Biographical Sketch
advertisement
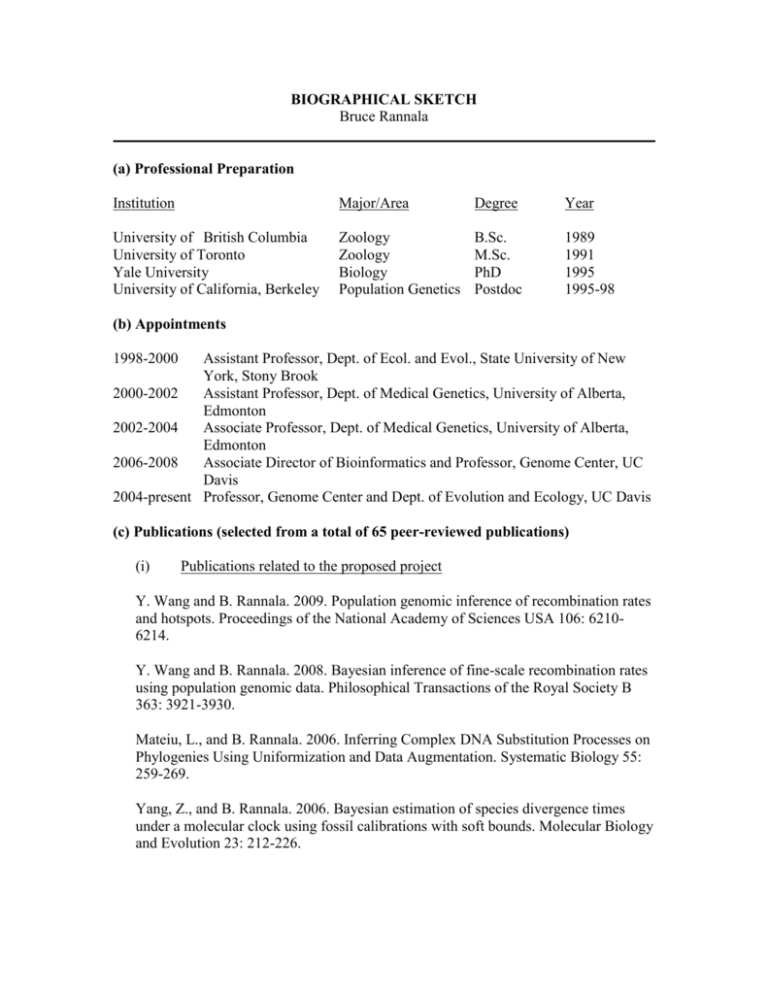
BIOGRAPHICAL SKETCH Bruce Rannala (a) Professional Preparation Institution Major/Area Degree Year University of British Columbia University of Toronto Yale University University of California, Berkeley Zoology Zoology Biology Population Genetics B.Sc. M.Sc. PhD Postdoc 1989 1991 1995 1995-98 (b) Appointments 1998-2000 Assistant Professor, Dept. of Ecol. and Evol., State University of New York, Stony Brook 2000-2002 Assistant Professor, Dept. of Medical Genetics, University of Alberta, Edmonton 2002-2004 Associate Professor, Dept. of Medical Genetics, University of Alberta, Edmonton 2006-2008 Associate Director of Bioinformatics and Professor, Genome Center, UC Davis 2004-present Professor, Genome Center and Dept. of Evolution and Ecology, UC Davis (c) Publications (selected from a total of 65 peer-reviewed publications) (i) Publications related to the proposed project Y. Wang and B. Rannala. 2009. Population genomic inference of recombination rates and hotspots. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences USA 106: 62106214. Y. Wang and B. Rannala. 2008. Bayesian inference of fine-scale recombination rates using population genomic data. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B 363: 3921-3930. Mateiu, L., and B. Rannala. 2006. Inferring Complex DNA Substitution Processes on Phylogenies Using Uniformization and Data Augmentation. Systematic Biology 55: 259-269. Yang, Z., and B. Rannala. 2006. Bayesian estimation of species divergence times under a molecular clock using fossil calibrations with soft bounds. Molecular Biology and Evolution 23: 212-226. Wang, Y., and B. Rannala. 2005. In Silico Analysis of Disease-Association Mapping Strategies Using the Coalescent Process and Incorporating Ascertainment and Selection. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 76: 1066-1073. (ii) Other publications B. Rannala and Z. Yang. 2008. Phylogenetic inference using whole genomes. Annual Review of Genomics and Human Genetics 9: 217-231. L. Mateiu and B. Rannala. 2008. Bayesian inference of errors in ancient DNA caused by postmortem degradation. Molecular Biology and Evolution 25: 1503-1511. Cranston, K., and B. Rannala. 2007. Summarizing a posterior distribution of trees using agreement subtrees. Systematic Biology 56: 578-590. Rannala, B., and Z. Yang. 2007. Inferring speciation times under an episodic molecular clock. Systematic Biology 56: 453-466. Yang, Z., and B. Rannala. 2005. Branch-length prior influences Bayesian posterior probability of phylogeny. Systematic Biology 54: 455-470. (d) Synergistic Activities Dr. Rannala’s research group has developed (and supports) several open source population genetics software packages including BayesAss, DMLE, Immanc and InferRho. He also collaborated in the development of the BPP program for Bayesian phylogenetics (distributed by Ziheng Yang). Dr. Rannala has contributed to the diversity of the (predominantly male) community of theoretical population geneticists, with 4 of 5 students completing a Ph.D. under his supervision being female. Dr. Rannala has also