Methylene Chloride SOP
advertisement

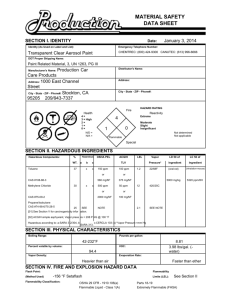
1 Standard Operating Procedure Methylene Chloride / Dichloromethane This is an SOP template and is not complete until: 1) lab specific information is entered into the box below 2) lab specific protocol/procedure is added to the protocol/procedure section and 3) SOP has been signed and dated by the PI and relevant lab personnel. Print a copy and insert into your Safety on Site (SOS) Binder. Department: Chemistry Date SOP was written: 11/20/2012 Date SOP was approved by PI/lab supervisor: Principal Investigator: 1/13/2013 Richmond Sarpong Internal Lab Safety Coordinator/Lab Manager: Lab Phone: Rebecca Murphy 510-643-2485 Office Phone: 510-643-6312 Emergency Contact: Rebecca Murphy (510-643-2485) Location(s) covered by this SOP: Latimer 834, 836, 837, 838, 839, 842, 844, 847, 849, 907 (Name and Phone Number) (Building/Room Number) Refer to instructions for assistance. Type of SOP: ☐ Process Methylene Chloride/Dichloromethane ☒Hazardous Chemical ☐ Hazardous Class 01/10/13 2 Purpose Methylene chloride or dichloromethane (DCM) is commonly used as a solvent for reactions and purifications. Methylene chloride is one of California’s Regulated Carcinogens. This SOP documents the safe use of DCM including the minimization of inhalation of dichloromethane. Use of methylene chloride in the laboratory would result in “short term exposure,” which the State limits to 125 ppm for 15 minutes. Physical & Chemical Properties/Definition of Chemical Group CAS#: 75-09-2 Class: Cal/OSHA regulated carcinogen Carcinogen (IARC Group 2B) Molecular Formula: CH2Cl2 Form (Physical State): Liquid Potential Hazards/Toxicity LD50 Oral: 1600 mg/kg [Rat] Permission Exposure Limits (PEL): 25 ppm (8-hour TWA) 12.5 ppm (8-hour TWA – Action Level) 125 ppm (short term exposure limit (STEL) 15 minutes) Acute Effects Very hazardous in case of eye contact (irritant), of ingestion, of inhalation. In case of ingestion, DCM may cause irritation of the gastrointestinal tract with vomiting. If vomiting results in aspiration, chemical pneumonia could follow. Absorption through gastrointestinal tract may produce symptoms of central nervous system depression ranging from light headedness to unconsciousness. Exposure by inhalation may result in irritation to the respiratory tract, as well as strong narcotic effects, with symptoms of mental confusion, light-headedness, staggering, and unconsciousness. Exposure may make symptoms of angina (chest pain) worse. Hazardous in case of skin contact (irritant, permeator). May be absorbed through the skin and may cause skin burns. Inflammation of the eye is characterized by redness, watering, and itching. Eye contact may cause temporal eye damage. Chronic Effects Can cause dermatitis upon prolonged skin contact. Central nervous system and liver effects. Possible carcinogenic (cancer causing) effects. Carcinogenic Effects Methylene chloride may cause cancer in humans. Developmental Toxicity May cause mutagenic effects (effects on developing fetus). Engineering Controls Methylene Chloride/Dichloromethane 01/10/13 3 NOTE: Lab-specific information on engineering controls may be included in the Protocol/Procedure section. All operations involving methylene chloride and dilutions should be carried out in a chemical fume hood or a ducted Biosafety cabinet to keep airborne level below recommended exposure limits. Chemical fume hoods used as containment areas for particularly hazardous chemicals must have a face velocity of 100 cfm, averaged over the face of the hood and must be certified annually. Laboratory rooms must be at negative pressure with respect to the corridors and external environment. The laboratory/room door must be kept closed at all times. Vacuum lines are to be protected by HEPA (high efficiency particulate air) filters or higher efficiency scrubbers. Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) NOTE: Lab-specific information on PPE selection may be included in the Protocol/Procedure section. The level of skin and eye protection should be selected based on the potential for splashing and other forms of exposure. Minimum potential for splash & exposure: Single pair of chemical resistant gloves. (Nitrile and neoprene degrade quickly on contact with methylene chloride so should be replaced if any splashes onto gloves. PVA, butyl, and Viton are more resistant to degradation by contact with methylene chloride). Protective clothing (e.g. flame-resistant lab coat, impervious sleeves; closed-toed impervious shoes) ANSI approved properly fitting safety glasses or chemical splash goggles. Face shield is also recommended. When using or transferring large quantities (>1 L): Single pair of chemical resistant gloves o Immediately replace with new gloves when splash occurs. (Nitrile and neoprene degrade quickly on contact with methylene chloride so should be replaced if any splashes onto gloves. PVA, butyl, and Viton are more resistant to degradation by contact with methylene chloride). Chemical resistant lab coat o Avoid using the traditional cotton-polyester white lab coat, which readily collects/absorbs compounds. Protective clothing (e.g. non-porous sleeves, closed-toed impervious footwear). ANSI approved properly fitting safety glasses or chemical splash goggles. Face shield is also recommended. Respiratory Protection NOTE: Lab personnel intending to use/wear a respirator mask must be trained and fit-tested by EH&S. This is a regulatory requirement. Methylene Chloride/Dichloromethane 01/10/13 4 Refer to 8 CCR 5144 for selection of respirators. A respiratory protection program that meets 8 CCR 5144 must be followed whenever workplace conditions warrant use of a respirator. Respirators may be used only under any of the following circumstances: As a last line of defense (i.e., after engineering and administrative controls have been exhausted). When Permissible Exposure Limit (PEL) has been exceeded or when there is a possibility that PEL will be exceeded, and the material has adequate warning properties (e.g., odor, taste). Regulations require the use of a respirator. An employer requires the use of a respirator. There is potential for harmful exposure due to an atmospheric contaminant (in the absence of PEL) As PPE in the event of a chemical spill clean-up process Hand Protection Handle with gloves. Gloves must be inspected prior to use. Use proper glove removal technique (without touching glove's outer surface) to avoid skin contact with this product. Wash and dry hands. NOTE: Lab-specific information on glove selection may be included in the Protocol/Procedure section. For glove selection, go to: http://ehs.berkeley.edu/hs/63-laboratory-safety/94-glove-selection-andusage.html Refer to glove selection chart from the links below: http://www.ansellpro.com/download/Ansell_8thEditionChemicalResistanceGuide.pdf OR http://www.allsafetyproducts.biz/page/74172 OR http://www.showabestglove.com/site/default.aspx OR http://www.mapaglove.com/ Eye Protection Use safety glasses with side shields or tightly fitting safety goggles. Use face shield (8-inch minimum) over goggles when appropriate. Use equipment for eye protection tested and approved under appropriate government standards such as ANSI Z87.1, NIOSH (US), or EN 166(EU). Hygiene Measures Handle in accordance with good industrial hygiene and safety practices. Wash hands immediately after handling, before breaks, and at the end of the workday. Remove any contaminated clothing and wash before reuse. First Aid Procedures Notify supervisor and EH&S immediately after an incident. Follow up with a call to 510-642-9090 to report the incident. Methylene Chloride/Dichloromethane 01/10/13 5 Before beginning work with chemicals, review the relevant Safety Data Sheet and appropriate chemical safety resources as listed in the Training/Approval section of this document. Develop specific procedures for emergency response and chemical exposure or injury to staff, including any special first aid measures required for the relevant chemical. Skin & Eye Exposure: Minor skin contact requires washing with soap and water. Soaking or flushing contaminated areas of the skin with water for periods up to 15 minutes is required if a large area comes into contact with the chemical, or if prolonged contact occurs. Contaminated clothing may hold the chemicals in contact with the skin without being immediately noticed. In the event of eye contact, the eye should be immediately be flushed with water for 15 minutes. If the chemical is very irritating, it is likely that the affected individual will require assistance to hold the eye open during the flushing. Ingestion: DO NOT induce vomiting, give milk or water if conscious, and get medical attention immediately. Inhalation: Remove rapidly to clean air. Administer rescue