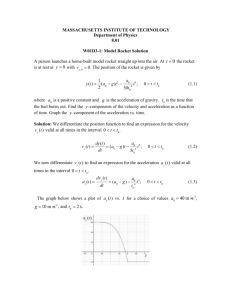
Introrough4science
advertisement

Name: Date: Period: Introduction Rough Draft Answer each question in the box below that question. Make sure you put your Name, Date, and Class in the header of this paper. To do this double click the text in the header. 1. 2. What is the title of the project? The effect of added density on the flight of a bottle rocket. What new terms or concepts are being explored in the research project? Define these using your background research. 1. Acceleration: How speed changes with time. 2. Aerodynamic: Aerodynamics is the way air moves around things. 3. Center of Gravity: The place on an object where the weight of it is centered. 4. Center of Pressure: The point considered to be the aerodynamic center. 5. Density: Density is the mass of an object divided by the volume of the object, something close to weight but not quite. 6. Drag: The amount of friction caused by the air as it passes the rocket. 7. Engine: The engine burns the fuel to power the rocket. 8. Fins: Fins keep a rocket flying straight. 9. Friction: One object rubbing against another object. 10. Gravity: Gravity is the downward force applied to all objects on earth. The force that is always acting on earth. (Presses downward on all objects on earth) 11. Inertia: A measure of an object’s resistance to changes in its motion. 12. Mass: The material in an object. 13. Momentum: The amount of motion something moving has. 14. Newton’s First Law: An object at rest tends to stay at rest, and an object in motion tends to stay in motion. 15. Newton’s Second Law: The acceleration of an object is directly proportional to the net force and inversely proportional to its mass. Name: Date: Period: 16. Newton’s Third Law: For every action there is an equal and opposite reaction. 17. Nose Cone: Carries all cargo. 18. Pressure: The force applied to an object against another object. 19. Rocket: Anything with a rocket’s engine. 20. Thrust: A force that propels rockets. 21. Velocity: The speed of an object. 3. 4. 5. What question/problem is being answered in the experiment? How does added density effect the flight of a rocket? What sparked your interest in this topic? (only time you can use personal pronouns) I enjoy studying density and how it effects other objects. Have others tried to answer this question in the past? If so, what research have they found to answer the question? Others have. _________________________________________________________________________ They have found for soap: The rocket will fly highest with dish soap. Soap causes foam, which causes the center of gravity to be higher, which makes the rocket more stable. It allows more water to be used. The thrust is a lot smoother. It can use the compressed air in a more efficient way. _________________________________________________________________________ For salt/sugar: Adding salt makes the rocket go faster per litre of fuel. This makes it go faster. It goes for longer as well. _________________________________________________________________________ Name: Date: Period: A little about why that makes sense: adding salt to water makes it heavier while not needing more space if the weight increases, the density of the water will increase as well if more salt makes it heavier, then it will be denser as well 6. 7. 8. What independent variable is to be tested? The material added to the water of the bottle rocket. ((Materials being: salt, sugar, and dish soap (because of a higher concentration of bubbles, which make it more stable, and also able to use more water in the mix)) Why was this independent variable chosen? If tests show that these materials make it travel better, then they may drastically effect the height the rocket flies. What background research supports the choice of the independent variable? They have found for soap: The rocket will fly highest with dish soap. Soap causes foam, which causes the center of gravity to be higher, which makes the rocket more stable. It allows more water to be used. The thrust is a lot smoother. It can use the compressed air in a more efficient way. If the soap foam adds stability, then it can fly for much longer in a straight path, which will make it go higher because the fastest way to get somewhere is in a straight line. If it flew in a straight line for longer, then it would gain height faster. With more water, it could have a more forceful thrust, and that could greatly increase its height. If it had a smoother thrust, that could need less stability and it could also take less time in straightening itself and gain more height in that way. If the compressed air is used more efficiently (less is used while getting more height and speed), then you could have the same amount of air as in any other rocket, and it would seem like you had tons more. That could increase height, especially if you put in more compressed air than usual. For salt/sugar: Adding salt makes the rocket go faster per litre of fuel. This makes it go faster. It goes for longer as well. This makes sense because the density of the salt/sugar would cause a more forceful thrust, which would propel the rocket more. The salt/sugar would make the water Name: Date: Period: “thicker” and “heavier” in a way, and that would come out of the rocket with a lot more power behind it than just plain water with nothing added. If the thrust is more forceful, then it would go faster with every litre of fuel, because every litre is adding more force to the last litre’s fuel, making more and more power in the thrust. 9. What is the dependent variable? How high the rocket flies. (Because it depends on the independent variables, soap, sugar, and salt.) 10. What research supports this choice of dependent variable? The fact that how high the rocket flies depends on the material added. Soap makes it more stable, able to hold more water, and able to more efficiently use the compressed air; salt/sugar make it travel for longer at a faster speed. The stability, ability to hold more water, and the ability to better use the compressed air make for a very high flight. The ability to travel longer and at a faster speed will let it fly very high because it can fly for a longer time and with greater speed than with other materials or just using water. 11. What is the hypothesis for this experiment? (be sure to use the “if…then…because” format) If dish soap is added to the water of a bottle rocket, then it will fly higher because dish soap won’t add as much weight to the rocket as salt and sugar and will still make it fly better.