INTRODUCTION TO THE - Brigham Young University
advertisement

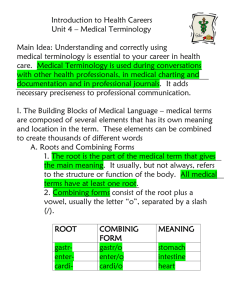
INTRODUCTION TO THE LANGUAGE OF MEDICINE AND THE ALLIED HEALTH PROFESSIONS: A WORKING TEXT BRIGHAM YOUNG UNIVERSITY - IDAHO DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH SCIENCES MEDICAL TERMINOLOGY H. S. 280 Fred R. Pearson, Ph.D. TABLE OF CONTENTS FOR INTRODUCTION TO THE LANGUAGE OF MEDICINE AND THE ALLIED HEALTH PROFESSIONS: A WORKING TEXT INTRODUCTION LESSON 1 BASIC STRUCTURE OF MEDICAL WORDS The Five Word Parts: 1. Prefixes 2. Suffixes 3. Word Roots 4. Combining Vowels 5. Combining Form Word Parts to Know Prefixes Suffixes Word Roots Word Lists Exercises Assignment Lesson 1 LESSON 2 BODY STRUCTURE AND CANCER TERMS Cellular Structure Cell Membrane Cytoplasm Organelles Nucleus Chromosome RNA DNA Mitosis Meiosis Tissue Organ Systems Body Cavities Cancer Terms Graphics Word Parts to Know Prefixes Suffixes Word Roots Word Lists Exercises Assignment Lesson 2 LESSON 3 DIRECTIONAL AND ANATOMICAL TERMS Planes and Regions Use of Directional Terms Word Parts Prefixes Suffixes Word Roots Directional Terms Anatomical Planes Anatomical Regions Anatomical Quadrants Cavities of the Body Graphics Word Lists Exercises Assignment Lesson 3 LESSON 4 INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEMS Anatomy of the Skin Accessory Structures and Organs Action Suffixes Word Parts Prefixes Suffixes Word Roots Diseases and Conditions of the Skin Graphics Surgical Terms and the Skin Additional Terms Word Lists Exercises Assignment Lesson 4 LESSON 5 THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM Anatomy Organs Functions Word Parts Prefixes Suffixes Word Roots Diseases and Conditions of the Respiratory System Graphics Surgical Terms Additional Terms Word Lists Exercises Assignment Lesson 5 LESSON 6 CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM AND LYMPHATICS Anatomy Organs Functions Word Parts Prefixes Suffixes Word Roots Diseases and Conditions of the Cardiovascular System Graphics Surgical Terms Additional Terms Word Lists Exercises Assignment Lesson 6 LESSON 7 URINARY SYSTEMS Anatomy Organs Functions Word Parts Prefixes Suffixes Word Roots Diseases and Conditions of the Urinary Systems Graphics Surgical Terms Additional Terms Word Lists Exercises Assignment Lesson 7 LESSON 8 MALE AND FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEMS Anatomy Organs Functions Word Parts Prefixes Suffixes Word Roots Diseases and Conditions of the Male and Female Reproductive Graphics Surgical Terms Additional Terms Word Lists Exercises Assignment Lesson 8 LESSON 9 OBSTETRICS AND NEONATOLOGY Anatomy Organs Functions Word Parts Prefixes Suffixes Word Roots Diseases and Conditions of Obstetrics and Neonatology Graphics Surgical Terms Additional Terms Word Lists Exercises Assignment Lesson 9 LESSON 10 THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Anatomy Organs Functions Word Parts Prefixes Suffixes Word Roots Diseases and Conditions of the Digestive System Graphics Surgical Terms Additional Terms Word Lists Exercises Assignment Lesson 10 LESSON 11 THE MUSCULOSKELETAL SYSTEM Anatomy Organs Functions Word Parts Prefixes Suffixes Word Roots Diseases and Conditions of the Musculoskeletal System Graphics Surgical Terms Additional Terms Word Lists Exercises Assignment Lesson 11 LESSON 12 THE NERVOUS SYSTEM Anatomy Organs Functions Word Parts Prefixes Suffixes Word Roots Disease and Conditions of the Nervous System Graphics Surgical Terms Additional Terms Word Lists Exercises Assignment Lesson 12 LESSON 13 THE EYE AND EAR Anatomy Organs Functions Word Parts Prefixes Suffixes Word Roots Diseases and Conditions of the Eye Graphics Surgical Terms Additional Terms Word Lists Exercises Assignment Lesson 13 LESSON 14 THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM Anatomy Organs Functions Word Parts Prefixes Suffixes Word Roots Diseases and Conditions of the Endocrine System Graphics Surgical Terms Additional Terms Word Lists Exercises Assignment Lesson 14 APPENDICES A B C D E F G Word Parts Word Parts Additional Word Parts Medicines Medical Specialties Videos Abbreviations INTRODUCTION TO THE LANGUAGES OF MEDICINE AND THE ALLIED HEALTH PROFESSIONS: A WORKING TEXT INTRODUCTION The world of medicine uses its own language based upon the ancient Latin and Greek languages. However, in the development of the medical language we use today, other word parts from several world languages have been added. Modern medicine and scientific languages use the word parts to make up many of the terms used in these fields of study. There are currently more than 150,000 medical and scientific terms in the modern medical dictionaries. This text does not try to teach every word part, but does teach the most commonly used medical word parts. The student will learn more than 1300 word parts and be