Unit 1: Diversity of Living Things
advertisement
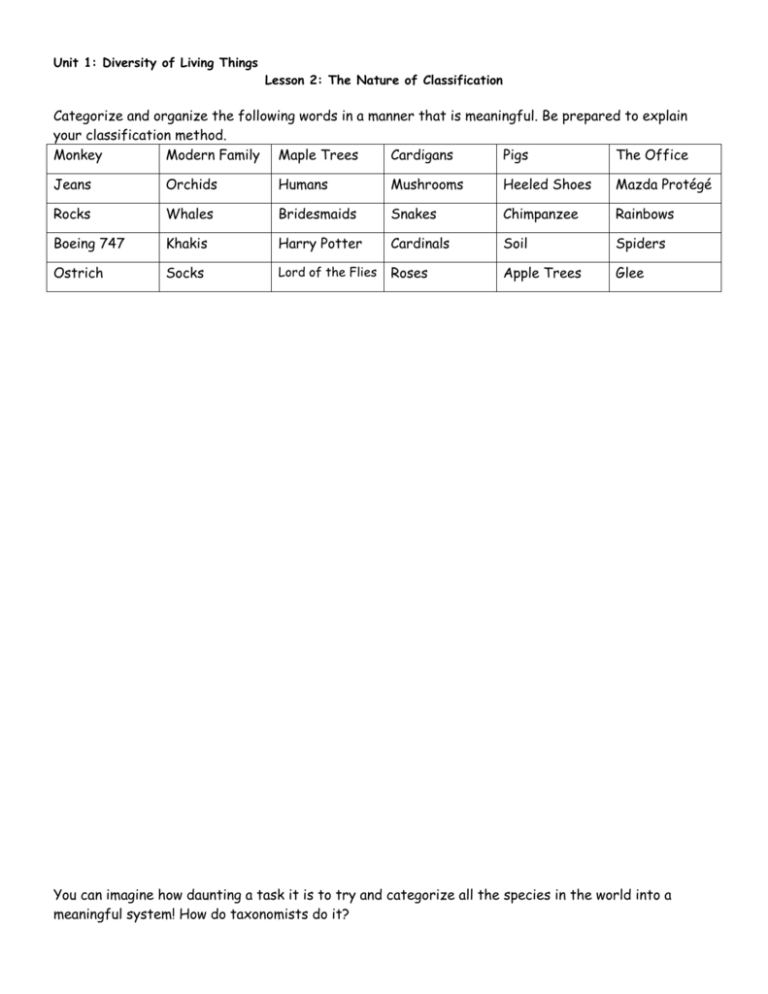
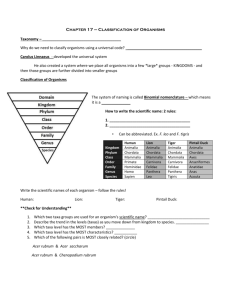
Unit 1: Diversity of Living Things Lesson 2: The Nature of Classification Categorize and organize the following words in a manner that is meaningful. Be prepared to explain your classification method. Monkey Modern Family Maple Trees Cardigans Pigs The Office Jeans Orchids Humans Mushrooms Heeled Shoes Mazda Protégé Rocks Whales Bridesmaids Snakes Chimpanzee Rainbows Boeing 747 Khakis Harry Potter Cardinals Soil Spiders Ostrich Socks Lord of the Flies Roses Apple Trees Glee You can imagine how daunting a task it is to try and categorize all the species in the world into a meaningful system! How do taxonomists do it? Taxonomy – Developing a Classification System Taxonomy: is the science of identifying and classifying all organisms. Carl Linnaeus (1707-1778) is considered the father of taxonomy. He established a naming system that is still in use today. He used binomial nomenclature. Binomial Nomenclature: the formal system of naming species whereby each species is assigned a genus name followed by a specific name; the two words taken together form the species name. Ex: Homo sapiens , Canis familiaris, Felis Catus Linnaeus grouped species into taxonomic ranks, or levels, based on shared characteristics. Each level is called a taxon (plural: taxa). Traditional Taxonomic Ranks of Classification: Taxon Human Walrus Animalia Animalia KINGDOM Bald Eagle Honey Bee Animalia Animalia PHYLUM Chordata Chordata Chordata Arthropoda CLASS Mammalia Mammalia Aves Insecta ORDER Primates Carnivora Accipitriformes Hymenoptera FAMILY Hominidae Odobenidae Accipitridae Apidae GENUS Homo Odobenus Haliaeetus Apis SPECIES Homo sapiens Odobenus rosmarus Haliaeetus leucocephalus Apis mellifera KINGDOM PHYLUM CLASS ORDER FAMILY GENUS SPECIES As you go from left to right, they become more closely related. Dichotomous Keys: a series of branching, two-part statements used to identify organisms (or objects) Taxonomy – Developing a Classification System Taxonomy: Carl Linnaeus (1707-1778) is considered the father of taxonomy. He established a naming system that is still in use today. He used_________________________. Binomial Nomenclature: Linnaeus grouped species into taxonomic ranks, or levels, based on shared characteristics. Each level is called a taxon (plural: taxa). Traditional Taxonomic Ranks of Classification: Taxon Human Walrus Bald Eagle Honey Bee Animalia Animalia Animalia Animalia Chordata Chordata Chordata Arthropoda Mammalia Mammalia Aves Insecta Primates Carnivora Accipitriformes Hymenoptera Hominidae Odobenidae Accipitridae Apidae Homo Odobenus Haliaeetus Apis Homo sapiens Odobenus rosmarus Haliaeetus leucocephalus Apis mellifera Dichotomous Keys: a series of branching, two-part statements used to identify organisms (or objects) Activity: How are dichotomous keys created? What are their key features that allow them to work? – start general and then get more specific. Start with making a grouping of categories. The features identified should have only two choices (ex: boys/girls) (taller than 5’3, shorter than 5’3) (glasses/no glasses) (dark hair/light hair) Create a dichotomous key to allow you to identify each student in the classroom. (need name tags) (be respectful – nothing that might be offensive or inappropriate). Create a dichotomous key to allow you to identify each student’s shoe in the classroom.