Pedigree Analysis IB Exam Questions
advertisement
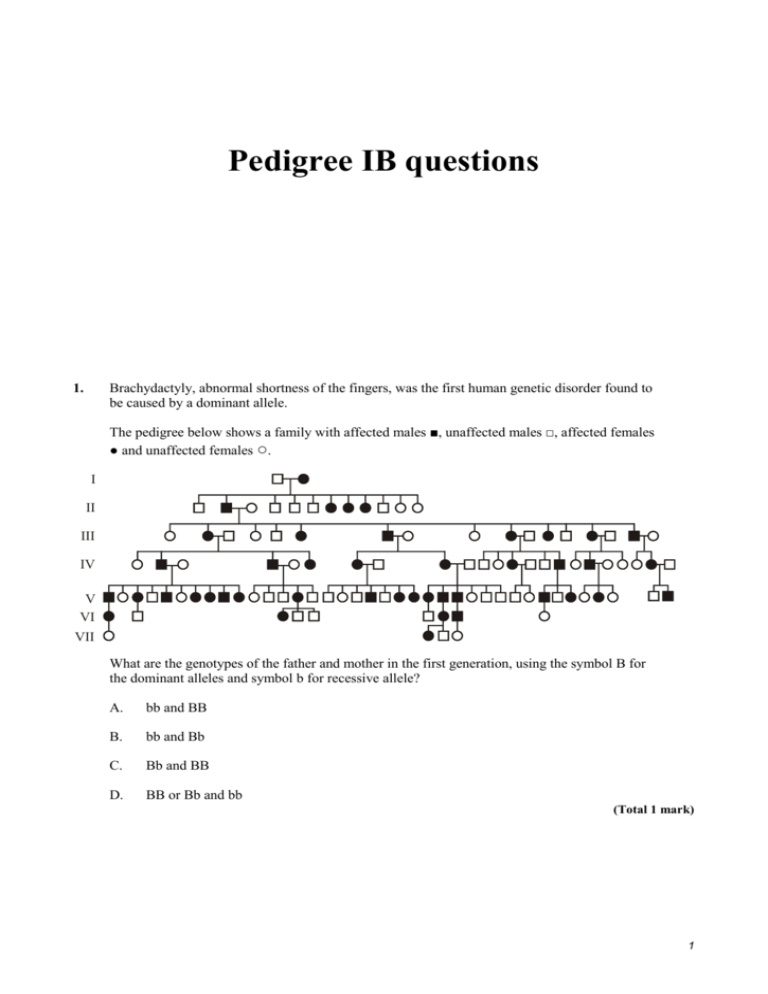
Pedigree IB questions 1. Brachydactyly, abnormal shortness of the fingers, was the first human genetic disorder found to be caused by a dominant allele. The pedigree below shows a family with affected males ■, unaffected males □, affected females ● and unaffected females ○. I II III IV V VI VII What are the genotypes of the father and mother in the first generation, using the symbol B for the dominant alleles and symbol b for recessive allele? A. bb and BB B. bb and Bb C. Bb and BB D. BB or Bb and bb (Total 1 mark) 1 2. Which feature of a genetic pedigree chart demonstrates that a characteristic is sex linked? A. Numbers of offspring carrying the characteristic decreased over several generations. B. One gender is more commonly affected than the other. C. Equal numbers of males and females inherit the characteristic. D. Boys and girls only inherit the characteristic from their mothers. (Total 1 mark) 3. (a) Define sex linkage. ..................................................................................................................................... (1) (b) State one example of sex linkage. ..................................................................................................................................... (1) 2 (c) Draw a simple pedigree chart that clearly shows sex linkage in humans. Use conventional symbols. Start with an affected woman and an unaffected man. (4) (Total 6 marks) 4. The diagram below shows the pedigree of a family with red green colour-blindness, a sex-linked condition. Key 1st generation 1 normal male 2 normal female male with condition 2nd generation 1 2 1 2 3 4 5 3 4 female with condition 3rd generation 3 (a) Define the term sex-linkage. ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... (1) (b) Deduce, with a reason, whether the allele producing the condition is dominant or recessive. ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... (2) (c) (i) Determine all the possible genotypes of the individual (2nd generation–1) using appropriate symbols. ........................................................................................................................... (1) (ii) Determine all the possible genotypes of the individual (3rd generation–4) using appropriate symbols. ........................................................................................................................... (1) (Total 5 marks) 4 5. The following diagram represents a two generation pedigree showing the blood groups of the individuals. The female has been married to two different individuals. O A AB Key 1st generation 1 2 Male 3 Female B O A AB 2nd generation 1 (a) 2 3 4 Define the term co-dominant alleles. ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... (1) (b) Deduce with a reason the probable father of 2nd generation–1. ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... (2) 5 (c) If 2nd generation–3 marries a man with blood group AB, predict the possible genotypes of the children. ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... (3) (Total 6marks) 6. The pedigree below shows which members of a family were Rhesus positive (■ and •) and Rhesus negative (□ and O). The allele for Rhesus positive blood (Rh+) is dominant over the allele for Rhesus negative blood (R-). Rhesus positive male I II III Rhesus negative male Rhesus positive female Rhesus negative female Which are possible genotypes of the individuals numbered I, II and III? I II III A. Rh+ Rh+ Rh+ Rh+ Rh+ Rh– B. Rh+ Rh+ Rh+ Rh– Rh+ Rh+ C. Rh+ Rh+ Rh+ Rh– Rh+ Rh– D. Rh+ Rh– Rh+ Rh– Rh+ Rh+ (Total 1 mark) 6 7. Hemophilia is caused by an X-linked recessive allele. In the pedigree shown below which two individuals in the pedigree must be carriers of hemophilia? A. I-1 and II-1 B. I-4 and II-2 C. II-1 and II-2 D. III-2 and III-3 (Total 1 mark) 7 8. In the pedigree shown below, the female, labelled I-2, is a carrier for colour blindness, however neither male (I-1 or II-1) is colour blind What is the probability that offspring III-1 will be colour blind? A. 50% B. 25% C. 12.5% D. 0% (Total 1 mark) 9. Colour blindness in humans is caused by an X chromosome linked recessive allele. In the pedigree chart below which two individuals must, for certain, be carriers of colour blindness? I II A. II and IV B. I and III C. II and III D. I and II III IV (Total 1 mark) 8