able to know more than 20,000 medical terms, diseases, conditions, surgical procedures and other terms related to the practice of medicine. Since there are numerous medical terms used in the different aspects of medical care, this text will instruct the student in how to learn and analyze these terms. This is accomplished by examining the field of study, learning the word parts and then building upon and analyzing the different word parts that make up the medical word to come up with the term's correct definition. Exercises at the end of each lesson are designed to help the student use the medical terms in various ways. Medical words are constructed of small pieces that fit together like a puzzle to make unique medical words with exact meanings. This is why the medical and scientific communities use word parts to create words--because of the exactness of the meaning they construct when they are built together. As students memorize the word parts they learn how to construct and recognize many medical terms. Once learned, these medical word parts may be used over and over to build thousands of slightly different medical terms. Most word parts are related either to the body’s structure or to a disease state. The language of medicine taught in this text identifies the medical term in the context of the body part and the disease state. For example, consider the medical term enteritis. Divided into word parts, “enter” means intestines, “itis” means inflammation. The two together create the word “enteritis”, which means the intestines are in a state of being inflamed. Medical words mean exactly what the term is trying to portray. Original Latin and Greek words have their beginnings from ancient writings using visual images to portray the meaning of the words. Students learning and remembering medical terms will need to form a visual image of every word part in order to memorize the definitions of thousands of medical terms. In this way, the process of learning and remembering these terms becomes less difficult. Like the learning of languages, some medical word parts have more than one meaning. For example, the term “phren” means both mind and diaphragm. The student must decide in what context the term is being used in order to differentiate between the two meanings. Slight changes in the spelling of medical words may change the meaning quite drastically. For example, “ante-” means before or in front of, “anti-” means against or stopping something, and “antr-” has only one meaning, the antrum of the heart. All have close spellings but with very different meanings. Close attention must be made to the spelling of the word part in order to determine the correct definition. Along with differences in spelling and meaning, there are differences in pronunciation. While the spelling changes the meaning, pronunciation does not change the meaning. It is proper to use the pronunciation that becomes most familiar to the student. More than one pronunciation may be appropriate for some medical terms. Students of medical languages will quickly get used to different pronunciations used by medical personnel. Online Resources The students of this course may go online at byui.edu to receive many helps for this class. The materials are available by going to Dr. Fred Pearson's Faculty site at www.byui.edu/RICKS/employee/PEARSONF. Go to the Medical Terminology class on this site. The syllabus will appear with all the course information and the resources available with each lesson. Be sure to use these helps to check your work and to help you with terms that you cannot identify. Videos Videos for this course may be purchased from the Instructional Technology Office on the third floor of the McKay Library for $ 12.00. The videos are very helpful in memorizing the medical word parts required for this course. There are four cd's in the video set of ten videos. Students can download the video for free by going online and following the directions above under online resources. However, these are very large files and may take some time to download. Medical Dictionaries It is highly recommended that students in this course buy a Medical Dictionary. Flash cards Flash cards are provided for many of the word parts required for this course. LESSON 1 BASIC STRUCTURE OF MEDICAL WORDS THE FIVE WORD PARTS Most medical terms use some or all of the five word parts. These are: Prefixes. Prefixes come at the beginning of the medical word to modify the meaning. Suffixes. Suffixes come at the end of the medical word to modify the meaning and to explain the state of the word root. Word Root. Word roots are the main part of the medical word that usually identifies a body structure, body function or disease process as its main meaning. Combining Vowel. Combining vowels come after a prefix or word root to help in the pronunciation of the