Block A: Counting, partitioning and calculating Unit 1 – 10 days
advertisement

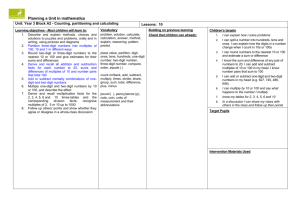
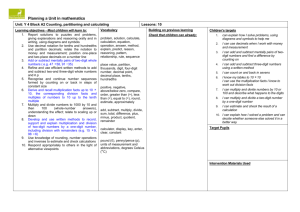
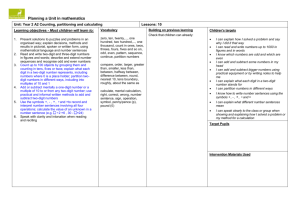
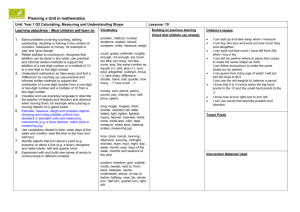
1 of 8 The National Strategies Primary Years 2 to 4 mixed-age objective planner Key - Italic text signifies objectives which do not appear in the single-age version of this unit but have been added to create a coherent mixed-age unit - Smaller font indicates objectives which do appear in the single-age version of this unit, but which are addressed elsewhere within the mixed-age units - Bold font indicates ‘End-of-year’ objectives. I can… statements: red are MA1 Using and Applying, green are MA2, MA3 or MA4 Block A: Counting, partitioning and calculating Unit 1 – 10 days Year 2 Year 3 Year 4 Present solutions to puzzles and problems in an organised way; explain decisions, methods and results in pictorial, spoken or written form, using mathematical language and number sentences I can explain to others how I solved a problem Describe and explain methods, choices and solutions to puzzles and problems, orally and in writing, using pictures and diagrams I can explain how I solve problems Report solutions to puzzles and problems, giving explanations and reasoning orally and in writing, using diagrams and symbols I can explain to someone else how I solve problems and puzzles Count up to 100 objects by grouping them and counting in tens, fives or twos; explain what each digit in a two-digit number represents, including numbers where 0 is a place holder; partition twodigit numbers in different ways, including into multiples of 10 and 1 Partition three-digit numbers into multiples of 100, 10 and 1 in different ways I can split a number into hundreds, tens and ones I can explain how the digits in a number change when I count in 10s or 100s Partition, round and order four-digit whole numbers; use positive and negative numbers in context and position them on a number line; state inequalities using the symbols < and > (e.g. -3 > -5, -1 < 1) I can read, write and put in order four-digit numbers and positive and negative numbers 00317-2008DWO-EN © Crown copyright 2008 2 of 8 The National Strategies Primary Years 2 to 4 mixed-age objective planner I can count objects by putting them into groups I can partition numbers Order two-digit numbers and position them on a number line; use the greater than > and less than < signs I can write numbers in order and position them on a number line I can use the greater than and less than symbols to show that one number is larger or smaller than another Read and write two-digit and three-digit numbers in figures and words; describe and extend number sequences and recognise odd and even numbers I can read and write two-digit numbers (A1) I know which numbers are odd and which are even (A1/A2) I can use the < and > signs with positive and negative numbers (e.g. -3 < 1) Read, write and order whole numbers to at least 1000 and position them on a number line; count on from and back to zero in single-digit steps or multiples of 10 I can read and write numbers to 1000 and put them in order Recognise and continue number sequences formed by counting on or back in steps of constant size I can count on and back in eights Estimate a number of objects; round two-digit numbers to the nearest 10 (to A3) 00317-2008DWO-EN © Crown copyright 2008 3 of 8 The National Strategies Primary Years 2 to 4 mixed-age objective planner Derive and recall all addition and subtraction facts for each number to at least 10, all pairs with totals to 20 and all pairs of multiples of 10 with totals up to 100 I can recall number facts for each number up to 10 Understand that halving is the inverse of doubling and derive and recall doubles of all numbers to 20, and the corresponding halves I know doubles of numbers to 10 Derive and recall all addition and subtraction facts for each number to 20, sums and differences of multiples of 10 and number pairs that total 100 I know the sum and difference of any pair of numbers to 20 I can add and subtract multiples of 10 or 100 in my head Derive and recall multiplication facts for the 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 and 10 times-tables and the corresponding division facts; recognise multiples of 2, 5 or 10 up to 1000 I know my 3, 4 and 6 times tables Use knowledge of addition and subtraction facts and place value to derive sums and differences of pairs of multiples of 10, 100 or 1000 I can work out sums and differences of multiples of 100 or 1000 Derive and recall multiplication facts up to 10 × 10, the corresponding division facts and multiples of numbers to 10 up to the tenth multiple I know my 8 times table and my 9 times table Identify the doubles of two-digit numbers; use these to calculate doubles of multiples of 10 and 100 and derive the corresponding halves I can double two-digit numbers Use knowledge of rounding, number operations and inverses to estimate and check calculations (to B1) 00317-2008DWO-EN © Crown copyright 2008 4 of 8 The National Strategies Primary Years 2 to 4 mixed-age objective planner Understand that subtraction is the inverse of addition and vice versa; use this to derive and record related addition and subtraction number sentences I know that addition