A2.S.IC.3-6.12.08.11
advertisement
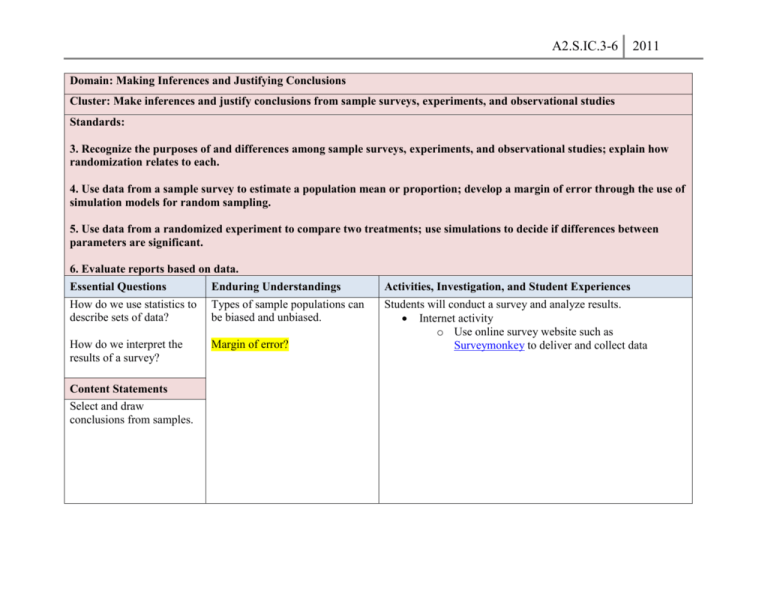
A2.S.IC.3-6 2011 Domain: Making Inferences and Justifying Conclusions Cluster: Make inferences and justify conclusions from sample surveys, experiments, and observational studies Standards: 3. Recognize the purposes of and differences among sample surveys, experiments, and observational studies; explain how randomization relates to each. 4. Use data from a sample survey to estimate a population mean or proportion; develop a margin of error through the use of simulation models for random sampling. 5. Use data from a randomized experiment to compare two treatments; use simulations to decide if differences between parameters are significant. 6. Evaluate reports based on data. Essential Questions How do we use statistics to describe sets of data? Enduring Understandings Types of sample populations can be biased and unbiased. How do we interpret the results of a survey? Margin of error? Content Statements Select and draw conclusions from samples. Activities, Investigation, and Student Experiences Students will conduct a survey and analyze results. Internet activity o Use online survey website such as Surveymonkey to deliver and collect data A2.S.IC.3-6 Assessments Describe the difference between an unbiased sample and a biased sample. (open ended) Identify the sampling method and identify any bias in each method. A supermarket wants to find the percent of shoppers who uses coupons. A manager interviews every shopper entering the greeting card aisle Solution Convenience sampling; This sampling method over represents shoppers that buy greeting cards. A university researcher is studying the effect of watching television on residents of the city. Describe the sampling method that can be used for all teenagers. Solution: A convenience sampling; interview students at a local high school. In a survey of 1600 voters, 51% said that voted for candidate A. What is the margin of sampling error for the survey? Answer 2.5% Equipment Needed: Teacher Resources: 2011 A2.S.IC.3-6 Office suite Internet access www.surveymonkey.com 2011











