classification
advertisement

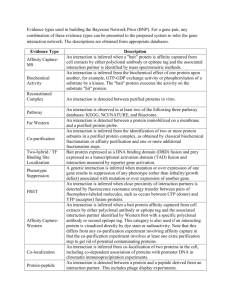
EVIDENCE CLASSIFICATION EcoCyc/RegulonDB team We wish to classify the evidences associated to RegulonDB/EcoCyc objects as strong or weak. This classification will be translated to the graphical display of objects, as weak evidence objects will be plotted with dotted lines in contrast with strong evidences. If the same object has different evidence sources, it should be displayed according to the strongest. EXAMPLES OF GRAPHICAL DISPLAY CAPTION: RI = regulatory interaction TU = transcription unit FIG1. Promoter and TU with weak evidence FIG2. Promoter, RI and TU with strong evidence FIG3. TU with a weak evidence CRP RI and a strong DgsA RI. The evidence associated with the promoter is strong, while the TU evidence is weak. CLASSIFICATION 1. PROMOTERS STRONG EVIDENCE 1.1 Transcription initiation mapping Example: Primer extension, S1 mapping 1.2 RNA polymerase footprinting 1.3 Inferred from mutant phenotype Example: Deletions of promoter regions WEAK EVIDENCE 1.4 Automated inference of promoter position Example: computational prediction 1.5 Human inference of promoter position Example: possible promoter identified by expert by reading the sequence 1.6 Inferred by curator 1.7 Non-traceable author statement Example: an article refers to a promoter citing a paper that cannot be traced 1.8 Traceable author statement Example: an article refers to a promoter citing a traceable paper for which the curation team has no access 1.9 Traceable author statement to experimental support Example: an article refers to a promoter citing a paper that we have access to 2. REGULATORY_INTERACTIONS STRONG EVIDENCE 2.1 Binding of cellular extracts Example: Gel shift analysis 2.2 Binding of purified proteins Example: Footprinting 2.3 Inferred from genetic interaction Example: in vitro titration assay 2.4 Assay of purified protein Example: in vitro transcription 2.5 Site mutation Example: expression analysis when putative regulator binding sites are mutated WEAK EVIDENCE 2.6 Gene expression analysis Example: transcriptional fusions (lacZ) 2.7 Inferred from mutant phenotype Example: a mutation on a transcription factors has a visible cell phenotype, and it is inferred that the regulator might be regulating the genes responsible for the phenotype 2.8 Automated inference based on similarity to consensus sequences Example: computational method (ie PATSER) used to identify binding site 2.9 Human inference based on similarity to consensus sequences Example: putative binding site identified by an expert by reading the sequence 2.10 Non-traceable author statement 2.11 Traceable author statement 2.12 Traceable author statement to experimental support 3. TRANSCRIPTION UNITS STRONG EVIDENCE 3.1 Length of transcript experimentally determined Example: Northern blot 3.2 Polar mutation Example: a mutation on the promoter or the first gene affects the expression of neighbouring genes 3.3 Boundaries of transcription experimentally identified Example: when promoter and terminator are identified 3.4 Automated inference that a single-gene directon is a transcription unit Example: a gene surrounded by genes in opposite transcription directions WEAK EVIDENCE 3.5 Inferred through co-regulation Example: 2+ adjacent genes show the same expression pattern across conditions 3.6 Inferred by a human based on computational evidence 3.7 Products of adjacent genes in the same biological process 3.8 Inferred computationally without human oversight Example: computational results with no expert review 3.9 Inferred by curator 3.10 Non-traceable author statement 3.11 Traceable author statement 3.12 Traceable author statement to experimental support TAXONOMY UNIQUE-ID - |EV-IC| UNIQUE-ID - |EV-IC-ADJ-GENES-SAME-BIO-PROCESS UNIQUE-ID - |EV-EXP| UNIQUE-ID - |EV-EXP-IMP| UNIQUE-ID - |EV-EXP-IMP-SITE-MUTATION| UNIQUE-ID - |EV-EXP-IMP-REACTION-BLOCKED| UNIQUE-ID - |EV-EXP-IMP-POLAR-MUTATION| UNIQUE-ID - |EV-EXP-IMP-REACTION-ENHANCED| UNIQUE-ID - |EV-EXP-IGI| UNIQUE-ID - |EV-EXP-IGI-FUNC-COMPLEMENTATION| UNIQUE-ID - |EV-EXP-IEP| UNIQUE-ID - |EV-EXP-IEP-COREGULATION| UNIQUE-ID - |EV-EXP-IEP-GENE-EXPRESSION-ANALYSIS| UNIQUE-ID - |EV-EXP-IDA| UNIQUE-ID - |EV-EXP-IDA-BINDING-OF-CELLULAR-EXTRACTS| UNIQUE-ID - |EV-EXP-IDA-BINDING-OF-PURIFIED-PROTEINS| UNIQUE-ID - |EV-EXP-IDA-PART-PURIFIED-PROTEIN| UNIQUE-ID - |EV-EXP-IDA-PURIFIED-PROTEIN| UNIQUE-ID - |EV-EXP-IDA-PURIFIED-PROTEIN-MULTSPECIES| UNIQUE-ID - |EV-EXP-IDA-TRANSCRIPT-LEN-DETERMINATION| UNIQUE-ID - |EV-EXP-IDA-TRANSCRIPTION-INIT-MAPPING| UNIQUE-ID - |EV-EXP-IDA-UNPURIFIED-PROTEIN| UNIQUE-ID - |EV-EXP-IDA-BOUNDARIES-DEFINED| UNIQUE-ID - |EV-EXP-IDA-RNA-POLYMERASE-FOOTPRINTING| UNIQUE-ID - |EV-EXP-TAS| UNIQUE-ID - |EV-EXP-IPI| UNIQUE-ID - |EV-COMP| UNIQUE-ID - |EV-COMP-AINF| UNIQUE-ID - |EV-COMP-AINF-FN-FROM-SEQ| UNIQUE-ID - |EV-COMP-AINF-SIMILAR-TO-CONSENSUS| UNIQUE-ID - |EV-COMP-AINF-SINGLE-DIRECTON| UNIQUE-ID - |EV-COMP-AINF-POSITIONAL-IDENTIFICATION| UNIQUE-ID - |EV-COMP-HINF| UNIQUE-ID - |EV-COMP-HINF-FN-FROM-SEQ| UNIQUE-ID - |EV-COMP-HINF-POSITIONAL-IDENTIFICATION| UNIQUE-ID - |EV-COMP-HINF-SIMILAR-TO-CONSENSUS| UNIQUE-ID - |EV-AS| UNIQUE-ID - |EV-AS-TAS| UNIQUE-ID - |EV-AS-NAS| DESCRIPCION // UNIQUE-ID - |EV-IC| COMMON-NAME - Inferred by curator COMMENT - Inferred by curator. An assertion was inferred by a curator from relevant information such as other assertions in a database. COMMENT-INTERNAL // UNIQUE-ID - |EV-EXP| COMMON-NAME - Inferred from experiment COMMENT - Inferred from experiment. The evidence for an assertion comes from a wet-lab experiment of some type. COMMENT-INTERNAL // UNIQUE-ID - |EV-EXP-IMP-SITE-MUTATION| COMMON-NAME - Site mutation PERTAINS-TO - |DNA-Binding-Sites| COMMENT - A cis-mutation in the DNA sequence of the transcription-factor binding site interferes with the operation of the regulatory function. This is considered strong evidence for the existence and functional role of the DNA binding site. COMMENT-INTERNAL // UNIQUE-ID - |EV-EXP-IMP-REACTION-BLOCKED| COMMON-NAME - Reaction blocked in mutant PERTAINS-TO - |Enzymatic-Reactions| COMMENT - Mutant is characterized, and blocking of reaction is demonstrated. COMMENT-INTERNAL // UNIQUE-ID - |EV-EXP-IMP-POLAR-MUTATION| COMMON-NAME - Polar mutation PERTAINS-TO - |Transcription-Units| COMMENT - If a mutation in a gene or promoter prevents expression of the downstream genes due to a polar effect, the mutated gene is clearly part of the transcription unit. COMMENT-INTERNAL It is used for TUs with two or more genes. It may be wrong to assign a TU on such evidence if the first gene is a regulator which regulates a promoter upstream of the second gene. // UNIQUE-ID - |EV-EXP-IMP-REACTION-ENHANCED| COMMON-NAME - Reaction enhanced in mutant PERTAINS-TO - |Enzymatic-Reactions| COMMENT - Gene is isolated and over-expressed, and increased accumulation of reaction product is observed. COMMENT-INTERNAL // UNIQUE-ID - |EV-EXP-IGI-FUNC-COMPLEMENTATION| COMMON-NAME - Inferred by functional complementation PERTAINS-TO - |Proteins| PERTAINS-TO - |Enzymatic-Reactions| COMMENT - Protein activity inferred by isolating its gene and performing functional complementation of a well characterized heterologous mutant for the protein. COMMENT-INTERNAL // UNIQUE-ID - |EV-EXP-IEP-COREGULATION| COMMON-NAME - Inferred through co-regulation PERTAINS-TO - |Transcription-Units| COMMENT - Inferred through co-regulation. A transcription unit is inferred because a set of adjacent genes that are transcribed in the same direction exhibit similar expression patterns under a range of environmental conditions. COMMENT-INTERNAL – Comentario adicional: A TU is defined assuming there is ony one promoter upsream of all genes of the TU. However, although unlikely, there may be a promoter for each gene and all of them co-regulated and active and inactive under the same conditions. // UNIQUE-ID - |EV-EXP-IEP-GENE-EXPRESSION-ANALYSIS| COMMON-NAME - Gene expression analysis PERTAINS-TO - |DNA-Binding-Sites| COMMENT - The expression of the gene is analyzed through a transcriptional fusion (i.e. lacZ), and a difference in expression levels is observed when the regulatory protein is present (wild type) vs in its absence. Note that this evidence does not eliminate the possiblity of an indirect effect of the regulator on the regulated gene. COMMENT-INTERNAL // UNIQUE-ID - |EV-EXP-IDA-BINDING-OF-CELLULAR-EXTRACTS| COMMON-NAME - Binding of cellular extracts