and subtraction ‘undo’ each other I can write three other related number sentences for 6 + 3 = 9 Add or subtract mentally a one-digit number or a multiple of 10 to or from any two-digit number; use practical and informal written methods to add and subtract two-digit numbers I can add and subtract some numbers in my head 00317-2008DWO-EN Add or subtract mentally combinations of one-digit and two-digit numbers I can add and subtract one-digit and twodigit numbers in my head (e.g. 62 + 7, 7 + 45, 4 8 - 6, 60 - 8) Add or subtract mentally pairs of twodigit whole numbers (e.g. 47 + 58, 91 35) I can add and subtract two-digit numbers in my head (e.g. 26 + 47, 43 – 16) Multiply one-digit and two-digit numbers by 10 or 100, and describe the effect I can multiply a number by 10 or 100 and say what happens to the number I multiply (from E2) Multiply and divide numbers to 1000 by 10 and then 100 (whole-number answers), understanding the effect; relate to scaling up or down I can multiply and divide by 10 and 100. I can explain what happens to the digits when I do this Use a calculator to carry out one-step and two-step calculations involving all four operations; recognise negative numbers in the display, correct mistaken entries and interpret the display correctly in the context of money I can use a calculator to help me solve onestep and two-step problems I know how to enter prices such as £1.29 and £2.30 into a calculator I know that -7 on a calculator means negative 7 © Crown copyright 2008 5 of 8 The National Strategies Primary Years 2 to 4 mixed-age objective planner Block A: Counting, partitioning and calculating Unit 2 – 10 days Year 2 Year 3 Year 4 Present solutions to puzzles and problems in an organised way; explain decisions, methods and results in pictorial, spoken or written form, using mathematical language and number sentences I can explain how I solved a problem and say why I did it that way Describe and explain methods, choices and solutions to puzzles and problems, orally and in writing, using pictures and diagrams I can explain how I solve problems Report solutions to puzzles and problems, giving explanations and reasoning orally and in writing, using diagrams and symbols I can explain how I solve problems, using diagrams and symbols to help me Read and write two-digit and three-digit numbers in figures and words; describe and extend number sequences and recognise odd and even numbers I can read and write numbers up to 1000 in figures and words (A2) I can describe and explain the patterns in a set of calculations (from B2) I can explain the pattern for the sequence of numbers and work out the next few numbers in the list (from A3) Partition three-digit numbers into multiples of 100, 10 and 1 in different ways I can split a number into hundreds, tens and ones I can explain how the digits in a number change when I count in 10s or 100s Recognise and continue number sequences formed by counting on or back in steps of constant size I can count on and back in sevens Count up to 100 objects by grouping them and counting in tens, fives or twos; 00317-2008DWO-EN Read, write and order whole numbers to at least 1000 and position them on a number line; count on and back to zero in singledigit steps or multiples of 10 I can count on from and back to zero in steps of 1,2,3,4,5,6, 10 and 100 Use decimal notation for tenths and hundredths and partition decimals; relate the notation to money and measurement; position one-place and two-place decimals on a number line I can use decimals when I work with money and measurements © Crown copyright 2008 6 of 8 The National Strategies Primary Years 2 to 4 mixed-age objective planner explain what each digit in a two-digit number represents, including numbers where 0 is a place holder; partition twodigit numbers in different ways, including into multiples of 10 and 1 I can explain what each digit in a two-digit number stands for I can partition numbers in different ways Derive and recall multiplication facts for the 2, 5 and 10 times-tables and the related division facts; recognise multiples of 2, 5 and 10 I know some of the number facts in the 2, 5 and 10 times tables Round two-digit or three-digit numbers to the nearest 10 or 100 and give estimates for their sums and differences (moved to A3) Derive and recall multiplication facts for the 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 and 10 times-tables and the corresponding division facts; recognise multiples of 2, 5 or 10 up to 1000 I know my tables for 2, 3, 4, 5 ,6 and 10 Derive and recall multiplication facts up to 10 × 10, the corresponding division facts and multiples of numbers to 10 up to the tenth multiple I know my tables to 10 x 10 I can use the multiplication facts I know to Derive and recall all addition and subtraction facts for work out division facts each number to 20, sums and differences of multiples of 10 and number pairs that total 100 (combined with B2) Add or subtract mentally a one-digit number or a multiple of 10 to or from any two-digit number; use practical and informal written methods to add and subtract two-digit numbers I can add and subtract some numbers in my head 00317-2008DWO-EN Add or subtract mentally combinations of one-digit and two-digit numbers I can add or subtract one-digit and two-digit numbers in my head (e.g. 62 + 7, 7 + 45, 