cosupervised, or mentored, Ph.D. students from several developing countries including China and Thailand and regularly teaches in international phylogenetics workshops in China, Sweden, the UK and the US. (NSF description of synergistic activities: A list of up to five examples that demonstrate the broader impact of the individual’s professional and scholarly activities that focuses on the integration and transfer of knowledge as well as its creation. Examples could include, among others: innovations in teaching and training (e.g., development of curricular materials and pedagogical methods); contributions to the science of learning; development and/or refinement of research tools; computation methodologies, and algorithms for problem-solving; development of databases to support research and education; broadening the participation of groups underrepresented in science, mathematics, engineering and technology; and service to the scientific and engineering community outside of the individual’s immediate organization.) (e) Collaborators and other Affiliations Collaborators Bumroongkit, K. Cranston, K. Fetterman, C. D. Kangwanpong, D. Mateiu, L. Ro, S. Srikummool, M. Traisathit, P. Walter, M. A. Wang, Y. Wongchai, Y. Yang, Z. Chiang Mai University, Thailand NESCent, Durham NC University of Alberta Chiang Mai University, Thailand Universiteit Antwerpen, Belgium Yonsei University Medical School, South Korea Chiang Mai University, Thailand Chiang Mai University, Thailand University of Alberta University of Chicago Chiang Mai University, Thailand University College London Graduate Advisors (if not listed above) Hartigan, J.A. Yale University Wagner, G.P. Yale University Thesis Advisors and Postdoctoral-Scholar Sponsor (if not listed above) Leache, A. University of Washington Qin, X.J. Duke University Reeve, J. University of Alberta Wilson, G. Canadian Wildlife Service (NSF description of Collaborators and other Affiliations: Collaborators and Co-Editors. A list of all persons in alphabetical order (including their current organizational affiliations) who are currently, or who have been collaborators or co-authors with the individual on a project, book, article, report, abstract or paper during the 48 months preceding the submission of the proposal. Also include those individuals who are currently or have been coeditors of a journal, compendium, or conference proceedings during the 24 months preceding the submission of the proposal. If there are no collaborators or co-editors to report, this should be so indicated. • Graduate Advisors and Postdoctoral Sponsors. A list of the names of the individual’s own graduate advisor(s) and principal postdoctoral sponsor(s), and their current organizational affiliations. • Thesis Advisor and Postgraduate-Scholar Sponsor. A list of all persons (including their organizational affiliations), with whom the individual has had an association as thesis advisor, or with whom the individual has had an association within the last five years as a postgraduatescholar sponsor. The total number of graduate students advised and postdoctoral scholars sponsored also must be identified.)






