC) Bowling for Columbine, dir Michael Moore, 2002, rated M (extracts) Frontline: ‘Add Sex and Stir’ episode Bowling for Columbine editing footage entertainment factor. Frontline: role of a perceived public interest news as a reflection of the general public ratings editing the ‘creation’ of news stories. Presenting ‘the facts’ in news presentations – role play task: In groups of no more than 3 you will be allocated a news program from either SBS or Channel 10. Your group is to reproduce the ‘style’ of your given news bulletin and present it as a reenactment. You may select your own news items, including sport and weather if you believe these are appropriate for your re-enactment. English Stage 5 October 2005 Page 5 of 11 NSW Department of Education and Training Curriculum K-12 Directorate http://www.curriculumsupport.nsw.edu.au/english Out Teaching and learning focus Resources comes Your presentation should clearly identify elements apparent in your allocated news bulletin. Your presentation must be 5-6 minutes in length and will be filmed in class. Props and other special effects should be included, as appropriate. Alternate/additional task: Groups choose the same 2-3 news items and using different styles of presentation suitable for commercial news bulletins ABC news bulletins SBS news bulletins different sets and news desks. These may be filmed if camera is available. Class and groups comment on how the presentation affects the information conveyed. 3 4 9 7. Interviews Students watch different types and make notes on: the elements of an interview role of the interviewer role of the interviewee strategies of interviewing agendas styles purpose getting the ‘expert’ in for an interview editing power of the news station choice of interviewee personal background of interviewer. Additional activities: Compare and contrast the interview styles of news items with current affairs programs other interview programs: Enough Rope, Parkinson, etc A Fine Line, E Fanning, SBS TV, 2004: episodes 13 Questions from A Fine Line study guide on MetroMagazine website: http://www.metro magazine.com.au/ metro/frm.htm?hig hlight=2 Reflect on Frontline: ‘Add Sex and Stir’ episode English Stage 5 October 2005 Page 6 of 11 NSW Department of Education and Training Curriculum K-12 Directorate http://www.curriculumsupport.nsw.edu.au/english Out Teaching and learning focus Resources comes entertainment shows: Rove Live, David Letterman, Kerri-Anne Kennerley, Bert Newton, morning TV programs (local and overseas), etc. Frontline: ‘The Siege’ episode Look at other media tie-ups with either or both interviewer and interviewee. How does print media (especially newspapers and magazines) ownership impact on the selection of guests and topics discussed? 1 8. What do we want from the media? What we would change? How difficult is it to present ‘the truth’? The ideal journalist, style and medium of news presentation. What has been learnt from their own productions and the ‘behind the scenes’ information supplied by A Fine Line? Conclusions: What would we change regarding the presentation of news? How difficult is it to present the truth? What is the ‘ideal’ journalist? What is the ‘ideal’ style and medium of news presentation? Is it the same for all audiences? Additional activities Compare and contrast news bulletins and items: same channel, different times of the day: early morning, mid morning, afternoon, evening, late different channels at the same/similar time news on cable/pay TV: local, global, different languages Sunday morning programs – commercial & ABC. English Stage 5 October 2005 Page 7 of 11 NSW Department of Education and Training Curriculum K-12 Directorate http://www.curriculumsupport.nsw.edu.au/english Girraween High School Stage Five English Presentations of Truth unit Assessment task Part A: (5 marks) table format You are required to select one week-night and watch three telecasts of nightly news (from the same night – you must clearly state your chosen date). One telecast must be either ABC or SBS. You are required to list all the items of news as they appear in the telecast and take note of the time each item takes. The list should comprise a two-column table where each item is described/summarised (no more than 75 words) with time allocated to that item in the second column. Part B: (15 marks) essay format You are required to evaluate, compare and contrast the different styles of news presentation and the different content in each of the telecasts. Write this in the form of an essay. You may like to consider the following in your response: Structure range of items covered means of presentation (the set) target audience image of the presenters (personalities) language used to present items. You must include an evaluation dealing with which telecast you think is most effective in its presentation of the nightly news. Word limit: 1250 - 1500 words English Stage 5 October 2005 Page 8 of 11 NSW Department of Education and Training Curriculum K-12 Directorate http://www.curriculumsupport.nsw.edu.au/english Stage 5 Outcomes assessed: A student: 1 responds to and composes increasingly sophisticated and sustained texts for understanding, interpretation, critical analysis and pleasure 3 selects, uses, describes and explains how different technologies affect and shape meaning 4 selects and uses and describes language forms and features, and structures of texts appropriate to different purposes, audiences and contexts, and explains their effects on meaning 6 experiments with different ways of imaginatively and interpretively transforming experiences, information and ideas into texts 7 thinks critically and interpretively using information, ideas and increasingly