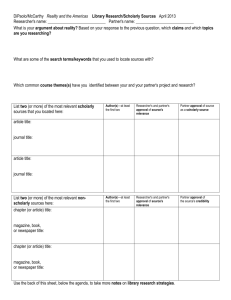
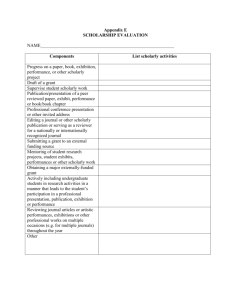
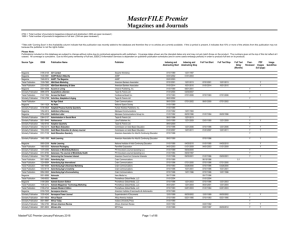
An abstract is a self-contained, short, and
advertisement

Vocabulary for Information Literacy A B CD E F G H I J K L M N OPQRST UV WXYZ A Abstract - An abstract is a self-contained, short, and powerful statement that describes a larger work. It is a summary. Almanac – An almanac is a publication, usually annually released, which contains information for a given year such as meteorological, astrological, statistical and general information. APA Citation Style – APA style refers to the writing style described in the Publication Manual of the American Psychological Association. This publication also covers many rules about how to organize, write, and publish a manuscript including rules for citing references. APA style is normally used for psychology, education, and other social sciences. Authoritative – When mentioned in reference to an information source, this refers to information that is created by experts in the field and is trustworthy. Authority - An individual or organization regarded as an expert in a particular field. Autobiography – A biography of a person written by that person. B Bias - A personal and sometimes unreasoned judgment. An opinion not based on facts or objective reasoning. Bibliography – A list of the works used or cited by an author in the creation of a paper or manuscript. Biography – A written account of someone’s life. Blog (Weblog) - A web site that contains an online personal journal with reflections and comments provided by the writer. Boolean Operators – OR, AND, NOT. These are operators you can use to better refine your searches. You can use + in place of AND. Use – in place of NOT. Browser - A computer program used for accessing sites or information on a network like the World Wide Web. C 1 Call Number - a combination of characters assigned to a library book to indicate its place on a shelf. Catalog (Library) - A complete listing of items arranged systematically with descriptive details Chicago Citation Style - used with all subjects in the "real world" by books, magazines, newspapers, and other non-scholarly publications Circulation Desk – The library circulation desk is typically the main patron service desk of the library. Generally materials are checked-out, returned, and renewed at this desk. Citation – Directly quoting another persons work with appropriate documentation. Controlled vocabulary - Vocabulary control is used to improve the effectiveness of information storage and retrieval systems, Web navigation systems, and other environments that seek to both identify and locate desired content via some sort of description using language. The primary purpose of vocabulary control is to achieve consistency in the description of content objects and to facilitate retrieval. Copyright - The exclusive legal right to reproduce, publish, sell, or distribute the matter and form of something (as a literary, musical, or artistic work) Cross-Reference - A notation or direction at one place (as in a book) to important information at another place. D Database (subscription) – For libraries, this normally means electronic collections of articles from various publications in different subject areas. Dewey decimal classification System – A system of classifying books and other publications whereby main classes are designated by a 3-digit number and subdivisions are shown by numbers after a decimal point —called also Dewey decimal system Dewey Number – The location assigned to a book, normally printed on the spine, on the Dewey Decimal System. Directory – A list of names or computer folders. Download - To transfer (as data or files) from a usually large computer to the memory of another device (as a smaller computer). E 2 Encyclopedia - a work that contains information on all branches of knowledge or treats comprehensively a particular branch of knowledge usually in articles arranged alphabetically often by subject. F Fair Use - A legal doctrine noting that portions of copyrighted materials may be used without permission of the copyright owner provided the use is fair and reasonable, does not substantially impair the value of the materials, and does not curtail the profits reasonably expected by the owner. Fiction - Something invented by the imagination of a writer; an invented story. Full text – Full text searching refers to searching the entire text of a stored document for specific user inputted search words. This differs from other searches that only index stored documents. G Glossary - A brief explanation of specialized terms with their meanings. H Hyperlink - an electronic link providing direct access from one distinctively marked place in a hypertext or hypermedia document to another in the same or a different document HTTP - hypertext transfer protocol The communications protocol used to connect to Web servers on the Internet or on a local network (intranet). Its primary function is to establish a connection with the server and send HTML pages back to the user's browser. It is also used to download files from the server either to the browser or to any other requesting application that uses HTTP. I Index - A list of items (as topics or names) treated in a printed work that gives for each item the page number where it may be found Inter-library Loan – A service offered by a library where one of their patrons may borrow items from another library. The items borrowed are requested from the lending library, delivered to the borrowing library, checked-out to the patron. The patron returns the materials to the local library which then returns it to the lending library. Intellectual Property - Intellectual property refers to creations of the mind: inventions, literary and artistic works, and symbols, names, images, and designs used in commerce. 3 Internet - An electronic communications network that connects computer networks and organizational computer facilities around the world ISBN Number - The International Standard Book Number (ISBN) is a 10-digit number that uniquely identifies books and book-like products published internationally. The purpose of the ISBN is to establish and identify one title or edition of a title from one specific publisher and is unique to that edition, allowing for more efficient marketing of products by booksellers, libraries, universities, wholesalers and distributors. L Library of Congress Classification System – This is the classification system used in college libraries. Listserv - An electronic discussion group based on common interests that uses a mailing list to distribute messages to all members' electronic mail boxes K Keyword - A significant word used for search which describes your topic. The system then searches for this word in titles and in documents. M Magazine - A periodical containing miscellaneous pieces (as articles, stories, poems) and often