The USGA Putting Green Profile
advertisement

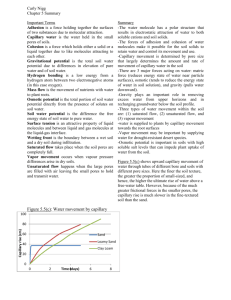
The USGA Putting Green Profile Profile consist of the surface, root zone, gravel layer, drain lines and the sub grade The USGA green when constructed properly creates a perched water table In the root zone water will not move readily from small pores of the root zone to larger pores of the gravel layer until the finer layer is saturated with water to some depth. Micro pores- pore that are filled with water not drained by gravity Macro pores- pores that hold air water is removed by gravity Saturated soil- all pore spaces are filled with water Gravitational water- water that is removed by the force of gravity Field capacity-when all micro pore spaces are filled with water and when the macro pores are drained by gravity and have filled with air Adhesion- when water molecules stick to an object stronger than the force of cohesion Cohesion when water molecules stick to them selves creates surface tension Infiltration (hydraulic conductivity)-the rate at which water move into the soil Peculation- the rate at which water moves through the soil Perched water table occurs when fine textured soil is placed over coarse textured soil Depth of perched water table is dictated by particle size of root zone and by the shape and size of the gravel laver (about 9 inches in a USGA spec green) The capillary fringe and how water gets into drains The lateral movement of water in soils is extremely slow- increase in slope adds to the height of the head, which increases pressure which forces the water down the slope Free water- soil that is saturated- soil must be saturated before water will move in it Capillary fringe- zone of quasi saturated soil above the free water zone- this water cannot move sideways in the soil- this water is a perched water table Capillary fringe water cannot move into drains- water in the zone is held in place by the force of adhesion and cohesion and are stronger than the force of gravity Air entry point- point above which the pull of gravity is strong enough to break the surface tension on the top of the menisci of the large pores, and water in these pores drains down the profile The turf is now at field capacity large pores drained small pores filled with water Capillary fringe height increases a soil particle size decreases Compacted soils have less large pore space this also increases the height of the capillary fringe The perched water table the concept and its use Perched water table occurs when a fine textured soil is placed over a coarse textured soil If the height of a capillary fringe exceeds the depth of the topsoil above the interface with the coarse material, the topsoil will never drain downward USGA sands must be tested a two levels light compaction and heavy compaction if they vary greatly then the sand must be refused The height of the perched water table can cause root zones to be droughty or too wet Gravel affects height of perched water table- the finer the gravel the less height (more contact with the sand above it)