4 8 - 6, 60 - 8) Use knowledge of rounding, number operations and inverses to estimate and check calculations. I can estimate and check the results of a calculation Add or subtract mentally pairs of twodigit whole numbers (e.g. 47 + 58, 91 35) I can add and subtract mentally pairs of twodigit numbers and find a difference by counting on © Crown copyright 2008 7 of 8 The National Strategies Primary Years 2 to 4 mixed-age objective planner I can add and subtract bigger numbers using practical equipment or by writing notes to help me Use the symbols +, -, ×, ÷ and = to record and interpret number sentences involving all four operations; calculate the value of an unknown in a number sentence (e.g. □ ÷ 2 = 6, 30 - □ = 24) I know how to write number sentences using the symbols +, -, x, ÷ and = I can explain what different number sentences mean Represent repeated addition and arrays as multiplication, and sharing and repeated subtraction (grouping) as division; use practical and informal written methods and related vocabulary to support multiplication and division, including calculations with remainders I can use practical equipment or a number line to do multiplication and division and can explain remainders if there are any 00317-2008DWO-EN Develop and use written methods to record, support or explain addition and subtraction of two-digit and three-digit numbers I can record how I work out an addition or subtraction calculation showing each step Multiply one-digit and two-digit numbers by 10 or 100, and describe the effect I can multiply by 10 or 100 and say what happens to the number I multiply Use practical and informal written methods to multiply and divide two-digit numbers (e.g. 13 × 3, 50 ÷ 4); round remainders up or down, depending on the context I can multiply a ‘teens number by a one-digit number I can divide a two-digit number by a onedigit number Refine and use efficient written methods to add and subtract two-digit and three-digit whole numbers and £.p I can add and subtract three digit numbers using a written method Multiply and divide numbers to 1000 by 10 and then 100 (whole-number answers), understanding the effect; relate to scaling up or down I can multiply and divide numbers by 10 or 100 and describe what happens to the digits Develop and use written methods to record, support and explain multiplication and division of two-digit numbers by a one-digit number, including division with remainders (e.g. 15 × 9, 98 ÷ 6) I can multiply and divide a two-digit number by a one-digit number © Crown copyright 2008 8 of 8 The National Strategies Primary Years 2 to 4 mixed-age objective planner Block A: Counting, partitioning and calculating Unit 3 – 10 days Year 2 Year 3 Year 4 Solve problems involving addition, subtraction, multiplication or division in contexts of numbers, measures or pounds and pence I can use calculations to solve problems and I know which calculations to use (from E2) Solve one-step and two-step problems involving numbers, money or measures, including time, choosing and carrying out appropriate calculations I can explain how I solve problems (B2) I can recognise when a word problem involves multiplication or division (E2) I can solve a problem by writing down what calculation I should do (A3) Solve one-step and two-step problems involving numbers, money or measures, including time; choose and carry out appropriate calculations, using calculator methods where appropriate I can work out how to solve problems with one or two steps I can choose what calculation to work out and I can decide whether a calculator will help me Round two-digit or three-digit numbers to the nearest 10 or 100 and give estimates for their sums and differences I can round numbers to the nearest 10 or 100 and estimate a sum or difference (from A2, A3 moved to B3) Partition, round and order four-digit whole numbers; use positive and negative numbers in context and position them on a number line; state inequalities using the symbols < and > (e.g. -3 > -5, -1 < 1) I can read, write and put in order four-digit numbers and positive and negative numbers I can use the < and > signs with positive and negative numbers (e.g. -3 < 1) Present solutions to puzzles and problems in an organised way; explain decisions, methods and results in pictorial, spoken or written form, using mathematical language and number sentences (moved to B3) Estimate a number of objects; round twodigit numbers to the nearest 10 I can round numbers to the nearest 10 (from A1, A3 moved to B3) Order two-digit numbers and position them on a number line; use the greater than and less than signs I can write numbers in order and position them on a number line I can use the greater than and less than 00317-2008DWO-EN Partition three-digit numbers into multiples of 100, 10 and 1 in different ways I can partition numbers in different ways © Crown copyright 2008 9 of 8 The National Strategies Primary Years 2 to 4 mixed-age objective planner symbols to show that one number is larger or smaller than another (from E3) Count up to 100 objects by grouping them and counting in tens, fives or twos; explain what each digit in a twodigit number represents, including numbers where 0 is a place holder; partition two-digit numbers in different ways, including into multiples of 10 and 1 I can use partitioning to help me to