for research involving recombinant dna
advertisement

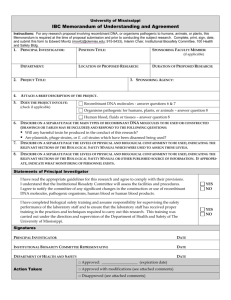
REQUIREMENTS AND PROCEDURES FOR RESEARCH INVOLVING RECOMBINANT DNA AT TEXAS A&M UNIVERSITY March 1999 REQUIREMENTS AND PROCEDURES FOR RESEARCH INVOLVING RECOMBINANT DNA AT TEXAS A&M UNIVERSITY CONTENTS I. GENERAL REQUIREMENTS AND PROCEDURES FOR RECOMBINANT DNA RESEARCH II. REGISTRATION, REVIEW AND APPROVAL OF RECOMBINANT DNA RESEARCH III. RESPONSIBILITIES OF PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATORS IV. THE INSTITUTIONAL BIOSAFETY COMMITTEE (IBC) V. THE BIOLOGICAL SAFETY OFFICER (BSO) APPENDICES A. Members of the Institutional Biosafety Committee B. Form for Submission of Documents for Registration and Review of Research Involving Recombinant DNA at Texas A&M University REQUIREMENTS AND PROCEDURES FOR RESEARCH INVOLVING RECOMBINANT DNA AT TEXAS A&M UNIVERSITY I. GENERAL REQUIREMENTS AND PROCEDURES FOR RECOMBINANT DNA RESEARCH Recombinant DNA research is conducted with molecules constructed outside living cells, where DNA segments are joined or replicated, where a DNA sequence may be modified, or where related research is conducted with this type of material. The purpose of this document is to summarize requirements, procedures and expectations for conducting recombinant DNA research at Texas A&M University (including all facilities in Brazos County, Galveston and the Institute for Biosciences and Technology). Certain general procedures are outlined to aid scientists in compliance. Any research conducted with recombinant DNA, regardless of the source of funding or source of recombinant material, must be conducted in accordance with Institutional requirements and federal guidelines. Texas A&M University adheres to NIH Guidelines for Research Involving Recombinant DNA1 and appropriate Administrative Supplements, as issued. Research on recombinant DNA should also be conducted in accordance with CDC/NIH Biosafety Guidelines (Biosafety in Microbiological and Biomedical Laboratories1,2), as appropriate. Experiments involving livestock or plants may require compliance with additional regulations and approval by the Office of Agricultural Biotechnology, U. S. Department of Agriculture 3. Copies of these references are available for review in the TAMU Environmental Health and Safety Department. It is essential that recombinant DNA research be conducted in accordance with the intent, as well as specific requirements and guidelines. Because research is dynamic, it is not possible to anticipate every situation. The conscientious effort and good judgment of personnel are essential for protection of health and the environment during recombinant DNA research. Primary responsibility for compliance with institutional and governmental requirements and for safe and proper experimentation resides with the principal investigator (PI). The Institutional Biosafety Committee (IBC, APPENDIX A) and the Biological Safety Officer (BSO) are appointed to review and monitor recombinant DNA research on behalf of Texas A&M University. II. REGISTRATION, REVIEW AND APPROVAL OF RECOMBINANT DNA RESEARCH All recombinant DNA research conducted at Texas A&M University must be registered with the IBC. All proposals for recombinant DNA research, unless specifically exempted by the NIH Guidelines1, must be reviewed and approved by the IBC prior to initiating work. This includes, but is not limited to: recombinant products, DNA probes, vector systems, and related material received from outside sources4. Review and approval by the IBC of cooperating institutions may be required. Coordinated reviews may be arranged by IBC chairpersons of cooperating institutions or agencies. PIs and unit heads should seek clarification regarding institutional requirements for protocol or project approval and safety (independent of their own interpretations or uncertainties). Review by the IBC includes evaluation for compliance and conformance with the NIH Guidelines 1; assessment of the containment levels required by the Guidelines; assessment of the facilities, procedures and practices; and consideration of the training and expertise of recombinant DNA personnel. A. Research and Related Activities Requiring IBC Review and Approval 1 NIH Guidelines for Research Involving Recombinant DNA Molecules, Federal Register, 62 FR 59032, October 31, 1997 and updates. 2 Biosafety in Microbiological and Biomedical Laboratories, U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, Public Health Service, Centers for Disease Control and National Institutes of Health, 3rd Edition, May, 1993. HHS Publication No. (CDC) 93-8395. 3 USDA Guidelines for Research with Genetically Modified Organisms Outside Contained Facilities, Office of Agricultural Biotechnology, USDA, Washington D.C., May, 1989 and updates. 4 Certain restrictions and regulations may apply to shipment and transport of genetically altered material. 1. 2. 3. 