medical word. The combining vowel is usually an “o.” Combining Form. Combining form is the word root and combining vowel used together for pronunciation of the word part. Following are examples of the use of the five word parts. Prefix and Word Root Examples Using the word bicycle, first divide the word into its word parts: Bi/cycle Then define each word part: Prefix: Word Root: Bi Cycle Meaning: Two Meaning: Wheeled vehicle Next, combine the two word part meanings into a term definition: Combined Meaning: Two-wheeled vehicle In the English language, we generally define words from the front to the back (prefix to suffix). In medical terms, we generally define the word from back to front. For example, if the word bicycle was a medical term, it would be defined as a “vehicle with two wheels” rather than as a “two-wheeled vehicle.” Other examples of prefix and word root combinations: Tricycle Tri/cycle Three-wheeled vehicle Three/wheeled vehicle Prefix/Word root Uniform Uni/form One classification One/classify Prefix/Word Root Prefix, Combining Vowel, and Word Root Examples Automobile Aut/o/mobile Self-moving vehicle Self/o/moving vehicle Prefix/combining vowel/word root Streptococci Strept/o/cocci A twisted bacteria Twisted chain/o/rounded bacteria Prefix/combining vowel/word root Aeroplane Aer/o/plane In air over flat surface Air/o/flat surface Prefix/combining vowel/word root Prefix, Combining Vowel, Word Root, and Suffix Examples Orthodontist Orth/o/dont/ist One who straightens teeth Straight/o/tooth/one who practices Prefix/combining vowel/word root/suffix Electrophrenic Electr/o/phren/ic Mind and electricity Electricity/o/mind/related to Prefix/combining vowel/word root/suffix Electrotherapist Electr/o/therap/ist One who uses electricity Electricity/o/therapy/one who practices for therapy Prefix/combining vowel/word root/suffix Word Root, Combining Vowel, and Suffix Examples Photograph Phot/o/graph Result of instrument using light Light/o/instrument Word root/combining vowel/suffix Angiogram Angi/o/gram Picture of blood vessel Blood vessel/o/picture Word root/combining vowel/suffix Gastrologist Gastro/o/logist One who studies stomach Stomach/o/one who studies Word root/combining vowel/suffix Examples of Common English Words Using the Five Word Parts COMMON WORD/ BREAKDOWN / MEANING Electric Thermometer Dental Claustrophobia Bronchitis Brachial Basic Paramedic Mania Pertaining to electricity Measuring temperature Pertaining to teeth Fear of closed spaces Inflammation of bronchial tubes Pertaining to upper arm Pertaining to fundamental things Pertaining to around medicine Pertaining to madness Electr/ic Therm/o/meter Dent/al Claustr/o/phobia Bronch/itis Brachi/al Bas/ic Para/med/ic Man/ia WORD PARTS FOR LESSON 1 A. Prefixes Meaning 1. a, an2. aut- not, without self 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. 22. 23. 24. 25. bicarcincontradiadysem-, enend, endo, ent, entoepi-, eperythretieuhyperhypognoleileukmelanmetaneopolysarctriuni- two cancer opposed, against through, apart, across bad, difficult, painful in, inside inner, within upon, on, over red causing, cause good excessive deficient to know smooth white black change new many connective tissue, flesh three one B. Suffixes Meaning 1. -algia 2. -dynia 3. -cyte 4. -ectomy 5. -gen, -genesis 6. -iatr 7. -ician 8. -ist 9. -itis 10. -ology 11. -ologist 12. -oma 13. -otomy 14. -plasty pain pain cell cut out, excision beginning of cause one who practices medicine one who practices on one who practices inflammation study of one who studies tumor cut into, incision into surgical repair, plastic repair Additional Suffixes Meaning 1. -ac 2. -al 3. -ar 4. -ary 5. -ic 6. -ous 7. -ia 8. -osis 9. -tic 10. -y pertaining to pertaining to pertaining to pertaining to pertaining to pertaining to condition, abnormal state condition, abnormal state condition, abnormal state condition, abnormal state C. Word Roots Meaning 1. aden 2. angi 3. cheil 4. cyte 5. dactyl 6. dent, dont 7. hist 8. lip 9. mast 10. phleb 11. phob 12. phren 13. pleg 14. zoo gland blood vessel lip cell digit, finger, toe tooth tissue fat breast vein fear mind, diaphragm paralysis animal WORD LIST FOR LESSON 1 (A medical dictionary may be needed to define some of the terms in this word list.) adactylia adenalgia adenodynia adenectomy adenology adenosis analgia analgesic angiologist angioma angioplasty autogenic autoplasty bifocal cheiloplasty cheilalgia contraception contraindication cytometer cytotoxin dactylitis diagnosis dysdentogenic dysphrenic empathic endoangitis endodontologist endodontitis epidermosis erythrocyte etiologist eubacterium euadenic euthyroid histocyte histoma hyperalgia hypodermic hyperdontial hypomastia leukocyte leukodermia leioma lipoma melanosarcoma metagenesis neoplasty neozoology neovenologist phlebotomy phrenectomy phrenitis polydontia polyplegia sarcoma sarcosis trilogy uniplegic venotomy zoophobia zoology PRACTICE EXERCISES FOR LESSON 1 BASIC STRUCTURE OF MEDICAL WORDS TRUE OR FALSE? ____ The combining of word parts can be made into thousands of medical terms. ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ Medical words use only Latin and Greek word elements. There are currently 15,000 medical terms. Prefixes come at the end of medical terms. Suffixes come at the beginning of medical terms. Word roots are the main part of medical terms. Only one word root can be used in each medical term. Combining vowel helps in spelling. ____ More than one suffix may be used in a medical term. ____ Suffixes are used to define the state of the tissue, organ, or disease. USING A SLASH (/), DIVIDE THE FOLLOWING MEDICAL TERMS INTO THE CORRECT WORD PARTS. analgia angioplasty bifocal contraception dysdentogenic empathic endoangitis euthyroid neoplasty venotomy polyplegic trilogy unicellular dentotomy cheilalgia angioma phrenalgia venoplegia DEFINE THE FOLLOWING WORD PARTS: a-, an__________________ bicarcincontradiadysem, enepi- __________________ __________________ __________________ __________________ __________________ __________________ __________________ etihyper- __________________ __________________ hypogno- __________________ __________________ leileukmeta- __________________ __________________ __________________ neopoly- __________________ __________________ uni-cyte -ectomy -genesis -iatr -ician __________________ __________________ __________________ __________________ __________________ __________________ -ologist -itis -otomy __________________ __________________ __________________ -plasty __________________ -ac -ary -ous -tic -osis -ia cheil __________________ __________________ __________________ __________________ __________________ __________________ __________________ dent hist aden cyte mast phleb phren __________________ __________________ __________________ __________________ __________________ __________________ __________________ phob pleg __________________ __________________ DEFINITIONS: BREAK DOWN AND DEFINE EACH MEDICAL TERM Medical Term Break down and Define autogenic brachitis _________________________________________________ _________________________________________________ dysphrenia endodontitis neozoology polyplegia polyangiogenesis polyoma _________________________________________________ _________________________________________________ _________________________________________________ _________________________________________________ _________________________________________________ _________________________________________________ uniplegia dentectomy cheiloplasty _________________________________________________ _________________________________________________ _________________________________________________ cytology _________________________________________________ phrenic trilogy venotomy zoology _________________________________________________ _________________________________________________ _________________________________________________ _________________________________________________ PROVIDE THE DEFINITION OF EACH MEDICAL TERM polyoma ________________________________ etiology cytalgia neoplasty phlebotomy venotomy adenoplasty dentist ________________________________ ________________________________ ________________________________ ________________________________ ________________________________ ________________________________ ________________________________ erythrocyte polycytosis ________________________________ ________________________________ melanocyte lipoma ________________________________ ________________________________ mastitis adenomastitis zoophobia ________________________________ ________________________________ ________________________________ dentophobia uniplegia ________________________________ ________________________________ dactylodynia geneology tricytosis genetics phrenitis adenosis ________________________________ ________________________________ ________________________________ ________________________________ ________________________________ ________________________________ cytogenic dactylology zoogenic ________________________________ ________________________________ ________________________________ unilipoma ________________________________ MATCHING: ---- a, an---- auto---- contra---- dys---- endo---- eu---- neo---- poly---- tri---- uni- a b c d e f g h i j new against inside one three self many good without difficult MATCHING ---- algia ---- cyte ---- ectomy ---- it is ---- oma ---- otomy ---- dactyl ---- phleb ---aden ---- zoo a b c d e f g h i j incision, into tumor, growth pain cell to cut out or remove inflammation vein animal digit gland PROVIDE THE CORRECT COMBINING FORM FOR EACH OF THE FOLLOWING Example: fear - phob/o Vein Mind ___________________ ___________________ Breast Fat Cell ___________________ ___________________ ___________________ Tissue ___________________ Connective tissue, flesh Diaphragm Blood vessel Gland Finger Toe Hand Tooth ___________________ ___________________ ___________________ ___________________ ___________________ ___________________ ___________________ ___________________ Paralysis ___________________ WRITE THE PREFIX FOR THE FOLLOWING DEFINITIONS: Self Without Red __________ __________ __________ Cause, causing Excessive __________ __________ Deficient To know __________ __________ In, inside Upon, over Bad, difficult, painful __________ __________ __________ Through, apart, across Opposed, against __________ __________ Cancer Inner, within Two, twice __________ ___________ ___________ MULTIPLE CHOICE: Circle the letter of the most correct answer. The word part that contains the basic meaning of the word is called: a Prefix b Suffix c Combining vowel d Word root The word part that is attached to the beginning of a term is called: a Prefix b Suffix c Combining vowel d Word root The word part that is attached to the ending of the term is called: a Prefix b Suffix c Combining vowel d Word root In the medical term dermatitis, itis is the: a Prefix b Suffix c Combining vowel d Word root In the medical term, dysadenic, dys is the: a Prefix b Suffix c Combining vowel d Word root In the medical term, cytogenic, cyt is the: a b c d Prefix Suffix Combining vowel Word root In the medical word, adenopathy, o is the: a Prefix b Suffix c Combining vowel d Word root The most common combining vowel is: a A b E c I d O All medical terms must contain at least one: a Prefix b Suffix c Combining vowel d Word root The combining form is made from a: a Prefix and word root b Word root and combining vowel c Word root and suffix d Combining vowel and suffix In the divided medical word, hist/o/plasty, which part is the word root? a hist b o c plasty d o/plasty In the divided medical term, lip/o/genic, which part is the suffix? a ic b o c genic d lip In the divided medical term, poly/pleg/ia, which part is the prefix? a poly b plegia c pleg d ia Hist/o is the combining form that means: a Cells b Organs c Tissue d Against The combining form that means cause of disease is: a Melan/o b Cyt/o c Path/o d Eti/o Lei/o is the combining form that means: a Fat b Smooth c Loin d Striated The suffix that means surgical repair is: a -plegia b -plasty c -phoria d -dynia The prefix that means beyond, change, after is: a hypob hyperc metad epi- The suffix that means tumor or swelling is: a -cyte b -plegia c -plasty d -oma The combining form that means red is: a leuk/o b erythr/o c melan/o d sarc/o Assignment for Lesson 1 Medical Terminology - HS 280 Introduction Complete the following statements: a. b. c. d. The majority of medical terms currently in use are composed of ------- and Latin word parts. The primary meaning of a term is found in the -----------. The meaning of a word is changed by the addition of either a ------- or a-------. The word part attached to the end of the word root is a ----------. Rewrite misspelled terms. 1. angioectomy 2. hematocret 3. phoneocardiogram 4. histalogy 5. 6. 7. 8. pathojenic unelipoma analgisic peditrican Write P for prefix, S for suffix or WR for word root in the space beside each term to identify the word part that is underlined. 1. paramedic ___ 2. zoologist ___ 3. appendicitis ___ 4. carcinogenic ___ 5. visceral ___ 6. metastasis ___ Circle the LETTER of the best answer. 1. The purpose of a combining vowel: a. To ease word pronunciation b. To modify the meaning of a word 2. A specialist in the study of teeth: a. Dentist b. Histologist 3. A cancerous tumor: a. Carcinoma b. Lipoma 4. Pertaining to the vein: a. Phlebic b. Phrenic 7. lipoma ___ 8. histology ___ 9. mastitis ___ 5. The study of tissues: a. Cellology b. Histology 6. Pertaining to the breast: a. Adrenic b. Mastic 7. Pertaining to organs of the body: a. Abdominal b. Visceral 8. The topics of study in adenology a. Glands b. Teeth TRUE OR FALSE? 1. The word part placed before the root of the term is the suffix. __________ 2. The word part meaning the “study of” is -ologist. __________ 3. The suffix in pathology is “y.” __________ 4. The word part meta means change. __________ 5. The word root meaning cell is cyt.` __________ 6. The suffix - oma is used for either cancerous or noncancerous tumors. _________ Circle the LETTER of the best answer. 1. Most medical terms have at least one: a. prefix c. word root b. suffix d. a, b, and c 2. The word root meaning flesh: a. epitheli c. b. sarc d. viscer my 3. A tumor of fatty tissue: a. lipoma c. sarcoma b. myoma d. neuroma Circle a or b in each pair of terms to indicate which one is the correct Word Root. a. HISTology b. histOLGY a. carcinOMA b. CARCINoma a. CYTogenic b. cytoGENIC a. VISCERal b. viscerAL