Solutions to 2010 Prelim H2 9646/9745 Physics
advertisement
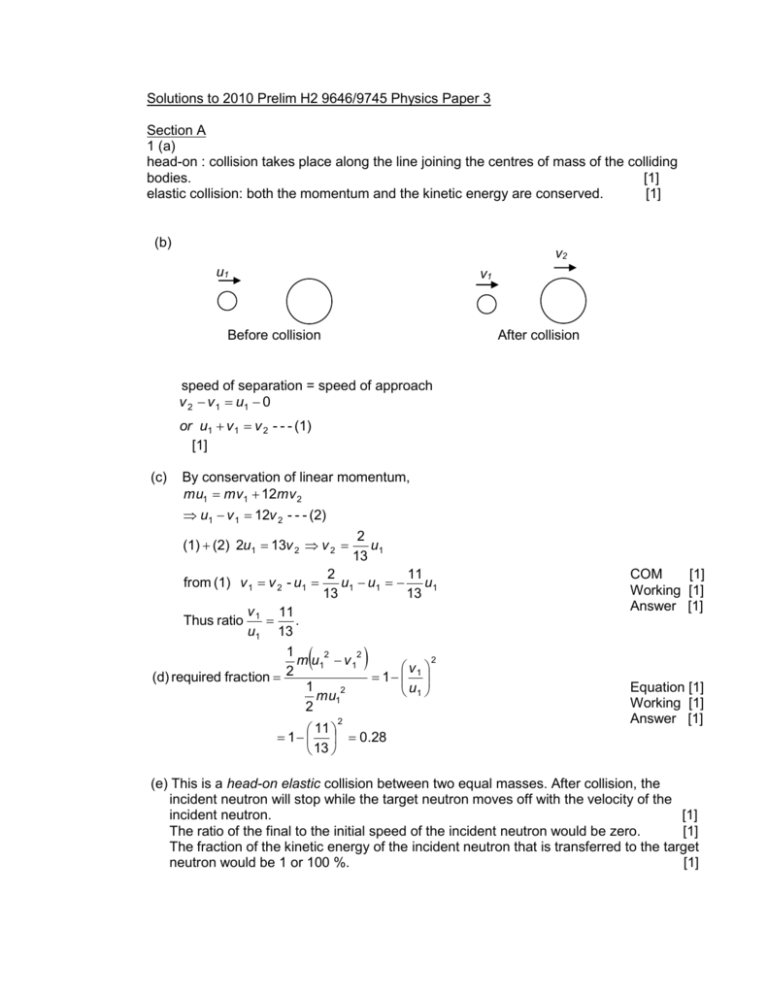
Solutions to 2010 Prelim H2 9646/9745 Physics Paper 3 Section A 1 (a) head-on : collision takes place along the line joining the centres of mass of the colliding bodies. [1] elastic collision: both the momentum and the kinetic energy are conserved. [1] (b) v2 u1 v1 Before collision After collision speed of separation = speed of approach v 2 v 1 u1 0 or u1 v 1 v 2 - - - (1) [1] (c) By conservation of linear momentum, mu1 mv1 12mv 2 u1 v 1 12v 2 - - - (2) (1) (2) 2u1 13v 2 v 2 from (1) v 1 v 2 - u1 2 u1 13 2 11 u1 u1 u1 13 13 v 1 11 . u1 13 1 2 2 2 m u1 v 1 v 2 (d) required fraction 1 1 1 2 u1 mu1 2 COM [1] Working [1] Answer [1] Thus ratio 2 11 1 0.28 13 Equation [1] Working [1] Answer [1] (e) This is a head-on elastic collision between two equal masses. After collision, the incident neutron will stop while the target neutron moves off with the velocity of the incident neutron. [1] The ratio of the final to the initial speed of the incident neutron would be zero. [1] The fraction of the kinetic energy of the incident neutron that is transferred to the target neutron would be 1 or 100 %. [1] 2 2(a) (i) Curve concave downwards, crossing all field lines at right angle (by visual) (ii) (b) (i) Electrons are stripped off the molecule. [1] Electrons and positive ions move off in opposite direction, giving rise to an electric current. [1] 2 12 3 2 7 1. Q 4 r E 4 8.85 10 (2.00 10 ) 1.13 10 [1] o -9 = 5.03 x 10 C [1] 2. (c) (i) (ii) [1] Q = 1.13 x 107 4o r 2 1 Q V E r = 1.13 x 107 x (2.0 x 10-3 ) 4o r = 2.26 x 104 V E 1 1 (5.03 10 9 ) 2 4 o r 2 4 8.85 10 12 ( 4.0 10 2 ) 2 = 1.42 x 10-4 N This Coulomb’s repulsion results in greater apparent weight of sphere. N = mg + F N mg F F 1.42 10 4 m 8.205 1000 m’ = g g g 9.81 = 8.219 g F 1 Q1Q2 [1] [1] [1] [1] [1] Due to repulsion, more charges accumulate on the outer sides of the 2 spheres. Thus the distance between centre of charge of the spheres is increased. [1] The electrostatic force F will be lesser. The reading m’ will be lesser. Thus answer in (b)(ii)1 is an over-estimate. [1] 3 3.(a) The magnetic flux linkage through the coil is the product of the number of turns of the coil and the magnetic flux density that is perpendicular to the coil and the area of the coil. [1] (b) Field is in XY direction [1] (c) When the current increases, the magnetic flux density of the solenoid XY increases. [1] Flux linkage with the small coil increases. [1] According to Faraday’s law, an emf is induced in the coil. [1] (d) e.m.f. time Fig 4.3 -cosine graph [1] 4 4 (a) (i) The binding energy of a nucleus is the energy released when a nucleus is formed from its constituent protons and neutrons. [1] (ii) 1. BE per nucleon/MeV 8.8 correct shape [1] 0 56 nucleon number A (iii) 2 In nuclear fission, a heavy