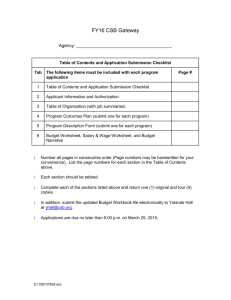
Molecular Shapes and Polarity
advertisement

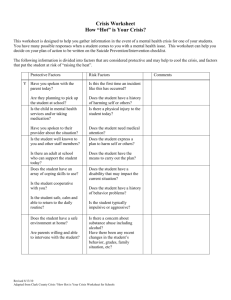
Matter and Chemical Change Workbook Science 9 Mr. J. Dulku Matter and Chemical Change Workbook Science 9 Worksheet 1: Safety in the Science Class (1.1) 1. Provide an example of a hazardous material that you would find in your: a) Bathroom b) Kitchen c) Garage 2. What is a key difference in the appearance of WHMIS symbols and safety hazard symbols? 3. For the following symbols: i) identify the type of symbol (WHMIS or Safety Hazard), ii) identify the specific hazard, and iii) identify the degree of hazard, where appropriate. 4. a) b) c) d) e) f) g) h) i) A grade 12 student has to prepare a caustic (heavily basic) solution for your teacher. The student has long hair and is using very old glassware and equipment. What are five different precautions that this student must take before preparing the solution? Worksheet 2: Organizing Matter (1.2) 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. Identify the change of state when a substance goes from liquid to solid. Identify the change of state when a substance goes from solid to gas. Identify the change of state when a substance goes from gas to liquid. What is the difference between malleability and ductility? (hint: see table on page 99) Salt dissolves easily in water, but not very easily in oil. Is solubility a chemical property or a physical one? Explain. Suspensions and colloids are both cloudy mixtures. What makes a suspension different from a colloid? A mud puddle is considered a suspension. A combination of rocks, sand and water is considered a mechanical mixture. Explain why the latter is a mechanical mixture. Identify the two types of pure substances. Graphite is made only of carbon. Is graphite an element or compound? Create a table like the one below, list the different types of physical properties and chemical properties. Physical Properties of Matter Chemical Properties of Matter Science 9 – Matter and Chemical Change – Workbook Mr. J. Dulku 11. Identify the different physical properties in the table below: Observation Solid oxygen melts at –218C Diamonds can scratch ordinary glass Gold can be pulled into wire Iron can be beat into thin sheets 12. 13. Physical Property of Matter A solution is not limited to a solid dissolving in a liquid. List two other combinations of solutions. Determine the state for each of the following substances: Substance water oxygen ammonium nitrate ethanol mercury Melting Point (C) 0 -218 170 -117 -39 Boiling Point (C) 100 -183 210 79 357 State at Room Temperature (25 C) Worksheet 3: Observing Changes in Matter (1.3) 1. From the list below, sort out the physical changes from the chemical changes: A plant grows. Sugar disappears in water. A carrot is cooked. An alcohol evaporates. A student breathes. Vinegar reacts with baking soda. Ice melts. 2. List two different observations that may suggest a new substance has been created (i.e. a chemical change). 3. Determine what kind of change (physical or chemical) occurs in each of the following situations. Using the table on page 105, identify at least one observation that supports your choice. You will not get credit for just identifying the type of change! Physical Changes Chemical Changes Observable Changes Type of Change Baking muffins from batter Burning wood into ash Melting ice cream Mixing salt with water A cat breathes 4. Blue crystals are mixed with water. After mixing, what remains is a clear blue liquid with a white powder at the bottom. After heating the mixture, only blue crystals remain. Is this a chemical change or a physical one? Explain. Science 9 – Matter and Chemical Change – Workbook Mr. J. Dulku Worksheet 4: Evolving Theories of Matter (2.1) 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Why was copper considered so valuable an element to humans? Offer two reasons why gold was considered valuable. Why were Democritus’ ideas ignored for 2000 years? What are three different practical discoveries made by alchemists? Use a Venn diagram to compare and contrast Democritus’ ideas with those of Boyle. Include at least one