4. III. Projects - All research (regardless of the source of funding) conducted at Texas A&M University, involving recombinant DNA (including recombinant DNA used as probes or obtained from another laboratory) must be registered, reviewed and approved by the IBC. NOTE: Certain types of research that are specifically exempted (by NIH Guidelines) from review only require registration with the IBC (See II.B below). Grant Proposals - All extramural grant proposals for research involving recombinant DNA should be identified as such by the PI, acknowledged by the unit head, and reviewed by the IBC prior to submission to the sponsor. The project number should be included if the research is supported by the Texas Agricultural Experiment Station (TAES). Project Modifications - Additional IBC review and approval is required if the nature or content of research changes significantly, or if recombinant DNA, either cloned or received from an outside source is involved. For example, collaborative work may require evaluation of unanticipated recombinant products or in locations where prior recombinant DNA research was not anticipated. Proposal changes must be reviewed and approved before work proceeds. Testing, Evaluation and/or Release - Research plans, protocols and provisions for containment for recombinant DNA work under field conditions (outside a lab, growth chamber, containment or cage) require additional information and IBC review. Environmental safety and risk must be considered for potentially self-replicating biological material. Investigators should anticipate potential testing, evaluation or release of recombinant DNA products (at least one year lead time) for preparation and review of approval documents. B. Registration of Recombinant DNA Research All research projects involving recombinant DNA must be registered with the IBC. Completion of the form, Registration and Review of Research Involving Recombinant DNA Molecules at Texas A&M University (APPENDIX B) will fulfill this requirement. Submission of additional documentation is not required for research that is specifically exempted from IBC review1. C. Submitting Protocols for IBC Review 1. The completed form "Registration and Review of Research Involving Recombinant DNA Molecules at Texas A&M University" (APPENDIX B), must accompany material submitted for review. 2. Documents for recombinant DNA review by the IBC should be submitted through established administrative channels; that is, TAMU departments and research groups should route proposals to the Vice President for Research or the Texas A&M Research Foundation. Proposals from research units, departments and centers supported by TAES should be routed to the TAES Project Records Office. 3. NOTE: Prior review by the IBC is required for all documents to be forwarded to the Recombinant DNA Advisory Committee of the National Institutes of Health (NIH/RAC). 4. Documents submitted to the IBC for review must include complete and adequate information and protocols to allow appropriate peer review. RESPONSIBILITIES OF PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATORS A. The Principal Investigator, on behalf of the Institution, is responsible for fully complying with the NIH Guidelines in conducting any recombinant DNA research. As part of that responsibility, the PI shall: 1. Be aware of recombinant DNA biosafety requirements and assure that requirements and procedures of Texas A&M University are followed; assure that all work involving recombinant DNA is registered with the IBC; assure that necessary safeguards and procedures are maintained in the work place: follow the NIH Guidelines for Research Involving Recombinant DNA Molecules1 It is essential for PIs working with recombinant DNA to be thoroughly familiar with the NIH Guidelines and follow appropriate CDC/NIH Biosafety Guidelines1,2; a. Make the initial determination of the required levels of physical or biological containment in accordance with the NIH Guidelines; b. Select appropriate microbiological practices and laboratory techniques to be used in the research; (See NIH Guidelines for Research Involving Recombinant DNA Molecules for information on containment requirements. Appendix G specifies physical containment requirements for standard laboratory experiments and defines Biosafety Level 1 through Biosafety Level 4. For large scale (>10 liters) research or production, Appendix K (Physical Containment for Large Scale Uses of Organisms Containing Recombinant Molecules) supersedes Appendix G. Appendix K defines 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. IV. Good Large Scale Practice BL1-LS through- BL3-LS. For certain work with plants, Appendix P (Physical and Biological Containment for Recombinant DNA Research Involving Plants) supersedes Appendix G. Appendix P defines Biosafety Levels BL1-P through BL4-P. For certain work with certain animals, Appendix Q (Physical and Biological Containment for Recombinant DNA Research Involving Animals) supersedes Appendix G. Appendix Q defines Biosafety Levels BL1-N through BL4-N.) Assure that all review and approval requirements are fulfilled prior to initiating any new or modified research procedures; Comply with shipping requirements for recombinant DNA molecules; Submit the initial research protocol if required by NIH Guidelines or