SPCH 20: Interpersonal Communication
advertisement
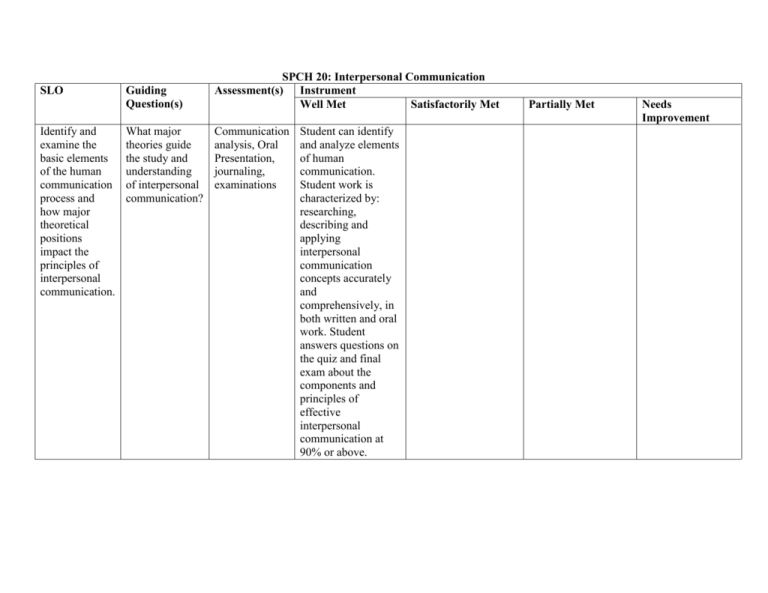
SLO Identify and examine the basic elements of the human communication process and how major theoretical positions impact the principles of interpersonal communication. Guiding Question(s) What major theories guide the study and understanding of interpersonal communication? SPCH 20: Interpersonal Communication Assessment(s) Instrument Well Met Satisfactorily Met Communication analysis, Oral Presentation, journaling, examinations Student can identify and analyze elements of human communication. Student work is characterized by: researching, describing and applying interpersonal communication concepts accurately and comprehensively, in both written and oral work. Student answers questions on the quiz and final exam about the components and principles of effective interpersonal communication at 90% or above. Partially Met Needs Improvement Analyze the significant role that verbal messages, nonverbal communication, self-concept, emotions, perception, listening and conflict play in shaping interpersonal communication. What elements guide the perception process? How do styles of listening affect interpersonal relationships? How do conflicts and strategies for navigating conflict influence the dynamics of interpersonal communication? Communication analysis, Oral Presentation, journaling, examinations Student explains how different factors affect the communication process. Student presents clear, wellreasoned and supported ideas about language and listening effectively. Student accurately analyzes verbal and nonverbal messages and answers at least 90% of quiz questions on listening skills and verbal and nonverbal communication correctly. Examine and evaluate how self-identity is socially constructed through interactions with others and society; and how this impacts interpersonal communication. Examine the complexity of interpersonal communication in multiple social contexts such as family interaction, friendships, intercultural settings, intimate relationships, gender communication and work situations. Compare and contrast how How are understandings of identity socially constructed? What is the effect of these socially constructed notions of identity? Reflective selfevaluation, Communication analysis, Oral Presentation, journaling, examinations Student demonstrates an advanced understanding of how identities are socially constructed and how these identities impact interpersonal communication. How do contextual details/norms affect the dynamics of interpersonal relationships? Communication analysis, Oral Presentation, journaling, examinations Student demonstrates a sophisticated understanding of how relationship types and contextual details/norms affect the dynamics of interpersonal communication in oral presentations, journals, and/or examinations. How do different aspects Communication Student defines and analysis, Oral applies a power, identity, technology, sexual orientation, class, physicality, age, culture and gender impact all stages of relational development and dissolution. Select, interpret, and distinguish the interpersonal skills necessary to build, maintain and enhance social relationships. of identity affect Presentation, relational journaling, maintenance? examinations How does technology alter these dynamics? sophisticated understanding of relational stages. Student demonstrates nuanced understanding of dynamics that affect interpersonal communication, including identity, power, technology, and globalization. What skills help Communication Student identifies people to analysis, Oral and utilizes multiple maintain Presentation, communication healthy/effective journaling, styles and conflict interpersonal quizzes management relationships? strategies to successfully navigate real or hypothetical interpersonal communication. Student uses research, creativity, and critical thinking skills to examine the role culture plays in interpersonal communication. Student answers at least 90 percent of exam questions on relationship Construct and present speeches demonstrating an understanding and application of interpersonal communication theories. How can interpersonal theories and concepts be applied to better understand and navigate interpersonal relationships Outlines, Oral Presentations, peer evaluation maintenance correctly. Student demonstrates a comprehensive understanding of and ability to apply interpersonal theories and concepts. Student skillfully develops ideas with purposeful organization and sophisticated sentence structure. Student produces a writer/speaker’s voice that is clear and focused on a specific purpose. Student’s oral communication in speech assignments and classroom discussions is fluent and effortless. Student demonstrates a thorough understanding of and ability to apply interpersonal theories and concepts. Student makes occasional syntactic errors but ideas are clearly expressed and modestly developed throughout the written/oral work. Student’s oral communication in speech assignments and classroom discussions is generally fluent, Student demonstrates a moderate understanding of and ability to apply interpersonal theories and concepts. Student exhibits some communication and organizational skills but does not comprehensively develop main ideas. Student presents ideas with moderate clarity, sometimes misusing words and making grammatical mistakes. Nothing is included about how to research, structure, craft, and deliver speeches. SLOs that are not being met – How? (What assignments/class activities/tests allow us to measure that learning (SLO). Student demonstrates little understanding of and no ability to apply interpersonal theories and concepts. Student generates little to no communication, does not organize ideas. Student crafts poorly structured (run-on or incomplete) sentences wherein ideas lack focus and clarity. Student’s oral communication in speech assignments and classroom discussions is fragmented and unintelligible.





