Text 7- Pre and Post Reading Activities BioChemical Reactions
advertisement

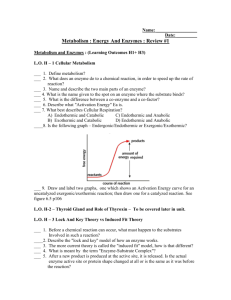
Grade 11 Science Related Reading/Chemistry Chemistry ChemistryGr10 11F Name:____________________ Class:____________________ Date:____________________ Chlorinated hydrocarbons Biochemical Reactions and their uses Task 1 – Pre-Reading Activity Using your prior knowledge about reactions and write if the following statements are True or False. 1. A substance that forms as a result of a chemical reaction is called a reactant. _______________ 2. Only some chemical reactions need energy to get started. ________________ 3. A chemical reaction that releases heat is an endothermic reaction. ________________ 4. Biochemical reactions take place inside cells. ________________ 5. The energy needed to start a reaction is called Activation energy. _______________ 6. Enzymes are Biocatalysts. _____________________ 7. Enzymes speed up reactions by increasing the activation energy. _____________ 8. Increasing the temperature speeds up reactions. ________________ Page 1 of 6 Task 2 – Reading Activity Biochemical reactions are chemical reactions that take place inside the cells of living things. The two most important biochemical reactions are respiration and photosynthesis. The sum of all the biochemical reactions in an organism is called metabolism. It includes both exothermic and endothermic reactions. Exothermic reactions in an organism are called catabolic reactions. These reactions break down molecules into smaller units and release energy. An example of a catabolic reaction is the breakdown of glucose , which releases energy that cells need to carry out life processes. Endothermic reactions in organisms are called anabolic reactions. These reactions build up bigger molecules from smaller ones. An example of an anabolic reaction is the joining of amino acids to form a protein. Most biochemical reactions in organisms need help in order to take place. Why is this the case? For one thing, temperatures are usually too low inside living things for biochemical reactions to occur quickly enough to maintain life. The concentrations of reactants may also be too low for them to come together and react. Where do the biochemical reactions get the help they need to proceed. The help comes from enzymes. An enzyme is a protein that speeds up a biochemical reaction. An enzyme works by reducing the amount of activation energy needed to start the reaction. Less activation energy is needed when the correct enzyme is present . Enzymes are involved in most biochemical reactions and they do their job very well. A typical biochemical reaction can take several days to occur without an enzyme. With the proper enzyme the same reaction could occur in a split second. Without enzymes to speed up biochemical reactions , most organisms could not survive. The activities of enzymes depend on temperature , ionic conditions and pH . The South American Bombardier beetle has an unusual way of defending itself against predators. It sprays a hot corrosive liquid from a gland on the tip of its abdomen. The gland has two separate chambers one contains a mixture of hydroquinone and hydrogen peroxide and the other Page 2 of 6 contains two enzymes , catalase and peroxidase. When the beetle is threatened it mixes the contents of the two chambers. The enzymes catalyze the decomposition of hydroquinone and hydrogen peroxide in a rapid exothermic reaction. The oxygen produced from the decomposition reaction builds up pressure which propels the hot spray towards the attacker. Key Vocabulary Biochemical exothermic endothermic catabolic anabolic temperature concentration reactant enzyme Activation energy A. Choose the correct answer: 1. Activities of enzyme depend on a. pH b. temperature c. ionic conditions d. all of the above 2. An enzyme is classified as a. lipid b. carbohydrate c. protein d. nucleic acid 3. Reactions that take place inside cells are called a. Cellular reactions b. Enzyme reactions c. Biochemical reactions d. Metabolic reactions Page 3 of 6 4. Another name for a “bio catalyst ” is a. reactant b. enzyme c. activator d. metabolism 5. The joining of amino acids to form a protein is a(n) a. Anabolic reaction b. Catabolic reaction c. Amino acid reaction d. Polypeptide reaction B. Compare Endothermic and Exothermic reactions with atleast one example. Page 4 of 6 C. Match the terms with the right definitions by writing the numeral in the middle : Terms Definitions 1. Activation energy Represents a chemical reaction 2. Anabolic reaction A protein that speeds up a biochemical reaction 3. Biochemical reaction A substance that forms as a result of a chemical reaction 4. Catabolic reaction Substance that starts a chemical reaction 5. Chemical equation Sum of all the biochemical reactions in an organism 6. Chemical reaction A process that changes some chemical substances into others 7. Enzyme Endothermic reactions in organisms 8. Endothermic Exothermic reactions in organisms 9. Exothermic Chemical reactions taking place inside the cells of living things 10. Metabolism Chemical reaction that releases energy 11. Product Chemical reaction that absorbs energy 12. Reactant The energy needed to start a chemical reaction D. The chemical reaction that takes place in the abdomen of the Bombardier beetle is as shown: C6H4(OH)2(aq) + H2O2(aq) --> C6H4O2(aq) + H2O(l) Balance this chemical equation and represent it properly to show whether the reaction is endothermic or exothermic. __________________________________________________________________ Page 5 of 6 Task 3 – Post Reading Activity Use the given writing frame to write about the Bombardier Beetle and explain how it uses a chemical reaction for self defense Page 6 of 6