EOC Homework for Honors Biology I
advertisement

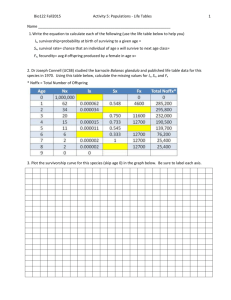
Name ______________________ Number _______ Date_________ EOC Homework for Honors Biology I Ecology: Population and Community Ecology Due Date ________________ 1. Vocabulary Write ALL the definitions for the assigned terms in the unit. Population Emigration Density dependent density Exponential factor Dispersion model Predation Birth rate Limiting factor Interspecific Death rate Logistic model competition Life expectancy Carrying Symbiosis Age structure capacity Parasitism Survivorship DensityMutualism curve independent Commensalism Growth rate factor Disturbance Immigration Stability Ecological succession Primary succession Secondary succession Pioneer species Climax Community Chapter 19 Section 1 1. Explain what birth rate and death rate mean. 2. Compare the three types of survivorship curves. 3. What would the survivorship curve for humans look like if there were a worldwide epidemic of a fatal disease that affected only children under five years of age? 4. Explain the difficulty an ecologist might have in counting a population of migratory birds. Develop and explain a method for estimating the size of such a population. 5. Explain how two populations can be the same size and have different densities. 6. The graph below shows three different types of survivorship curves. a. Which curve corresponds to a species in which 0.3% of the individuals are alive after one-quarter of their lifespan has passed and 0.1% are alive after one-half of their lifespan has passed? Name ______________________ Number _______ Date_________ b. Which curve corresponds to a species in which 95% of the individuals are alive after one-quarter of their lifespan has passed and 90% are alive after one-half of their lifespan has passed? c. Which curve corresponds to a species in which 10% of the individuals are alive after one-third of their lifespan has passed and 1% are alive after two-thirds of their lifespan has passed? d. Give an example of a species that would have each type of survivorship curve. X___________________ Y___________________ Z___________________ Section 2 1. What type of limiting factor is a disease that is transmitted by parasites? 2. Explain the pattern described by the exponential model of population growth. 3. The graph below shows the growth of a population over time. a. Describe the birth rate and death rate in region A. _____________________ b. Describe the birth rate and death rate in region C. _____________________ c. Identify the line labeled K. _______________________________________ d._______________ What model best describes the growth of this population? Section 3 1. How might vaccines against diseases affect population growth? 2. Why did the population growth increase rapidly after Word War II? 3. How is it possible for some countries with low birth rates to have high rates of population growth? Chapter 20 Section 1. 1. What is the difference between the fundamental niche of a species and the realized niche of the species? 2. A biologist finds that when two species of paramecia are grown together in the laboratory, one species always outcompetes and eliminates the other. In ponds and other natural environments, however, the two species coexist. Suggest a hypothesis to explain this phenomenon. Name ______________________ Number _______ Date_________ 4. How does predation on plants differ from predation on animals in terms of the usual effect on the prey? 5. Section 2 1. Explain the relationship between species richness and latitude. 2. Identify differences between primary and secondary succession. 3. Describe how a disturbance could benefit some species in a community. 4. Why does primary succession often proceed very slowly? STRUCTURES AND FUNCTIONS Label each drawing below with the most appropriate term from the following list: pollinator, physical defense, secondary compound, endoparasite, ectoparasite, mimicry. MULTIPLE CHOICE Write the correct letter in the blank. 1. One can estimate a population’s size by counting individuals in a sample of the population if the a. distribution of individuals in the sample is the same as that in the population. b. density in the sample is greater than the population density. c. dispersion in the sample is less than that in the population. d. sample size is larger than the population size. 2. A random distribution of individuals in a population would be most likely to result from a. clumped food resources. b. territorial behavior by the individuals in the population. Name ______________________ Number _______ Date_________ c. herding behavior by the individuals in the population. d. the dispersal of seeds by the wind. 3. Although the United States has a larger total population than Japan, population density is greater in Japan because the a. people in the United States have less education and medical care. b. people in Japan all live in the cities. c. geographical area is greater in the United States. d. birth rate is lower than the death rate in Japan. 4. A population is likely to grow most rapidly if it has a. a high percentage of old individuals. b. a high percentage of young individuals. c. about the same percentage of individuals in each age range. d. individuals with a low birth rate. 5. In a population with a Type I survivorship curve, the likelihood of dying is a. low until late in life, when it increases rapidly. b. high early in life and much lower in older individuals. c. high early in life and late in life, but much lower in middle-aged individuals. d. fairly constant throughout life. 6. One example of a density-dependent limiting factor is a a. forest fire. c. period of very severe weather. b. flood. d. shortage of nesting sites. 7. A country may have a negative growth rate if its a. population is mostly young people.c. death rate is higher than its birth rate. b. birth rate is higher than its death rate. d. population has access to health care. 8. An example of mimicry that is important in anti-predator defenses is when a. a harmless species resembles a dangerous species. b. two harmless species look similar. c. a species resembles an inedible object. d. one individual uses bright colors to warn others of danger. 9. Species that predominate early in the development of a community are called a. pioneer species. c. dominant species. b. climax species. d. succession species. 10. The stable end point of succession is called a. staged community. c. climatic change. b. climax community. d. community development. Standardized Test Prep 1. In a grassland ecosystem, a certain species of predator preys mainly on the large herbivores. Which would most likely result if there were a sudden decrease in the predator population? a. a decrease in primary consumer populations b. An increase in grassland biodiversity Name ______________________ Number _______ Date_________ c. Overgrazing of producers d. Greater competition among predators 2. Which would most likely increase the carrying capacity for a deer population in a forest ecosystem? f. a decrease in parasites g. a decrease in predators h. a decrease in producers j. a decrease in competitors 3. Scientists hypothesize that the use of certain pesticides is causing a decline in the population of honey bees, which pollinate many fruit and vegetable plants. How would a decline in the honeybee population most impact the environment? a. Populations of plants that reproduce asexually would decline. b. Populations of primary consumers would increase. c. Production of some food crops would decrease. d. Flowering plants would produce more nectar. 4. The kudzu plant was imported into the United States as an ornamental plant and was later planted to help soil erosion. Kudzu is a vine that grows in a wide range of conditions and soil types. Due to its rapid growth, the plant has taken over many native plant species, resulting in f. a decrease in biodiversity. g. a decrease in the rate of cellular respiration. h. an increase in surface runoff. j. an increase in habitat for native species. 5. Which environmental disturbance would most likely result in lichens colonizing an area? a. the burning of a forest. b. abandoning farm fields for many years. c. melting of a glacier that exposes rock. d. clearing a meadow for new construction.