nucleus splits to give two daughter nuclei of greater binding energy per nucleon. [1] The difference in the total BE results in a large amount energy release during the process. This is a potential source of energy. [1] (b)(i) Energy released in one reaction = (mu+ mn – (mxe + msr + 2mn)) uc2 [1] = [235.043929 + 1.008665 – (138.918793 + 94.919359 + 2(1.008665)) x 1.66 x 10-27 x (3.00 x 108)2 [1] = 2.94 x 10-11 J [1] (ii) 235 u of Uranium produces 2.94 x 10-11 J in each fission reaction. 2000 kg of Uranium produces, by proportion, 2000 2.94 x 10-11 x = 1.51 x 1017 J [1] 27 235 x1.66 x10 Useful Energy from 2000 kg of Uranium = 0.080 x 1.51 x 1017 = 1.21 x 1016 J [1] Amount of time to last, t = (1.21 x 1016/1.15 x1017) = 0.105 years = 38 days [1] 5 Section B 5 (a) In a uniform circular motion, although the linear speed remains unchanged, its direction changes with time, hence the velocity is always changing. So the motion is accelerated. By Newton’s second law, a resultant force must be acting on it. Since the change in velocity is directed towards the centre of the circle, the acceleration, and hence the resultant force is directed towards the centre of the circle. [2] (b) (i) T = Mg = 1.0 x 9.81 = 9.81 N [1] (ii) Resultant force = T 2 mg = 9.81 2 2 0.10×9.81 2 [1] [1] =9.76 N (iii) 2 Resultant force mr 9.76 mr 2 f r 2 9.76 180 0.10 2 60 2 0.275 m [2] (iii) It would not be possible for the string to be horizontal because the string needs to make an angle with the horizontal such that there is a vertical component of the tension to balance the weight the weight of the mass. [2] F G (c) m1m2 r2 [2] Where F is the gravitation force of attraction between the two point masses m1, m2; r is the distance between the two point masses, and G is the universal gravitational constant. (d) (i) 6 GMm 2 mr 2 mr 2 r T 4 2 3 T2 r GM 3 4 2 7 2 3.45 10 GM 2.00 1011 M 3.98 1030 kg 2 (ii) Concept [1] Working [1] Answer [1] Since both the star and the planet have a tangential velocity, the gravitational force of attraction provides the centripetal force for both the star and the planet to orbit about their centre of mass. [1] (iii) 1 GMm mv 2 + =0+0 2 r v= v= 2GM r 2 6.67×10 -11 1.20×10 24 Concept [1] Working [1] Answer [1] 7.5×10 6 2 =6.53×103 m s-1 (iv) Since average speed of the nitrogen gas is higher than the escape on the planet, most gases would have escaped and hence the planet does not have an atmosphere. [1] 7 6 (a) It is a phenomenon in which waves from 2 or more coherent sources superpose with one another producing a resultant wave. [1] (b)(i) Sound from the 2 sources undergo interference. As the source S1 moves, the path difference changes. [1] When the path difference between S1P and S2P is an integral number of the wavelength, constructive interference occurs at P and a maxima is detected. [1] When the path difference between S1P and S2P