complex arguments to respond to and compose texts in a range of contexts 9 demonstrates understanding of the ways texts reflect personal and public worlds Marking criteria Students will be assessed on how well they: Part A compile and record information in a table format with accuracy write in a concise manner capturing the essence of the focus piece. Part B evaluate, compare and contrast new telecasts in an essay format write in a sustained manner showing critical analysis and individual thought demonstrate an understanding of the elements of news telecasts and how they are used to present information to society. English Stage 5 October 2005 Page 9 of 11 NSW Department of Education and Training Curriculum K-12 Directorate http://www.curriculumsupport.nsw.edu.au/english Annotations of mentioned resources 1. The Sydney Morning Herald: ‘Sacked for photo Americans were not meant to see’, 23 April 2004 http://www.smh.com.au/articles/2004/04/22/1082616268111.html This article has a powerful image of the American flag drapped over coffins being loaded into a plane bound for the US. The article examines the US censorship laws. 2. The Sydney Morning Herald: ‘When a picture packs a punch’, 10 June 2004 http://www.smh.com.au/articles/2004/06/09/1086749774796.html 3. Cartoon by Jenny Coopes ‘The first casualty of war is truth’ The phrase alone would work well, as this text may be difficult to locate. 4. Australian Journalist Association (AJA) Code of Ethics http://www.australiannews.com.au/codethics.htm 5. Time Magazine: ‘The PG-Rated War’ by J Klein, 7 April 2003 6. Time Magazine ‘The Trouble with Sitting on the Story’ by J Poniewozik, 28/4/2003 7. The Insider, dir Michael Mann, 1999, rated M The opening sequence of this film is excellent when dealing with the lengths that journalists go to and the difficulties they face when attempting to get the elusive and exclusive interview. The opening sequence of approximately 8 minutes focuses on the need for cultural sensitivities when interviewing outside the realm of western understanding. The film as a whole is an excellent example of the pressures faced by journalists and their sources in a bid to tell the truth. 8. Cutting Edge series: Operation Saddam, America’s Propaganda Battle (Part I) SBS, 29 July 2003 This documentary series has dealt with many facets of the media. However, this episode is the most suitable for this unit. It deals with the American media’s presentation of the war in Iraq. The focus is on the orchestrated features of the war coverage presented by the media. It also looks at the style of presentation and the need for ‘info-tainment’. The ‘football game style’ of presentation of the Iraq invasion is particularly interesting. 9. Shattered Glass, dir Billy Ray, 2003, rated M The true story of a young journalist, Stephen Glass, who fell from grace when it was found he had fabricated over half of his articles, this film is an excellent example of the external pressures placed on a journalist, not only to get the facts, but also to entertain an audience. Having achieved initial success with earlier stories, the journalist is pushed to creating his own in a bid to maintain his status as a successful and flamboyant journalist. English Stage 5 October 2005 Page 10 of 11 NSW Department of Education and Training Curriculum K-12 Directorate http://www.curriculumsupport.nsw.edu.au/english 10. Frontline, (ABC TV), R Sitch, 1994 http://www.workingdog.com/frontline Episodes: ‘Playing the Ego Card’; ‘Add Sex and Stir’; ‘The Siege’ These episodes examine the role of the status of the journalist when presenting information and effectively satirises the personalities behind the presentation of information to the public; the editing techniques and in general the power that networks have in presenting a version of a story, as well as examining perceived public expectations regarding the presentation of gender in sport; the role of the interviewer and the interviewee and the agendas behind the presentation of information. Note: these episodes are from the prescribed HSC 2004-2007 Advanced English Frontline text in Module C Representation and Text, Elective 1 Telling the Truth 11. Targeting Media: Television and Film, A Lopez et al, 2000 Structure of the news Conflict on the news Facts versus opinion Selection on the news This is a great resource giving details of the structure, purpose and audience of television news. There is also information on current affairs, sitcoms and dramas on television. 12. Media Watch, ABC TV, http://www.abc.net.au/mediawatch/ (Littlemore, Video Education Australia) This series is excellent when examining the media, all mediums. Series one (hosted by Stuart Littlemore) is particularly effective at comparing print and television. 13. Bowling for Columbine, dir Michael Moore, 2002, rated M This documentary is a very interesting presentation of contemporary American culture and its media. Extracts dealing with the selection of footage for the television series, COPS is particularly pertinent. It also deals with perceived public expectations and the role of entertainment in the presentation of information. 14. A Fine Line, Ellen Fanning, SBS TV, 2004 This series is excellent for all elements of the media. Episodes 1-3 are particularly relevant as they examine the role of the journalist’s personality in the presentation of information. Episode 1 is particularly informative about the elements of an interview. 15. A Fine Line study guide on MetroMagazine website: http://www.metromagazine.com.au/metro/frm.htm?highlight=2 English Stage 5 October 2005 Page 11 of 11 NSW Department of Education and Training Curriculum K-12 Directorate http://www.curriculumsupport.nsw.edu.au/english