illustrated; it can be published online. MLA Citation - MLA (Modern Language Association) style is most commonly used to write papers and cite sources within the liberal arts and humanities. This resource, the MLA Handbook for Writers of Research Papers (6th ed.), offers examples for the general format of MLA research papers, in-text citations, endnotes/footnotes, and the Works Cited page. N Network - a system of computers, peripherals, terminals, and databases connected by communications lines Non-fiction – An account or representation of a subject which is presented as fact. O OPAC (Online Public Access Catalog) – An OPAC is a computerized online database of the items being held at a library. The library’s catalog is an OPAC. P 4 Peer reviewed - In a peer reviewed journal, drafts of articles are critically assessed by other scholars in the author's field or specialty before they are accepted for publication. Peer review is a method for ensuring that information is of the highest quality. Periodical – A publication that is published with a fixed interval between the issues or numbers. Plagiarism - To steal and pass off (the ideas or words of another) as one's own: use (another's production) without attribution to commit literary theft: present as new and original an idea or product derived from an existing source. Primary Source - An original, authoritative document pertaining to an event or subject; a firsthand or eyewitness account of an event. Examples: Popular Journal - Articles from the popular press are written and published more quickly; they may represent a less "authoritative" or expert point of view. - Popular Press (often referred to as a "magazine" article) author often not listed; is a journalist or lay person text reports events or opinions; is aimed at a general audience (easy to read) articles rarely include "references" to other works hard copy of magazine includes a significant amount of advertising magazine lists an editor or editorial board who is a member of the magazine's staff magazine deals with current events or a popular field of general interest (review table of contents) magazine is published monthly or more often Pull Down/Drop Down Menu - A menu of commands or options that appears when you select an item with a mouse. R Reference Collection – A reference collection is a collection of materials specifically for providing background information on a variety of topics. Reference collections are generally held at large institutions, including libraries, for people to use to gain a better understanding of a topic. Reference Desk – The reference desk is the desk from which the librarian provides patrons with help finding library materials, advice on how to search the library, and information on library services. Results List - A successful search produces a summary listing of documents that match your search term(s). The results list gives you a quick look at key document information so you can tell at a glance if you want to view the full article. 5 Renewal (of a library item) – When you renew a library item, you extend the time you may keep the item. S Scholarly - Characteristic of or suitable for learned or experts in a particular field. Search Engine - computer software used to search data (as text or a database) for specified information; also: a site on the World Wide Web that uses such software to locate key words in other sites Search Term – A search term is a specific word or phrase you input into a search engine to find information on the topic you are interested in. Secondary Source - Any document that describes an event, person, place, or thing, usually created at a later time. Serial - a work appearing (as in a magazine or on television) in parts at intervals a publication (as a newspaper or journal) issued as one of a consecutively numbered and indefinitely continued series Scholarly Journal - In general, articles from the scholarly press are viewed as having more "authority"; they are written by experts in a field, reviewed by other experts and represent the results of scholarly research. Scholarly Press (often referred to as a "journal" article) author listed; is a professional or other expert text reports research results, includes specialized vocabulary, is aimed at a scholarly audience article includes "references" to other works; often at the end of the text hard copy of journal includes very little (or highly specialized) advertising journal lists an editorial board composed of scholars in the field (look for this near table of contents journal deals exclusively with a limited scholarly field (review table of contents) journal is published monthly or less often articles are listed in specialized indexes, such as "PsychLit" or "Biosis" or "Humanities Index" Search Strategy – A search strategy is a process where you clarify what information you will look for in catalogs and indexes. The steps to help you are 1. Summarize your topic, 2. Identify concepts, 3. Select concept words/phrases, and 4. Connect words and concepts with Boolean operators. 6 Subject Heading - Subject headings are official standardized terms added to the citation by the indexer. They help to identify the specific topics covered in the article and to retrieve articles on a topic which might be described by a number of different words or phrases. T Table of Contents – The table of contents is a list of the parts of a book or paper. Thesaurus - A book of words and their synonyms. Turban - This guide is based on Turabian's A Manual for Writers of Term Papers, Theses, and Dissertations 6th ed. 1996. Bibliography items are listed alphabetically at the end of the research paper. Items are referred to in the body of the paper using the Footnote or In-Text style. U Upload - To transfer (as data or files) from a computer to the memory of another device (as a larger or remote computer) URL (uniform resource locator) - The address of a resource (as a document or Web site) on the Internet that consists of a communications protocol followed by the name or address of a computer on the network and that often includes additional locating information (as directory and file names). V Virtual - Being on or simulated on a computer or computer network; occurring or existing primarily online. Volume Number - A series of issues of a periodical; this is usually part of the publication information. W Web Site - a group of World Wide Web pages usually containing hyperlinks to each other and made available online by an individual, company, educational institution, government, or organization Wiki - a Web site that allows visitors to make changes, contributions, or corrections World Wide Web - a part of the Internet accessed through a graphical user interface and containing documents often connected by hyperlinks —called also Web 7 http://www.hamline.edu/bush/research/guides_articleanalysis/ http://www.mclibrary.duke.edu/training/cinahlovid/start/terms 8