Applications of Equilibrium Solubility
advertisement

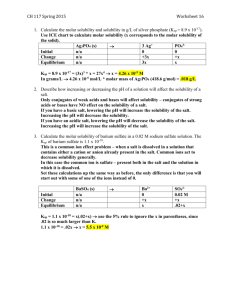
Applications of Equilibrium Solubility One important application of Equilibrium is Solubility Equilibrium which is also called Ksp. It is used when dealing with insoluble/sparingly soluble salt solutions Remember that salts disassociate into their respective ions when they dissolve. Example 1 Disassociate the following salts and write the K expression for the salt solutions. K KBr(s) P2S5(s) K2Cr04(s) Al2(CO3)3(s) NH4Cl(s) (NH4)2SO4(s) Molar Solubility = x in the ICE table = the # of moles of the solid that will dissolve in a given volume There are four types of equilibrium problems that we will be solving: Type 1- Solve for Ksp A saturated solution of Ag2CO3 can be made by dissolving 1.27 x 10-3 mol of solid silver carbonate in 10.0 L of water. What is the Ksp for Ag2CO3? Type 2- Solve for Molar Solubility/Concentration of the Ions in Solution What is the molar solubility of Ba(OH)2 if the Ksp is 2.22 x 10-2 at 15oC? Common Ion Effect= A reduction in a solubility of a salt caused by the presence of another salt having a common(the same) ion. Type 3- Determining the solubility of a salt when a Common Ion is present The Ksp for PbCrO4 (s) is 2.3 x 10 -13. Determine the solubility of PbCrO4 (s) in a 0.10 mol/L solution of Na2CrO4 (aq). Step 1- Disassociate the Soluble salt and determine the concentrations of all of the ions. Remember the balanced equation tells you the number of moles/concentrations involved in a reaction Step 2- Set up an ICE table Step 3- Write the Ksp expression and sub in the equilibrium concentrations solve for x (molar solubility of PbCrO4 (s)).