PERTAINS-TO - |DNA-Binding-Sites| COMMENT - There exists physical evidence of the binding of cellular extracts containing a regulatory protein to its DNA binding site. This can be either by footprinting or mobility shift assays. COMMENT-INTERNAL // UNIQUE-ID - |EV-EXP-IDA-BINDING-OF-PURIFIED-PROTEINS| COMMON-NAME - Binding of purified proteins PERTAINS-TO - |DNA-Binding-Sites| COMMENT COMMENT-INTERNAL // UNIQUE-ID - |EV-EXP-IDA-PART-PURIFIED-PROTEIN| COMMON-NAME - Assay of partially purified protein PERTAINS-TO - |Proteins| PERTAINS-TO - |Enzymatic-Reactions| COMMENT - Protein partially purified from specific species (or from heterologous expression vector), and activity measured through in vitro assay. COMMENT-INTERNAL // UNIQUE-ID - |EV-EXP-IDA-PURIFIED-PROTEIN| COMMON-NAME - Assay of purified protein PERTAINS-TO - |Proteins| PERTAINS-TO - |Enzymatic-Reactions| COMMENT - Protein purified to homogeneity from specific species (or from heterologous expression vector), and activity measured through in vitro assay. COMMENT-INTERNAL // UNIQUE-ID - |EV-EXP-IDA-PURIFIED-PROTEIN-MULTSPECIES| COMMON-NAME - Assay of protein purified from mixed culture PERTAINS-TO - |Proteins| PERTAINS-TO - |Enzymatic-Reactions| COMMENT - Protein purified from mixed culture or other multispecies environment (such as, infected plant or animal tissue), and activity measured through in vitro assay. COMMENT-INTERNAL // UNIQUE-ID - |EV-EXP-IDA-TRANSCRIPT-LEN-DETERMINATION| COMMON-NAME - Length of transcript experimentally determined PERTAINS-TO - |Transcription-Units| COMMENT - The length of the (transcribed) RNA is experimentally determined. The length of the mRNA is compared with that of the DNA sequence and by this means the number of genes transcribed are established. COMMENT-INTERNAL Comentario adicional: This is strong evidence, very hard to refute. // UNIQUE-ID - |EV-EXP-IDA-TRANSCRIPTION-INIT-MAPPING| COMMON-NAME - Transcription initiation mapping PERTAINS-TO - |Promoters| COMMENT - The transcription start site is identified by primer extension. COMMENT-INTERNAL // UNIQUE-ID - |EV-EXP-IDA-UNPURIFIED-PROTEIN| COMMON-NAME - Assay of unpurified protein PERTAINS-TO - |Proteins| PERTAINS-TO - |Enzymatic-Reactions| COMMENT - Direct assay of unpurified protein. Presence of a protein activity is indicated by an assay. However, the precise identity of the protein with that activity is not established by this experiment (protein has not been purified). COMMENT-INTERNAL // UNIQUE-ID - |EV-EXP-IDA-BOUNDARIES-DEFINED| COMMON-NAME - Boundaries of transcription experimentally identified PERTAINS-TO - |Transcription-Units| COMMENT - Sites or genes bounding the transcription unit are experimentally identified. Several possible cases exist, such as defining the boundaries of a transcription unit with an experimentally identified promoter and terminator, or with a promoter and a downstream gene that is transcribed in the opposite direction, or with a terminator and an upstream gene that is transcribed in the opposite direction. COMMENT-INTERNAL Comentario adicional: There could be a terminator or promoter not yet identified within the TU. // UNIQUE-ID - |EV-EXP-IDA-RNA-POLYMERASE-FOOTPRINTING| COMMON-NAME - RNA polymerase footprinting PERTAINS-TO - |Promoters| COMMENT - The binding of RNA polymerase to a DNA region (the promoter) is shown by footprinting. COMMENT-INTERNAL // UNIQUE-ID - |EV-EXP-IMP| COMMON-NAME - Inferred from mutant phenotype COMMENT - IMP inferred from mutant phenotype. The assertion was inferred from a mutant phenotype such as o Any gene mutation/knockout o Overexpression/ectopic expression of wild-type or mutant genes o Anti-sense experiments o RNA interference experiments o Specific protein inhibitors o Complementation Comment: Inferences made from examining mutations or abnormal levels of only the product(s) of the gene of interest are covered by code EV-IMP (compare to code EV-IGI). Use this code for experiments that use antibodies or other specific inhibitors of RNA or protein activity, even though no gene may be mutated (the rationale is that EV-IMP is used where an abnormal situation prevails in a cell or organism). COMMENT-INTERNAL // UNIQUE-ID - |EV-EXP-IGI| COMMON-NAME - Inferred