institutional requirements; Notify the Biological Safety Officer (BSO) when required safety inspections and certification of containment facilities and biological safety cabinets are needed; Notify the IBC of any significant changes in experimental protocol or location of research; Provide information to the IBC and BSO, as necessary. Remain in communication with the IBC throughout the conduct of the project. B. Responsibilities of the Principal Investigator prior to initiating research. The PI shall: 1. Assure that labs and work places are identified with appropriate warning signs; and that personnel are properly trained and are informed regarding biohazards; 2. Make available to the laboratory staff, copies of the protocols that describe the potential biohazards and the precautions to be taken; 3. Assure that staff members are trained in the safe work practices and techniques and in the procedures for dealing with accidental spills and personnel exposure; 4. Inform staff of the reasons and provisions for any precautionary medical practices advised or requested, such as vaccinations or serum collection; 5. Prepare a written contingency plan for handling emergency conditions such as spills, personnel exposure, loss of containment, power failure, etc. C. Responsibilities of the Principal Investigator during the research. The PI shall: 1. Supervise the staff to assure that the required safety practices and techniques are employed, and that the appropriate containment procedures are followed; 2. Investigate and provide written report to the BSO, the IBC and the NIH Office of Recombinant DNA Activities (ORDA) regarding any significant problems pertaining to the operation and implementation of biohazard-containment practices and procedures, violations of the NIH Guidelines and all significant research-related accidents and illnesses; 3. Correct work errors and conditions that may result in the release of recombinant DNA materials; 4. Ensure the integrity of physical containment (e.g., biological safety cabinets) and the biological containment (e.g., purity and genotypic and phenotypic characteristics); 5. Adhere to IBC-approved emergency plans for handling accidental spills and personnel contamination; 6. Assure proper handling and disposal of biohazardous waste. THE INSTITUTIONAL BIOSAFETY COMMITTEE (IBC) A. The IBC reviews and oversees all recombinant DNA research at Texas A&M University. The IBC reports directly to the TAMU Provost through the TAMU Vice President for Research, and has certain additional reporting responsibilities to NIH. Current members are listed in Appendix A. B. Appointment of IBC Members and Chair 1. IBC members and the Chair are appointed annually, in accordance with NIH Guidelines1 by the TAMU Vice President for Research. Members are generally appointed to serve a three-year term. 2. Members shall be qualified, by expertise and experience, to review recombinant DNA research proposals and shall serve from approximately September 1 through August 31. 3. Membership and representation on the IBC shall be in accordance with NIH Guidelines 1. At least two Members-at-Large shall be appointed to represent the community. 4. An IBC member shall be disqualified from review or approval of a proposal or activity in which he/she has been or expects to be engaged, except to provide information requested by the IBC. V. C. Specific Responsibilities 1. Provide interface between the Institution, the BSO and PIs concerning lab review, security, safety, emergency plans and other activities; 2. Maintain a registry of research projects and/or proposals involving the use of recombinant DNA at TAMU. 3. Provide oversight, review and assessment of: a. adherence to NIH requirements for recombinant DNA research; b. training and expertise of personnel; c. laboratory safety, security, and biological containment requirements and practices; d. emergency contingency plans including containment and cleanup of spills and exposure of personnel to biohazardous materials. 4. Investigate reports of problems of safety or non-compliance. Alert the TAMU Vice President for Research (or other administration officials as appropriate) and the PI to any non-compliance or other problems, and monitor corrective action. (NOTE: The IBC reviews and monitors research involving recombinant DNA and may assist PIs in voluntary compliance. However, the IBC assumes no responsibility for gaining compliance or for fulfilling research requirements.) 5. Coordinate and assist the BSO with safety and containment monitoring programs. 6. Meet as necessary and maintain a permanent record of IBC meetings and activities. 7. Periodically review the status of current recombinant DNA research at TAMU. 8. Provide guidance to PIs and review reports or proposals prepared for submission to the NIH Office for Recombinant DNA Activities (ORDA) and the NIH Recombinant DNA Advisory Committee (RAC). 9. Inform unit heads of recombinant DNA activities and proposals within their unit. 10. Other responsibilities as specified by the NIH Guidelines1. D. Reporting and Communications 1. The IBC Chair shall help inform and involve unit heads in the review and compliance of recombinant DNA research activities in their unit. Proposals, projects or other documents shall reflect unit head awareness and concurrence prior to IBC review. 