MSc Geophysical Hazards - University College London
advertisement

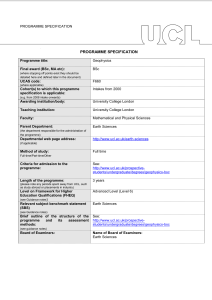
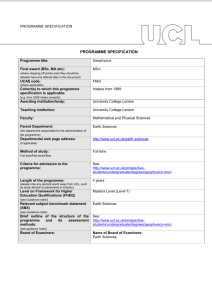
PROGRAMME SPECIFICATION PROGRAMME SPECIFICATION Programme title: Geophysical Hazards Final award (BSc, MA etc): MSc (where stopping off points exist they should be detailed here and defined later in the document) UCAS code: n/a (where applicable) Cohort(s) to which this programme specification is applicable: Intakes from 2003 (e.g. from 2008 intake onwards) Awarding institution/body: University College London Teaching institution: University College London Faculty: Mathematical and Physical Sciences Parent Department: Earth Sciences (the department responsible for the administration of the programme) Departmental web page address: http://www.ucl.ac.uk/earth-sciences (if applicable) Method of study: Full or part time Full-time/Part-time/Other Criteria for admission to the programme: Length of the programme: See: http://www.ucl.ac.uk/prospectivestudents/graduate/taught/degrees/geophysical-hazards-msc 1 year full time, 2 years part time (please note any periods spent away from UCL, such as study abroad or placements in industry) Level on Framework for Higher Education Qualifications (FHEQ) (see Guidance notes) Relevant subject benchmark statement (SBS) Masters Level (Level 7) Earth Sciences (see Guidance notes) Brief outline of the structure of the programme and its assessment methods: See: http://www.ucl.ac.uk/earthsciences/study/postgraduate/geophysical_hazards (see guidance notes) Board of Examiners: Professional body accreditation (if applicable): Name of Board of Examiners: Earth Sciences Date of next scheduled accreditation visit: EDUCATIONAL AIMS OF THE PROGRAMME: The programme will develop students' skills, knowledge and research ability in geophysical hazards, notably the mechanisms and processes associated with their formation and occurrence, their potential impact on society, and hazard-management and mitigation strategies, It will also prepare students for entry onto PhD streams and to appropriate positions in risk evaluation in commercial (including engineering and insurance) and vocational (including Non-governmental organisations) sectors. PROGRAMME OUTCOMES: The programme provides opportunities for students to develop and demonstrate knowledge and understanding, qualities, skills and other attributes in the following areas: A: Knowledge and understanding Knowledge and understanding of: 1. Geophysical processes operating at the Earth's surface and in its interior, and within the atmosphere and nearEarth space. 2. How geological, hydrological and atmospheric processes result in the formation and triggering of hazardous phenomena 3. The temporal and spatial distribution of hazards. 4. Quantitative modelling of geophysical hazards. 5. Strategies for managing and mitigating the risk of geophysical hazards to human activity. 6. Fundamental research skills, including (a) the planning and implementation of investigations (b) analysis of results, and (c) presentation of results and recommendations in written and oral form. Teaching/learning methods and strategies: A foundation core lecture programme covering essential elements of geophysical hazards (principal hazard types, associated processes and mechanisms, impacts, management and mitigation) and basic research methods (statistics, developing models, preparing hazard analyses); An advanced core lecture programme that address specialist topics in quantitative modelling and analysis of geophysical hazards, and practical application of results for decision-making; Directed reading: students will follow a programme of directed reading to support the lecture programmes; Independent research project: students will develop research skills by writing a 15,000 word dissertation based on a literature survey and appropriate new measurements, and give an oral presentation of the results. Assessment: Students will be assessed by a combination of unseen written examinations, practical problem-solving exercises, essays, and an independent research report (written with oral presentation). B: Skills and other attributes Intellectual (thinking) skills: Teaching/learning methods and strategies: The programme aims to help students: Aims (1) and (3) will be addressed by the taught modules and directed reading, all of which will introduce information that will need to be assessed critically, 1. Critically evaluate current and competing ideas about the mechanisms and processes associated with geophysical hazards, their impacts, and their forecasting. 2. Critically evaluate their own research results. 3. Apply knowledge of geophysical hazards to evaluate risk and to recommend appropriate mitigation strategies. Aim (2) will be addressed through directed reading and, predominantly, the independent research project. Assessment: Aims (1) and (3) will be assessed by a combination of unseen written examinations, practical problem-solving exercises, and essays. Aim (2) will be assessed through the independent research report (written with oral presentation). C: Skills and other attributes Practical skills (able to): Teaching/learning methods and strategies: 1. critically evaluate information, ideas and interpretations. 2. communicate geophysical hazards research in written and oral forms. 3. contribute effectively in presenting and discussing seminars. 4. develop research skills to design and implement an independent research project and to present the results in written and oral forms. (1) and (2) through practical problem-solving exercises, essays, directed reading and independent project. (3) through the independent research project and appropriate components involving seminar presentations. (4) through independent research project. Assessment: (1) and (2) will be assessed by a combination of unseen written examinations, practical problem-solving exercises, and essays. (3) will be assessed by presentation of results from independent research project, and the delivery, as appropriate, of seminars linked to components. (4) will be assessed through the independent research report, including its oral presentation. D: Skills and other attributes Transferable skills (able to): Teaching/learning methods and strategies: The programme will encourage students to: (1) effectively communicate research information orally and in writing. (2) critically evaluate information and to assess conflicting interpretations. (3) develop skills for quantitative modelling. (4) develop confidence in recommending best-practice strategies. (5) enhance capacity for independent thought and problem solving. (1) through essays and by presentation of results from Independent research project, as well as appropriate seminars linked to taught components. (2)-(4) through taught modules, essays and directed reading. (5) through independent research project. Assessment: (1) - (4) will be assessed by a combination of unseen written examinations, practical problem-solving exercises, and essays. (1) will be additionally assessed by presentation of results from independent research project, and the delivery, as appropriate, of seminars linked to taught components. (5) will be assessed by through the independent research report, including its oral presentation. The following reference points were used in designing the programme: the Framework for Higher Education Qualifications: (http://www.qaa.ac.uk/en/Publications/Documents/Framework-Higher-Education-Qualifications-08.pdf); the relevant Subject Benchmark Statements: (http://www.qaa.ac.uk/assuring-standards-and-quality/the-quality-code/subject-benchmark-statements); the programme specifications for UCL degree programmes in relevant subjects (where applicable); UCL teaching and learning policies; staff research. Please note: This specification provides a concise summary of the main features of the programme and the learning outcomes that a typical student might reasonably be expected to achieve and demonstrate if he/she takes full advantage of the learning opportunities that are provided. More detailed information on the learning outcomes, content and teaching, learning and assessment methods of each course unit/module can be found in the departmental course handbook. The accuracy of the information contained in this document is reviewed annually by UCL and may be checked by the Quality Assurance Agency. Programme Organiser(s) Christopher Kilburn Name(s): Date of Production: February 2003 Date of Review: February 2015 Date approved by Head of Department: Date approved by Chair of Departmental Teaching Committee: Date approved by Faculty Teaching Committee February 2015 December 2014 February 2015