breathing if necessary and call 911. Seek medical attention if needed. Special Handling and Storage Requirements NOTE: Lab-specific information on handling and storage may be included in the Protocol/Procedure section. Working alone: Certain extremely hazardous operations should not be performed if the PI or Lab Safety Contact(s) are not present. Never work alone with extremely hazardous materials/operations. See the Protocol/Procedure section below for specific prohibitions (if any) on working alone. Keep in a tightly closed container, stored in a cool, dry, ventilated area. Protect against physical damage. Isolate from any source of heat or ignition. Store in secondary containment, isolate from other chemical compounds with proper labeling: REGULATED CARCINOGEN DCM can be stored in the same cabinet as other regulated carcinogens. Segregate the chemicals from incompatible materials. Incompatible materials are strong oxidizers, strong caustics, plastics, rubber, nitric acid, water + heat, chemically active metals (such as aluminum and magnesium powder), sodium, potassium, lithium. Designated Areas Designated area(s) for use and storage of methylene chloride must be established. All containers of methylene chloride must be secondarily contained with proper signage. Signage is required for the container, designated work area and storage location. Sign wording must state the following: Methylene Chloride/Dichloromethane 01/10/13 6 “DANGER, CANCER HAZARD” Administrative Controls Never work alone. At least one other person must be present in the same laboratory when any work involving methylene chloride is carried out. Eliminate or substitute for a less hazardous material when possible. Design your experiment to use the least amount of material possible to achieve the desired result. Verify your experimental set-up and procedure prior to use. Inform colleagues that this material will be used and where. Only use if the area is properly equipped with a certified eye wash/safety shower within ten seconds of travel. Consult with the PI if work involves large quantities. Spill and Accident Procedure Chemical Spill Dial 911 Spill – Assess the extent of danger. Help contaminated or injured persons. Evacuate the spill area. Avoid breathing vapors. Eliminate sources of ignition. If possible, confine the spill to a small area using a spill kit or absorbent material. Keep others from entering contaminated area (e.g., use caution tape, barriers, etc.). Small (<1 L) – If you have training, you may assist in the clean-up effort. Use appropriate personal protective equipment and clean-up material for chemical spilled. Double bag spill waste in clear plastic bags, label and take to the next chemical waste pick-up. Large (>1 L) – Dial 911 and EH&S at x46200 510-642-9090 for assistance. Chemical Spill on Body or Clothes – Remove clothing and rinse body thoroughly in emergency shower for at least 15 minutes. Seek medical attention. Notify supervisor and EH&S at 510-642-9090 immediately. Chemical Splash Into Eyes – Immediately rinse eyeball and inner surface of eyelid with water from the emergency eyewash station for 15 minutes by forcibly holding the eye open. Seek medical attention. Notify supervisor and EH&S at 510-642-9090 immediately. Medical Emergency Dial 911 Life Threatening Emergency, Business Hours, After Hours, Weekends and Holidays – Dial 911. Call 911 if the condition is LIFE THREATENING OR REQUIRES IMMEDIATE MEDICAL ATTENTION. Note: All Serious injuries must be reported to EH&S AT 510-642-9090 within 8 hours. Non-Life Threatening Emergency – Notify your supervisor or faculty staff if condition is not life threatening. Go to the Occupational Health Facility (Tang Health Center). After hours go to the emergency room. Note: All serious injuries must be reported to EH&S within 8 hours. Follow up with a call to 510-642-9090 to report the incident. Methylene Chloride/Dichloromethane 01/10/13 7 Needle stick/puncture exposure (as applicable to chemical handling procedure) – Wash the affected area with antiseptic soap and warm water for 15 minutes. For mucous membrane exposure, flush the affected area for 15 minutes using an eyewash station. Go to the Occupational Health Facility (Tang Health Center). After hours, go to the emergency room. Note: All needle stick/puncture exposures must be reported to EH&S within 8 hours. Follow up with a call to 510-642-9090 to report the