carry out calculations Use decimal notation for tenths and hundredths and partition decimals; relate the notation to money and measurement; position one-place and two-place decimals on a number line I know how to use decimal notation to write numbers such as one and one tenth, two and three tenths, three hundredths Recognise and continue number sequences formed by counting on or back in steps of constant size I can count on and back using negative numbers Read and write two-digit and three-digit numbers in figures and words; describe and extend number sequences and recognise odd and even numbers (to A2) Derive and recall multiplication facts for the 2, 5 and 10 times-tables and the related division facts; recognise multiples of 2, 5 and 10 I know my 2, 5 and 10 times tables Derive and recall multiplication facts for the 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 and 10 times-tables and the corresponding division facts; recognise multiples of 2, 5 or 10 up to 1000 I can use my tables for 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 and 10 to work out division facts Use knowledge of number facts and operations to estimate and check answers to calculations I can estimate calculations I can check calculations by doing the Use knowledge of number operations and corresponding inverses, including doubling and halving, to estimate and check calculations I can check whether the answer to a 00317-2008DWO-EN Derive and recall multiplication facts up to 10 × 10, the corresponding division facts and multiples of numbers to 10 up to the tenth multiple I know my tables to 10 x 10 I can use the multiplication facts I know to work out division facts Use knowledge of rounding, number operations and inverses to estimate and check calculations I can estimate and check the results of a © Crown copyright 2008 10 of 8 The National Strategies Primary Years 2 to 4 mixed-age objective planner related addition or subtraction calculation is correct (from D3) calculation Add or subtract mentally a one-digit number or a multiple of 10 to or from any two-digit number; use practical and informal written methods to add and subtract two-digit numbers I can add and subtract two-digit numbers using practical equipment or written notes to help me Add or subtract mentally combinations of one-digit and two-digit numbers I can find the sum of or difference between one-digit and two-digit numbers in my head (e.g. 7 + 45, 45 – 7) I can add several one-digit numbers in my head Add or subtract mentally pairs of twodigit whole numbers (e.g. 47 + 58, 91 - 35) I can add and subtract mentally any two-digit numbers you give me, such as 56 + 22, 58 + 39, 64 – 37, 98 – 89 Develop and use written methods to record, support or explain addition and subtraction of two-digit and three-digit numbers I can add and subtract numbers using an empty number line I can add and subtract numbers by writing one number under the other and using partitioning Refine and use efficient written methods to add and subtract two-digit and three-digit whole numbers and £.p I can add and subtract two-digit and threedigit numbers using a written method Use practical and informal written methods to multiply and divide two-digit numbers (e.g. 13 × 3, 50 ÷ 4); round remainders up or down, depending on the context I can use tables facts that I know to work out division facts I can multiply or divide a two-digit number by a one-digit number If there is a remainder when I divide, I can work out whether to round the answer up or down Develop and use written methods to record, support and explain multiplication and division of two-digit numbers by a one-digit number, including division with remainders (e.g. 15 × 9, 98 ÷ 6) I can multiply and divide a two-digit number by a one-digit number. I know how to interpret a remainder. Understand that subtraction is the inverse of addition and vice versa; use this to derive and record related addition and subtraction number sentences I know when it is easier to use addition to work out a subtraction Use the symbols +, -, ×, ÷ and = to record and interpret number sentences involving all four operations; calculate the value of an unknown in a number sentence (e.g. □ ÷ 2 = 6, 30 - □ = 24) I can work out the missing number in a number sentence such as 14 + □ = 35 Represent repeated addition and arrays as multiplication, and sharing and repeated subtraction (grouping) as division; use practical and informal written methods and 00317-2008DWO-EN © Crown copyright 2008 11 of 8 The National Strategies Primary Years 2 to 4 mixed-age objective planner related vocabulary to support multiplication and division, including calculations with remainders I can do multiplication and division in different ways and explain what I did 00317-2008DWO-EN Understand that division is the inverse of multiplication and vice versa; use this to derive and record related multiplication and division number sentences I can say what multiplication fact I would use for a division calculation (from D3) Use a calculator to carry out one-step and two-step calculations involving all four operations; recognise negative numbers in the display, correct mistaken entries and interpret the display correctly in the context of money I know that when I am working with money, 5.4 on a calculator display means £5.40 © Crown copyright 2008