immunity
advertisement

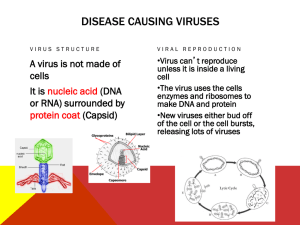
IMMUNE SYSTEM INFLAMMATORY REACTION: When you get stuck by a thorn or inhale a cold virus, the body goes through a series of events called an inflammatory reaction. Four outward signs: 1. Redness 2. Heat 3. Swelling 4. Pain Redness is caused from the blood vessels dilating to allow more blood flow to the area. Within the blood are platelets to clot the blood, proteins to repair the damage, and macrophages, which are white blood cells that eat up the foreign body, bacteria, or the dead cells. Heat is caused because of the extra amount of warm blood flow to the area. Swelling is caused from the plasma that leaks out of the swollen blood vessels. Pain is caused from the pressure of the extra fluid pressing on nerves in the area. CELL MEDIATED IMMUNITY: When the body is invaded by bacteria, other white blood cells produce a protein called an antibody, which is specific to those bacteria. The white blood secretes these antibodies which will continue to circulate sometimes for years, ready to attack that type of bacteria and cause them to pop like a balloon before the body can become sick. This is called ACTIVE IMMUNITY: the body is exposed to an infectious agent and produces these antibodies so the person never gets that disease again. For example, when an unvaccinated child is exposed to the measles at school and gets the disease, but never gets the disease again, it is active immunity. You can never get the same cold virus twice because you will have become immune to it. Your next cold is from a different virus. There are hundreds of thousands of cold viruses; that’s why there is no cure for the common cold. However, there are some diseases that you don’t want to get, even once, such as polio, diphtheria, tetanus, and influenza, because the first exposure could kill or disable you. For these diseases, we have vaccines which are made of those organisms which have been altered so that the body recognizes them as foreign, but they can’t cause disease. That way, if the person is exposed to the real organism, the antibodies are already there to kill it off without the body getting sick. This is IMMUNIZATION (or vaccination), which gives us PASSIVE IMMUNITY. An example is when a child is vaccinated against measles as a baby, so when he gets to school and is exposed to the disease, he doesn’t get sick. ALLERGIES are from a hypersensitivity to substances such as pollen or animal hair that would not ordinarily cause a reaction. There are two types of allergic responses: 1. Immediate allergic response occurs within seconds of contact with the thing causing the allergy. This is the case with anaphylactic allergies, where someone who is allergic to seafood or peanuts can actually die within minutes because the allergic reaction is so severe the throat swells shut and they can’t breath. They need an injection immediately of something that will stop the reaction. 2. Delayed allergic response is when the body’s first exposure to the substance will not cause a reaction, but all exposures afterward will trigger the response. An example is poison ivy. You won’t itch the first time you touch it. AUTOIMMUNE DISEASE is a hereditary problem where the body thinks its own tissues are foreign bodies, and it constantly tries to kill off its own tissues.