question analysis for summative assessment over probability
advertisement

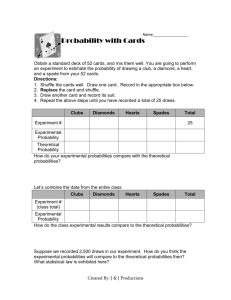
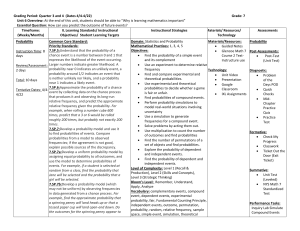
QUESTION ANALYSIS FOR SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT OVER PROBABILITY KNOWLEDGE I can identify an event that is complementary to another event. I can recognize whether a situation produces a simple or compound probability. I can apply the Fundamental Counting Principle to determine the number of outcomes for a situation. I can identify whether an arrangement of items is a combination. I can identify whether an arrangement of items is a permutation. I can define the Law of Large Numbers. I can define theoretical probability I can define experimental probability. I can define inference and give examples. I can define prediction. I can define simple probability. I can define compound probability. UNDERSTANDING/REASONING I can predict the number of times an event may occur based on a sample of data. I can explain how theoretical and experimental probabilities are related. I can explain how the Law of Large Numbers relates the theoretical and experimental probabilities. I can make inferences that compare theoretical and experimental probabilities. SKILL ACQUISITION I can calculate simple probability for an event in the form of fractions, decimals, and percents. I can calculate compound probability for an event in the form of fractions, decimals, and percents. I can calculate the percent of a complementary event occurring. I can organize data into charts or tables while doing an experiment. I can predict future outcomes from a set of data SUMMATIVE QUESTION NUMBER CA 18; CA 20 CA 18 CA 4; CA 10; CA 12; CA 17 CA 5 CA 11 CA 1; CA 21 CA 21 CA 21 CA 2; CA 3; CA 6; CA 7; CA 13; CA 19 CA 15; CA 16; CA 20 CA 8; CA 9; CA 20 CA 21 CA 14; LEGEND OF ASSESSMENTS: CA—Common Assessment Jamie-Marie Wilder—Probability: The Study of Chance—7/19/2010 Jamie-Marie Wilder—Probability: The Study of Chance—7/19/2010