2. Provide an Annual Report (September) on the status of recombinant DNA research, reviews, and compliance to the TAMU Vice President for Research. The Annual Report should include a summary of proposals reviewed during the year; status of regulatory compliance, safety and biological containment; emergency procedures; new issues and other items as appropriate. 3. Interim reports regarding significant deficiencies, non-compliance, or other emergency issues may be prepared and forwarded to the TAMU Vice President for Research, and others, as necessary. 4. The TAMU Vice President for Research should be provided advance written notification of any proposed IBC communication with federal agencies or committees, other than proposal review assessments and approvals. THE BIOLOGICAL SAFETY OFFICER The Biological Safety Officer is the designated administrative officer who assists in assuring compliance and biosafety of recombinant DNA research conducted at Texas A&M University. A. Appointment The BSO shall be designated by the TAMU Vice President for Research to provide services and assistance as required by federal guidelines and regulations and institutional requirements. B. Specific Duties and Responsibilities 1. Serve as an ex-officio member of the IBC to provide a focal point for compliance with recombinant DNA biological safety (lab, human and environmental aspects), biological containment, lab practices, and monitoring requirements in accordance with Federal Guidelines1,2 and institutional requirements. 2. Conduct or supervise annual inspection and review of recombinant DNA laboratories or facilities and authorize qualified labs to conduct recombinant DNA research following CDC/NIH Biological Safety Guidelines1,2 and institutional requirements. 3. Assist in certification of biological safety cabinets and BL-3 laboratories. Conduct or supervise safety inspection and testing of containment facilities. Maintain documents and results of certification. 4. 5. C. Provide technical advice to investigators and the IBC on safety procedures and lab containment. Assist investigators in defining and interpreting safety and regulatory requirements; identify procedures to be followed; assist PIs, staff and unit heads in maintaining awareness of responsibilities and regulatory developments; identify safety problems, seek voluntary compliance and report significant problems (such as containment, safety, lab techniques, and facilities) to the IBC, the PI, and others, as appropriate. Assist investigators in developing emergency plans for containment and cleanup accidental spills or releases; assist in emergencies; investigate and review recombinant DNA lab accidents. Maintain documents and reports associated with the investigations and actions. Reporting and Communications 1. The BSO shall inform unit heads, PIs, and others of biosafety requirements and assist with maintaining compliance with institutional and governmental guidelines and regulations. 2. The BSO shall assist the IBC chair with preparation of an annual report summarizing activities and findings during the past year. Interim reports or notifications may be forwarded any time that significant deficiencies, non-compliance or other emergency issues develop. 3. Inform the IBC Chair and others, as appropriate, of instances of safety problems or non-compliance with institutional and regulatory requirements. APPENDIX A. MEMBERS OF THE INSTITUTIONAL BIOSAFETY COMMITTEE Dr. Van Wilson, Chair (1999) Medical Microbiology & Immunology College of Medicine Texas A&M University College Station, TX 77843-1114 (409) 845-5207 Rev. Robert Leslie* (2001) First Presbyterian Church 1100 Carter Creek Parkway Bryan, TX 77802 (409) 823-8073 Virginia (Ginger) Brown, Ex-Officio Safety Coordinator , Biological Safety Environmental Health and Safety Department Texas A&M University College Station, TX 77843-4472 (409) 862-4038 Dr. Roger Smith (1999) Veterinary Pathobiology College of Veterinary Medicine Texas A&M University College Station, TX 77843-4463 (409) 845-5167 Dr. Laura Hendrix (2001) Medical Biochemistry & Genetics College of Medicine Texas A&M University College Station, TX 77843-1114 (409) 845-1313 Dr. Tom McKnight (2001) Department of Biology College of Science Texas A&M University College Station, TX 77843-3258 (409) 845-3896 Dr. Richard Miller (Ex-Officio) Director, Research Services Administration 312 Administration Building Texas A&M University College Station, TX 77843-1112 (409) 845-8585 Mr. Stephen W. Rogers* (2001) Caperton, Rogers & Miller, P.C. 4444 Carter Creek Parkway Bryan, TX 77802 (409) 260-9911 Dr. Jon Skare (2001) Medical Microbiology & Immunology College of Medicine Texas A&M University College Station, TX 77843-1114 (409) 845-1376 Dr. Ryland Young (1999) Biochemistry & Biophysics College of Agriculture & Life Sciences Texas A&M University College Station, TX 77843-2128 (409) 845-2087 *Community Representatives