Neural and Chemical Communication
advertisement

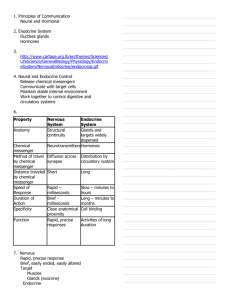
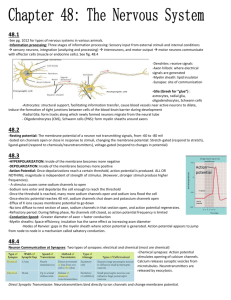
1. Principles of Communication Neural and Chemical 2 - 4. Cell-to-Cell Communication Intercellular communication How cells talk to each other Mechanisms Direct: gap junctions Indirect: chemical messengers Messenger produced by source cell Messenger transported to target cell Target cell has receptors for messenger Messenger binds to receptor Binding triggers response 5 - 10. Messenger Classification - Function Paracrine Signals a nearby cell Example: Histamine Autocrine Signals “self” Source and target are the same Neurotransmitter Chemical produced by neurons Released into the ECF at synaptic cleft Examples: Acetylcholine, glycine, serotonin Hormone Chemical produced by endocrine cells Secreted into blood via interstitial fluid Examples: Insulin, estrogen, thyroxin Neurohormone Chemical produced by neurons Secreted into blood via interstitial fluid Examples: Antidiuretic hormone (ADH), oxytocin 11 - 12. Messenger Classification - Solubility Lipophobic ligand Water soluble Does not easily cross cell membrane Receptors on cell membrane General response Enzyme activation Membrane permeability changes Lipophilic ligand Lipid soluble Easily crosses cell membrane Receptor location within cell (intracellular location) General response via gene activation _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ 13. Synthesis and Release Lipophillic ligands Synthesized on demand Immediate release from source Release rate depends on synthesis Lipophobic ligands Synthesis is independent of demand Stored in vesicles of source until needed Release by exocytosis Release rate determined by exocytosis 14 - 16.Messenger Transport Diffusion through interstitial fluid Source and target are close Ligand is quickly degraded Examples Paracrines, autocrines, neurotransmitters, and most cytokines Blood borne transport Source and target are distant Lipophobic ligands dissolve in plasma Lipophilic ligands bind to carrier protein Examples Hormones, neurohormones, and some cytokines 17. Signal Transduction Overview Messenger binds to receptor Binding results in cell response Signal transduction Process of producing response in target 18 –20.Receptor Binding Specificity Binding is brief and reversible Affinity = strength of binding Location of binding Lipophobic ligands cell membrane Lipophilic ligands within cell 21. Agonists and Antagonists Agonist Chemical which binds to receptor Action mimics normal response Antagonist Chemical which binds to receptor Binding does not result in response Competes with normal ligand _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ 22 - 25. Membrane Bound Receptors Response of the target Movement of ions Phosphorylation of enzymes Mechanisms Channel-linked receptors Enzyme-linked receptors G protein-linked receptors 26 – 28. Long Distance Communication Nervous system Nerve cells transmit signals Within neuron via long axons Between cells via the synapse Signals of axon = action potentials Axons via action potentials span distance to target Endocrine system Endocrine target secretes hormone Hormone enters blood Blood spans distance to target http://www.cartage.org.lb/en/themes/Sciences/LifeScience/Ge neralBiology/Physiology/EndocrineSystem/NervousEndocrine/e ndocrorgs.gif Property Nervous System Anatomy Structural Glands and targets continuity widely dispersed Neurotransmitters Hormones Chemical messenger Method of travel by chemical messenger Distance traveled by chemical messenger Speed of Response Endocrine System Diffusion across synapse Distribution by circulatory system Short Long Rapid – Slow – minutes to milliseconds hours Duration of Action Brief - milliseconds Long – minutes to months Specificity Close anatomical Cell binding proximity Function Rapid, precise Activities of long responses duration _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ 29 - 31. Neurons Gather and transmit information by: Responding to stimuli Producing and sending electrochemical impulses Releasing chemical messages http://www.enchantedlearning.com/subjects/anatomy/brain/gif s/Neuron.GIF Cell body Nucleus Synthesis of macromolecules Dendrites Receive & convey information to cell body Axon conduct impulses away from cell body 32. Functional Classification of Neurons Sensory/Afferent PNS CNS Motor/Efferent CNS PNS Association/ Interneurons integrate within CNS 33 - 34. Structural Classification of Neurons Pseudounipolar: single process sensory neurons Bipolar: two major processes retinal neurons Multipolar: many dendrites and a single axon motor neurons 35. Terminology Myelinated Unmyelinated 36. Myelin Sheath Formation 37 - 38. Function of Nervous System Input of sensory information Integration Motor output 39. Resting Potential 40. Electrical Potential _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ http://regentsprep.org/Regents/physics/phys03/apotdif /battery.gif 41 - 43. Leak Channels Chemical Gradient Concentration High to low Electrical Gradient + and - charges held apart by membrane Potential difference 44 - 45. Definitions Transmembrane potential Potential difference Measured across cell membrane Expressed in millivolts (mV) Results from uneven distribution of + and – ions across membrane Resting potential Transmembrane potential under homeostatic conditions 46. Graded Potential. 