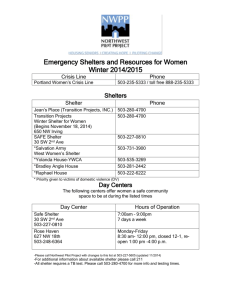
the need for shelter - bathurst schools alliance
advertisement

Glenorie Public Schoolt CONCEPT THE NEED FOR SHELTER Stage 1 DURATION – 10 WEEKS Assessment and Evaluation Children will be asked to carry out self-evaluation tasks related to their group work and individual efforts during the activities. Assessment will be carried out by peers for group presentations. Teacher observations / anecdotal notes will be ongoing throughout the unit. These will concentrate on research skills, group participation, effort, contribution to discussion, problem solving skills, communication skills and achievement of unit outcomes. During all activities emphasis will be placed on explicit and systematic teaching of literacy components related to activities covered. e.g. report writing, public speaking, journals, recounts etc. THE NEED FOR SHELTER The following pages contain a unit of work for Stage 1. The unit content has been developed from the Board of Studies HSIE K-6 Units of Work titled “THE NEED FOR SHELTER” (pp63-66). The unit provides opportunities for students to explore the need of people and other living things for shelter, and how built and natural environments can provide this. The unit focuses on the students’ local area and safety needs on familiar environments. Outcomes ENS1.5: ENS1.6: Compares and contrasts natural and built features in their local area and the ways in which people interact with these features. Demonstrates an understanding of the relationship between environments and people. Literacy Links Provides opportunities for students to explore information reports, descriptions and recounts. The HSIE teaching strategies/practices in this unit include flow charts. Links with other KLAs English: structure and language features of the text types students create and interpret Science & Technology: Built Environments / Products and Services strands Mathematics: 3D shapes, models, length, area, tracing, grouping PD/H/PE: Positive relationships, individual choices, safe practices Resources The following resources are recommended: Board of Studies website (http://www.boardofstudies.nsw.edu.au)list current available resources such as some background information sheets, websites, texts and other material to support this unit. Source material and resources about how animals and humans use the environment for shelter, about how the process of making shelters can change the environment, and about our responsibilities towards the environment. Glenorie Public School THE NEED FOR SHELTER AREAS OF INQUIRY: How do living things adapt their environment to meet their needs? How do plants use the environment for shelter? What is a shelter? How do people adapt to their environment? How did Aboriginal people use their environment to survive? DURATION - 6 to 8 WEEKS STAGE 1 LEARNING OVERVIEW KNOWLEDGE / UNDERSTANDING Children are able to: investigate ways in which humans and animals depend on their natural environment. investigate ways in which people are able to adapt their environment to meet their needs. read and view texts about caring for the environment, both natural and built. accept and fulfil responsibilities towards the class and school environments. appreciate that people are responsible for environmental change, both negative and positive. participate in activities to maintain and improve the school environment. draw and label aspects of the local area. SKILLS Children have developed skills in: acquiring information from a variety of sources through, accessing, selecting and critically evaluating information. using an inquiry process when participating in meaningful research related to important social and environmental issues. This involves initiating an investigation, gathering, analysing, synthesising, applying information and reflecting on their learning. social and civic participation that will allow them to accept and fulfil their social responsibilities. VALUES Children have developed: an appreciation of the environment, one’s personal relationship with it and one’s responsibility for its future. an understanding of the interdependence of people and the environment. a commitment to ecologically sustainable development and lifestyles. environmental responsibility. a responsibility for their own actions. a curiosity to learn about people, society and the environment. CONCEPTS people adapt their environment to meet their needs. all living things need shelter. Aboriginal people were able to survive in hostile environments. GENERALISATIONS groups provide for the needs and wants of community members the environment affects the availability and variety of group activities all people belong to groups UNIT EVALUATION Title of Unit: Outcomes: ENS1.5: ENS1.6: THE NEED FOR SHELTER EN Compares and contrasts natural and built features in their local area and the ways in which people interact with these features. Demonstrates an understanding of the relationship between environments and people. Indicators of Achievement examines how animals use the environment for shelter. examines how plants use the environment for shelter. defines the meaning of shelter examines how people adapt to different environments. investigates survival skills for people lost in a hostile environment. Teaching / Learning Activities Read and display texts that show how animals use the environment for shelter. Look at ways animals adapt to suit their environment. Research different animals and compare their lifestyles. Look in detail at how they survive and how they shelter. Find examples of animals that adapt their environment to suit their needs. eg platypus makes a burrow in the bank, kookaburra uses hollow in tree branch etc. Provide opportunities for students to explore ways plants adapt to different environments. Jointly construct a definition for shelter using the dictionary to verify or amend student ideas. Have students draw pictures or complete a model of an animal shelter or plant environment. Have students describe their picture. Include an explanation as to how they would feel in this environment and display with picture or model. Select text to read to students that show people adapt to different environments. Look at some harsh environments such as Antarctica or desert regions. Talk about what explorers and scientists went through to survive in the Antarctic. Point out changes that are occurring due to global warming etc. Read and jointly view texts about homes in different parts of Australia and the world that show how humans have built homes to adapt to the environment. eg. with stilts, steep roofs, wide verandahs, grass huts. Read Robinson Crusoe to children and discuss the needs for survival and how Robinson Crusoe addressed these needs. Relate other stories of survival after plane crashes, shipwrecks, getting lost etc. Jointly construct recounts or descriptions about the survival of people in different situations. Have students draw pictures of shelters they would construct if lost with an explanation of how they would build the shelter and materials they would use. If possible have a returned service person or current soldier talk to the class about survival skills. Watch Bush Tucker Man. explores survival skills used by Aboriginal people. examines ways people adapt to their environment. investigates how humans change the environment. identifies ways in which people’s interactions with the environment can change that environment. investigates safe practice in and around the home and school. Visit a museum or art gallery and investigate the traditional culture of Aboriginal people, or have an Aboriginal person talk to the class, about the skills that enabled them to survive in different environments such as the harsh desert environment. Provide opportunities for students to demonstrate their understanding of how Aboriginal people met their need for shelter through work sheets and individual activities. Look at household appliances/equipment such as heaters and air conditioning units and different rooms in the house which show adaptations to the environment. Ask students to look through magazines for pictures to use in a mural of built environments, equipment and rooms that show adaptation to different environments and weather conditions. Organise an excursion around the local area and observe and draw pictures of homes and other buildings that show adaptation to the environment, and discuss. Observe examples of how humans change the environment by using it to help provide shelter, eg farming for wool cotton for clothing, cutting down trees for building materials, building dams for water. Discuss the changes that occur and the effects on the environment (include the effects on other living things.) Jointly construct flow charts of the building of shelters, showing where the change to the environment can occur. Discuss the responsibilities that humans have to the environment when making shelters, and ways that the environment can be protected eg. using fewer natural resources and less energy, farming/logging sustainability, minimising environmental disturbance, recycling waste and water, regenerating cleared bushland. Explore the damage animals can make when they make their shelters. eg. rabbits. Provide opportunities for students to observe the homes in their local area, including their own home, and make judgements about efforts being made to protect the environment, any damage that is being caused and changes that could be made. Read and jointly view texts about safety at home and at school, and students’ responsibilities. Ask students to complete a poster showing a safety rule for their home.