is an odd integral number of half wavelength, destructive interference occurs at P and a minima is detected. [1] 6 (b)(ii) Path difference = = 0.082 m 2 = 0.164 m S1 X = 1 = 0.082 m (b)(iii) v f 4100 0.082 = 340 m s-1 (c) [1] [1] [1] [1] [1] (i) Wave travel down the tube and gets reflected. [1] The incident and the reflected waves, both having the same amplitude, frequency and speed travelling in opposite directions superpose to form standing wave. [1] (c) (ii) Air column in tube has natural frequency of vibration. [1] When fork frequency is equal to natural frequency, resonance occurs; there is maximum energy transfer and maximum amplitude of vibrations occurs, leading to maximum loudness. [1] When fork frequency is not equal to natural frequency, no resonance occurs and loudness drop. [1] (c) (iii) Sketch: Antinode at top, node at surface of water, 1 antinode and 1 node in between [1] (c) (iv) L1 c -------------(1) 4 3 L2 c --------------(2) 4 1 L2 L1 32.4 cm 2 = 64.8 cm v f 512 0.648 332 m s-1 (2) – (1) [1] [1] [1] 1 1 [1] L1 c 15.7 c c= 64.8 15.7 = 0.50 cm 4 4 Therefore, antinode is 0.50 cm above the top of the tube OR antinode is 16.2 cm above water surface. [1] (c)(v) 8 7 (a) 1. Emission line spectrum is observed is at A. It is due to the emissions of photons of specific energy when the excited He atoms return to ground states. The emission occurs in all directions and hence is detected at A. [2] 2. Absorption line spectrum observed is at B. It is due to the absorption of photons of specific energy from the white light by cool He atoms to jump to excited states. These photons are re-emitted in all directions and hence missing from the transmitted beam at point B. [2] (b) (i) The transitions are from n=3 to n=1, n=3 to n=2 and n=2 to n=1. [2] (ii) The longest wavelength comes form transition n=3 to n =2. E = hc/ [-6.04-(-13.6)] x 1.60 x 10-19 = 6.63 x 10-34 x 3.00 x108/, [1] = 1.64 x 10-7 m [1] (iii) 1. A metastable state is the state in which the electrons remain longer than usual so that the transition to the lower state occurs more likely by stimulated emission than by spontaneously emission. [2] 2. Population inversion is a condition of having more atoms in an excited state than in the lower energy state. [1] (c) (i) P = (N/t) hf N/t = P/hf = 3.8 x 10-3/4.7 x 1.60x10-19 = 5.1 x 1015 s-1 (ii) Current I = = N’e/t, from graph, max current = 0.80x10-8 A N’/t = 0.80x10-8 /1.60x10-19 = 5.0 x 1010 s-1 [1] [1] [1] [1] (iii) Rate of incident photons is very much larger than the rate of electrons emitted. Most of the photons rebound/reflect from the metal surface/electrons deep below surface requires more energy/presence of impurities on surface [2] (iii) Stopping potential Vs = -0.50 V. Maximum KE of electrons = eVs = 8.0 x 10-20 J (v) Work function = hf – KEmax = 4.7 x 1.60 x10-19 - 8.0 x 10-20 = 6.7 x 10-19 J [1] [1] [1]