47 - 49. Change in Membrane Potential Passive Leak channels Widespread Always open Active Gated channels Closed at rest Types Chemical - widespread Voltage - axon (Mechanical) (Temperature) States Closed but able to open Open (activated) Closed and not able to open (inactivated) 50 - 52. Definitions Depolarization Transmembrane potential moves toward zero or toward a more positive value Hyperpolarization Transmembrane potential moves away from resting potential and toward a more negative value Repolarization Transmembrane potential moves away from a positive value and toward the resting potential ___________________________ ___________________________ ___________________________ ___________________________ ___________________________ ___________________________ ___________________________ ___________________________ ___________________________ ___________________________ ___________________________ ___________________________ ___________________________ ___________________________ ___________________________ ___________________________ ___________________________ ___________________________ ___________________________ ___________________________ ___________________________ ___________________________ ___________________________ ___________________________ ___________________________ ___________________________ ___________________________ ___________________________ ___________________________ ___________________________ ___________________________ ___________________________ ___________________________ ___________________________ ___________________________ ___________________________ ___________________________ ___________________________ ___________________________ Restoring resting transmembrane potential 53 - 59. Graded Potential Open sodium channels Influx of Na+ Depolarization Open potassium channels Efflux of K+ Hyperpolarization Graded Potential Local changes Limited spread Trigger cell functions Trigger action potential Types Postsynaptic Receptor End-plate Pacemaker 60 - 68. Action Potentials Triggered by graded potentials All-or-none phenomenon Threshold http://www.learner.org/channel/courses/biology/a rchive/images/1968.html Handout 69 - 71. Refractory Period Absolute Opening of sodium activation gates to closing of inactivation gates Relative Requires greater than normal stimulus Sodium gates closed but able to open 72. Comparison of Potentials Graded Potentials Depolarizing or hyperpolarizing No threshold Intensity of stimulus determines polarization Effect on membrane potential decreases with distance No refractory period Most cells Action Potentials Depolarizing Requires depolarization to threshold _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ All-or-none Propagates along entire membrane without change in strength Refractory period Excitable membranes of neurons, muscles 73. Rate of Impulse Conduction Nerve diameter Myelination Saltatory conduction Multiple sclerosis Factors that influence excitability pH electrolytes 74 - 75. Conduction in an Unmyelinated Axon Axon hillock reaches threshold AP occurs Na+ influx depolarizes adjacent regions to threshold new AP Slow 76 – 77. Conduction in Myelinated Axon Ions can't cross myelin APs occur only at nodes of Ranvier Voltage-gated Na+ channels are present only at nodes Fast Saltatory conduction 78. Propagation of Action Potentials Action potential is generated at each new membrane patch Continuous - unmyelinated Transmembrane potential becomes positive Local currents established Can only move in one direction, away from stimulus Saltatory- myelinated Local current skips internodes, jumping from node to node 79. Synapse Specialized junction between a neuron and another cell Chemical Synaptic transmission via neurotransmitters (NT) Electrical synapses Rare in nervous system http://www.mirrorservice.org/sites/home.ubalt.ed u/ntsbarsh/Business-stat/opre/neurons.gif _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ 80. Electrical Synapse Ions move through gap junctions Found in smooth and cardiac muscles, brain, and glial cells 81. Chemical Synapse http://universe-review.ca/I10-40-synapse.jpg 82 - 83. Synaptic Terminology Presynaptic Postsynaptic Synaptic knob Synaptic vesicles Synaptic cleft Subsynaptic membrane 84 - 87. Sequence of Events 1. Action potential reaches synaptic knob 2. Local change in potential opens voltage gated Ca2+ channels 3. Ca2+ enters synaptic knob 4. Release of neurotransmitter from synaptic vesicles by exocytosis 5. Neurotransmitter diffuses across synaptic cleft 6. Neurotransmitter binds to receptors on postsynaptic membrane 7. Binding to receptor triggers opening of chemically-gated ion channels in subsynaptic membrane 88 - 89. Excitatory Synapses Neurotransmitter binding opens a chemically-gated channel that permits passage of Na+ and K+ Net movement of cations (Na+) into the cell Small depolarization Excitatory postsynaptic potential - EPSP 90 - 91. Inhibitory Synapses Neurotransmitter binding opens a chemically-gated channel that permits passage of Cl- or K+ Net movement of anions (Cl-) into the cell or net movement of cations (K+) out of the cell Small hyperpolarization Inhibitory postsynaptic potential - IPSP 92 - 93. Synapses Always excitatory or always inhibitory Same neurotransmitter is always released Synaptic delay Removal of neurotransmitters from cleft Diffusion Inactivated by enzymes _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ Taken up into axon terminal 94. Grand Post Synaptic Potential GPSP Composite of all EPSPs and IPSPs occurring at approximately the same time 95 - 101. How Is Threshold Reached? Temporal Summation Time A presynaptic neuron firing repeatedly in a very short period of time can bring the postsynaptic membrane to threshold Amount of neurotransmitter released is related to frequency of Aps More NT = more open channels = more ion movement = greater depolarization Spatial Summation Different points in space Multiple presynaptic neurons firing simultaneously can bring the postsynaptic membrane to threshold Amount of neurotransmitter released is related to number of presynaptic neurons More NT = more open channels = more ion movement = greater depolarization 102. Information Processing 103. Convergence/Divergence 104. http://www.mfi.ku.dk/ppaulev/chapter1/images/n16ok.jpg _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________