difference for each, and two similarities. Worksheet 5: Evolving Theories of Matter (2.1) 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. What was Lavoisier’s major contribution to science? Use a Venn diagram to compare and contrast Democritus’ ideas with those of Dalton. Include at least one difference for each, and one similarity. Describe the structure of Thomson’s “raisin bun model” of the atom. Use a picture if necessary. Rutherford improved on Nagaoka’s model of the atom by shrinking the size of the nucleus. Draw a picture of Rutherford’s model of the atom. Why were some high-speed particles deflected by the gold foil in Rutherford’s experiment? Worksheet 6: Organizing the Elements (2.2) 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. How many elements have been properly named so far by IUPAC? How many have been discovered but need to be named? [Hint: ask your teacher!] Suggest one reason why using celestial bodies may not be appropriate symbols for elements. What did Dalton base some of his symbols on? Dalton’s system of chemical symbols was abandoned a long time ago. Why is his symbol for hydrogen still considered interesting? [Hint: ask your teacher!] What was the first property used to put the chemical elements in order? Mendeleev decided to organize the 63 known elements into the first periodic table. What were three properties that he wrote on cards? There were many gaps in Mendeleev’s periodic table. What did these gaps represent? Use Toolbox 12 (page 506) to help you to identify the names of the chemical elements in the following four compounds: a) Aspirin (ASA) c) Urea b) Muriatic acid d) Vitamin C Science 9 – Matter and Chemical Change – Workbook Mr. J. Dulku Worksheet 7: The Periodic Table Today (2.3) 1. On the blank periodic table above, label the locations of the following groups: a) alkali metals c) halogens b) alkaline-earth metals d) noble gases 2. 3. What are the vertical columns of the periodic table called? Determine the mass numbers of the following elements: a) phosphorus b) chlorine c) scandium d) indium 4. 5. 6. 7. e) hydrogen Determine the neutron number for the following elements: a) Mg b) Li c) Se d) I What are two properties that make hydrogen a unique element? Which two elements are liquid at room temperature? Determine the element that corresponds to each property: a) symbol Sb b) has 47 protons c) has 2 neutrons d) has 16 electrons Worksheet 8: Naming Compounds (3.1) 1. 2. 3. Identify the symbols of the elements present in each of the following compounds: a) H2O b) LiCl c) F2 d) Au2S3 Identify the names of the elements present in each of the following compounds: a) H2O b) LiCl c) F2 d) Au2S3 Identify the number of atoms of each element in the following formulas: a) Fe2O3 d) Ag g) Sc2O3 b) Ca3P2 e) CsBr2 h) Na2O c) O2 f) Kr Science 9 – Matter and Chemical Change – Workbook Mr. J. Dulku 4. Write the chemical formula for the following combinations of elements: a) sodium sulphide, which contains 2 atoms of sodium and 1 atom of sulphur b) natural sulphur, which contains 8 atoms of sulphur c) magnesium oxide, which contains 1 atom of magnesium and 1 atom of oxygen d) dinitrogen tetroxide, which contains 2 atoms of nitrogen and 4 atoms of oxygen Worksheet 9: Ionic Compounds (3.2) Complete the following table. All compounds have the solid (s) state. # 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 Chemical Formula (with state!) SrCl2 (s) RbBr (s) Na2O (s) Name of Compound Aluminum sulphide Zinc chloride Magnesium iodide CoCl2 (s) TiO2 (s) Cu2O (s) Tin(II) sulphide Chromium(III) oxide Iron(II) sulphide Fe2O3 (s) ZnO (s) SnF2 (s) Potassium chloride Zinc sulfide Copper(II) chloride Worksheet 10: Molecular Compounds (3.3) 1. Complete the following table. # Chemical Formula a CS2 (l) b NO2 (g) c d SO3 (g) e f g h i P4O10 (s) j PH3 (g) k H2S ( g ) Science 9 – Matter and Chemical Change – Workbook Name of Compound Carbon tetrachloride Dinitrogen monoxide Sulphur dioxide Silicon dioxide Diarsenic trioxide Mr. J. Dulku 2. Identify the type of each compound. Use either “i” for ionic or “m” for molecular”. a) AuCl3 (s) c) CuBr2 (s) e) Cl2 (g) b) N2O (g) d) N2 (g) f) H2O (l) Worksheet 11: Chemical Reactions (4.1) 1. A chemical reaction produces electricity. Is the reaction endothermic or exothermic? 