incident. Decontamination/Waste Disposal Procedure NOTE: Lab-specific information on decontamination/waste disposal may be included in the Protocol/Procedure section. No waste streams containing methylene chloride shall be disposed of in sinks. Decontaminate work space with 70-75% ethanol. Wash hands and arms with soap and water after finished. Contaminated pipet tips, Eppendorf tubes, and gloves should be discarded as hazardous waste. Waste containers containing methylene chloride must be labeled: “DANGER, CANCER HAZARD” Safety Data Sheet (SDS) Location Hardcopy AND electronic copy MSDS from the same manufacturer must be available for Methylene Chloride. SDS can be accessed online at http://ucmsds.com. Protocol/Procedure Methylene Chloride (Dichloromethane, DCM) is used as a solvent for running reactions as well as for the purification of compounds by column chromatography All reactions and chromatography using DCM should be carried out inside a functioning chemical fume hood while wearing the appropriate PPE (flame-resistant lab coat, gloves, and chemical safety goggles). If DCM is to be evaporated using a rotary evaporator, the volatiles must be collected using a dry ice condenser and disposed of as hazardous waste. Reactions involving DCM can use amount ranging from <1mL to 1L, and can be conducted at temperatures of down to ~78 ºC. If reactions are run above the boiling point of DCM (40 ºC), then the reaction vessel must be able to handle in increased pressure, and if done on large scale (>100mL) a blast shield is recommended. When used for chromatography, larger amounts of DCM may sometimes be necessary (up to >1L). DCM should be kept inside the fume hood if being used for a column and if possible, covered to prevent excessive evaporation. After work is completed, the area should be cleaned, and any contaminated materials disposed of properly. Before leaving the work area, researchers should wash their hands in order to reduce the risk of contamination of non-lab areas. All DCM containers should be kept inside a ventilated chemical storage cabinet approved for the storage of solvents, or when in use, inside a properly functioning fume hood. Methylene Chloride/Dichloromethane 01/10/13 8 As a regulated carcinogen, DCM should be labeled as such and stored in a secondary container, segregated along with other carcinogens. All fume hoods and cabinets in which DCM is present should be labeled to indicate the presence of known carcinogens. Any deviation from this SOP requires approval from PI. Required Training / Approvals All work with methylene chloride requires the following prior to beginning work: Must be pre-approved by the Principal Investigator prior to use and all training must be well documented. Must be familiar with the Chemical Hygiene Plan. Must have documented Laboratory Safety Training. Must follow this SOP. Must read the relevant Safety Data Sheet (formerly referenced as Material Safety Data Sheets). Any additional laboratory specific training that is needed to support this SOP must be referenced in the Laboratory Specific Instructions' section and the signed and dated training documents must be uploaded into each assigned researchers training records. Examples include Safety Data Sheets, experimental procedures, journal articles, etc. Must read Prudent Practices in the Laboratory: Handling and Management of Chemical Hazards , Chapter 3.C Toxic Effects of Laboratory Chemicals: http://www.nap.edu/openbook.php?record_id=4911&page=29 Chapter 5 Working with Chemicals http://www.nap.edu/openbook.php?record_id=4911&page=79#p200063c99970079001 Documentation of Training (signature of all users is required) Prior to conducting any work with methylene chloride, designated personnel must provide training to his/her laboratory personnel specific to the hazards involved in working with this substance, work area decontamination, and emergency procedures. The Principal Investigator must provide his/her laboratory personnel with a copy of this SOP and a copy of the methylene chloride MSDS provided by the manufacturer. The Principal Investigator must ensure that his/her laboratory personnel have attended appropriate laboratory safety training or refresher training within the last two years. I have read and understand the content of this SOP: Name Signature Methylene Chloride/Dichloromethane Identifier Date 01/10/13 9 Methylene Chloride/Dichloromethane 01/10/13