from genetic interaction COMMENT - IGI inferred from genetic interaction. The assertion was inferred from a genetic interaction such as o \,Traditional\, genetic interactions such as suppressors, synthetic lethals, etc. o Functional complementation o Inference about one gene drawn from the phenotype of a mutation in a different gene This category includes any combination of alterations in the sequence (mutation) or expression of more than one gene/gene product. This category can therefore cover any of the IMP experiments that are done in a non-wild-type background, although we prefer to use it only when all mutations are documented. When redundant copies of a gene must all be mutated to see an informative phenotype, use the IGI code. (Yes, this implies some organisms, such as mouse, will have far, far more IGI than IMP annotations.) IMP also covers phenotypic similarity: a phenotype that is informative because it is similar to that of another independent phenotype (which may have been described earlier or documented more fully) is IMP (not IGI). We have also decided to use this category for situations where a mutation in one gene (gene A) provides information about the function, process, or component of another gene (gene B; i.e. annotate gene B using IGI). COMMENT-INTERNAL // UNIQUE-ID - |EV-EXP-TAS| COMMON-NAME - Traceable author statement to experimental support COMMENT - Traceable author statement to experimental support. The assertion was made in a publication -- such as a review or in another database -- that itself did not describe an experiment supporting the assertion. However, the statement did reference another publication describing an experiment that supports the assertion. The difference between the codes EV-EXP-TAS and EV-AS-TAS is that the former code is used when it is certain that experimental evidence supports the assertion, and the latter code is used when there is a possibility that an experiment was not done to support the assertion. In general, references to the primary literature are preferred, but this code can be used when the original article is difficult to locate. COMMENT-INTERNAL // UNIQUE-ID - |EV-EXP-IPI| COMMON-NAME - Inferred from physical interaction COMMENT - IPI inferred from physical interaction The assertion was inferred from a physical interaction such as o 2-hybrid interactions o Co-purification o Co-immunoprecipitation o Ion/protein binding experiments This code covers physical interactions between the gene product of interest and another molecule (or ion, or complex). For functions such as protein binding or nucleic acid binding, a binding assay is simultaneously IPI and IDA; IDA is preferred because the assay directly detects the binding. For both IPI and IGI, it would be good practice to qualify them with the gene/protein/ion. COMMENT-INTERNAL // UNIQUE-ID - |EV-EXP-IEP| COMMON-NAME - Inferred from expression pattern COMMENT - IEP inferred from expression pattern. The assertion was inferred from a pattern of expression data such as o Transcript levels (e.g. Northerns, microarray data) o Protein levels (e.g. Western blots) COMMENT-INTERNAL // UNIQUE-ID - |EV-EXP-IDA| COMMON-NAME - Inferred from direct assay COMMENT - IDA inferred from direct assay. The assertion was inferred from a direct experimental assay such as o Enzyme assays o In vitro reconstitution (e.g. transcription) o Immunofluorescence o Cell fractionation COMMENT-INTERNAL // UNIQUE-ID - |EV-COMP| COMMON-NAME - Inferred by computational analysis COMMENT - Inferred from computation. The evidence for an assertion comes from a computational analysis. The assertion itself might have been made by a person or by a computer, that is, EV-COMP does not specify whether manual interpretation of the computation occurred. COMMENT-INTERNAL // UNIQUE-ID - |EV-COMP-AINF-FN-FROM-SEQ| COMMON-NAME - Automated inference of function from sequence PERTAINS-TO - RNA PERTAINS-TO - |Proteins| PERTAINS-TO - |Enzymatic-Reactions| COMMENT - Artificial inference of function from sequence. A computer inferred a gene function based on sequence, profile, or structural similarity (as computed from sequence) to one or more other sequences. COMMENT-INTERNAL // UNIQUE-ID - |EV-COMP-AINF-SIMILAR-TO-CONSENSUS| COMMON-NAME - Automated inference based on similarity to consensus sequences PERTAINS-TO - |DNA-Binding-Sites| COMMENT - A DNA sequence similar to previously known consensus sequences is computationally identified. COMMENT-INTERNAL // UNIQUE-ID - |EV-COMP-AINF-SINGLE-DIRECTON| COMMON-NAME - Automated inference that a single-gene directon is a transcription unit PERTAINS-TO - |Transcription-Units| COMMENT - Artificial inference of transcription unit based on single-gene directon. Existence of a single-gene transcription unit for gene G is inferred computationally by the existence of upstream and downstream genes transcribed in the opposite direction of G. COMMENT-INTERNAL // UNIQUE-ID - |EV-COMP-AINF-POSITIONAL-IDENTIFICATION| COMMON-NAME - Automated inference of promoter position PERTAINS-TO - |Promoters| COMMENT - Automated inference of promoter position relative to the -10 and -35 boxes. COMMENT-INTERNAL // UNIQUE-ID - |EV-COMP-HINF-FN-FROM-SEQ| COMMON-NAME - Human inference of function from sequence PERTAINS-TO - RNA PERTAINS-TO - |Proteins| PERTAINS-TO - |Enzymatic-Reactions| COMMENT - A person inferred, or reviewed a computer inference of, gene function based on sequence, profile, or structural similarity (as computed from sequence) to one or more other sequences. COMMENT-INTERNAL // UNIQUE-ID - |EV-COMP-HINF-POSITIONAL-IDENTIFICATION| COMMON-NAME - Human inference of promoter position PERTAINS-TO - |Promoters| COMMENT - A person inferred, or reviewed a computer inference of, promoter position relative to the -10 and -35 boxes. COMMENT-INTERNAL // UNIQUE-ID - |EV-COMP-HINF-SIMILAR-TO-CONSENSUS| COMMON-NAME - Human inference based on similarity to consensus sequences PERTAINS-TO - |DNA-Binding-Sites| COMMENT - A person inferred, or reviewed a computer inference of, sequence function based on similarity to a consensus sequence. COMMENT-INTERNAL // UNIQUE-ID - |EV-COMP-AINF| COMMON-NAME - Inferred computationally without human oversight COMMENT - Artificial inference. A computer inferred this assertion through one of many possible methods such as sequence similarity, recognized motifs or consensus sequence, etc. When a person made the inference from computational evidence, use EV-HINF COMMENT-INTERNAL // UNIQUE-ID - |EV-COMP-HINF| COMMON-NAME - Inferred by a human based on computational evidence COMMENT - Human inference. A curator or author inferred this assertion after review of one or more possible types of computational evidence such as sequence similarity, recognized motifs or consensus sequence, etc. When the inference was made by a computer in an automated fashion, use EV-AINF. COMMENT-INTERNAL // UNIQUE-ID - |EV-AS| COMMON-NAME - Author statement COMMENT - Author statement. The evidence for an assertion comes from an author statement in a publication, where that publication does not state direct experimental support for the assertion. Ordinarily, this code will not be used directly -- generally one of its child codes, EV-TAS or EV-NAS, will be used instead. COMMENT-INTERNAL // UNIQUE-ID - |EV-AS-TAS| COMMON-NAME - Traceable author statement COMMENT - Traceable author statement. The assertion was made in a publication -- such as a review or in another database -- that itself did not describe an experiment supporting the assertion. The statement referenced another publication that supported the assertion, but it is unclear whether that publication described an experiment that supported the assertion. The difference between the codes EV-EXP-TAS and EV-AS-TAS is that the former code is used when it is certain that experimental evidence supports the assertion, and the latter code is used when there is a possibility that an experiment was not done to support the assertion. In general, references to the primary literature are preferred, but this code can be used when the original article is difficult to locate. COMMENT-INTERNAL // UNIQUE-ID - |EV-AS-NAS| COMMON-NAME - Non-traceable author statement COMMENT - Non-traceable author statement. The assertion was made in a publication such as a review, a meeting abstract, or another database without a reference to a publication describing an experiment that supports the assertion. COMMENT-INTERNAL //