2. A chemical reaction needs heat to proceed. Is the reaction endothermic or exothermic? 3. A chemical reaction results in a bright light. Is the reaction endothermic or exothermic? 4. Identify one example for each of the following types of chemical reactions: a) combustion b) cellular respiration c) corrosion 5. A gas furnace uses the following reaction to produce heat: CH4 (g) + O2 (g) CO2 (g) + H2O (g) a) Identify the formulas of the reactants. b) Identify the formulas of the products. c) Is this reaction exothermic or endothermic? d) Identify two observations that could suggest that this is a chemical change. 6. Write the chemical word equation for each of the following situations: a) magnesium reacts with oxygen to form magnesium oxide b) hydrogen peroxide decomposes into water and oxygen gas c) copper and hydrochloric acid react to form hydrogen gas and copper (II) chloride Worksheet 12: Conservation of Mass in Chemical Reactions (4.2) 1. 2. 50 g of reactant A is combined with 38 g of reactant B. A chemical reaction occurs, producing a solid and a gas. If the mass of the solid is 72 g, what is the mass of gas released? 102 g of white solid is exposed to the air. After an hour, a blue solid and a clear liquid remain. The mass of the blue solid and clear liquid is 146 g. a) Was this an open system or a closed system? Explain. b) Has the mass been conserved? Explain. 3. 53 g of white solid is sealed in a container. After three minutes, the container holds a green solid and pressurized gas. The mass of the green solid is 48 g, while the mass of the gas is 5 g. a) Was this an open system or a closed system? Explain. b) Has the mass been conserved? Explain. 4. 15 g of baking soda is mixed with 23 g of vinegar in a beaker. A gas is produced. The mass of the products is 35 g. a) Was there a lid on the beaker? Explain. b) Account for the change in mass. Science 9 – Matter and Chemical Change – Workbook Mr. J. Dulku Worksheet 13: Factors Affecting the Rate of a Chemical Reaction (4.3) 1. Name the four ways to increase the rate of chemical reaction. 2. A fire in a wood fireplace is occurring slowly. Name two different ways to increase the rate of burning. 3. How is a catalyst different from an enzyme? 4. When a certain type of candy is added to a bottle of pop, rapid fizzing occurs. What is the term given to the candy? 5. How does chewing help food to be better digested? 6. Human saliva contains compounds that help to digest food. What are these compounds called? 7. Storing batteries in a cold environment can make them last longer than at room temperature. Explain how this may occur. 8. Why do potatoes last longer if stored in a refrigerator? Science 9 – Matter and Chemical Change – Workbook Mr. J. Dulku Name: ______________________________________________________ Block: _____ Homework Stamp Sheet Science 9 Matter and Chemical Change Page: 1 Date: /06 Mark: ____ / ___ Late? Yes / No Completed by: ______________ Page: 2 Date: /06 Mark: ____ / ___ Late? Yes / No Completed by: ______________ Page: 3 Date: /06 Mark: ____ / ___ Late? Yes / No Completed by: ______________ Page: 4 Date: /06 Mark: ____ / ___ Late? Yes / No Completed by: ______________ Page: 5 Date: /06 Mark: ____ / ___ Late? Yes / No Completed by: ______________ Page: 6 Date: /06 Mark: ____ / ___ Late? Yes / No Completed by: ______________ Page: 7 Date: /06 Mark: ____ / ___ Late? Yes / No Completed by: ______________ Page: 8 Date: /06 Mark: ____ / ___ Late? Yes / No Completed by: ______________ Page: 9 Date: /06 Mark: ____ / ___ Late? Yes / No Completed by: ______________ Page: 10 Date: /06 Mark: ____ / ___ Late? Yes / No Completed by: ______________ Page: 11 Date: /06 Mark: ____ / ___ Late? Yes / No Completed by: ______________ Page: 12 Date: /06 Mark: ____ / ___ Late? Yes / No Completed by: ______________ Page: 13 Date: /06 Mark: ____ / ___ Late? Yes / No Completed by: ______________ Page: 14 Date: /06 Mark: ____ / ___ Late? Yes / No Completed by: ______________ Science 9 – Matter and Chemical Change – Workbook Mr. J. Dulku