99-50sr001doc
advertisement

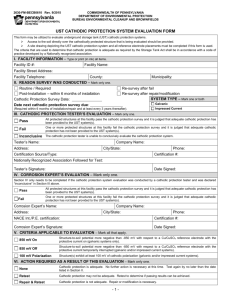
Version No. 001 Electricity Safety (Stray Current Corrosion) Regulations 1999 S.R. No. 50/1999 Version as at 3 May 1999 TABLE OF PROVISIONS Regulation Page PART 1—PRELIMINARY 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 1 Objectives Authorising provisions Commencement Revocation Definitions Prescribed systems Existing cathodic protection systems 1 1 1 1 2 2 3 PART 2—CATHODIC PROTECTION SYSTEMS 4 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. Design and installation of cathodic protection systems Operation of cathodic protection systems Application Waiver or rebate of fee Notification to affected persons Further information Certificate of registration Refusal of registration Register of certificates Notice of operation Provision for testing Audit by the operator Exemption from requirements PART 3—MITIGATION SYSTEMS 21. 22. 23. 24. Installation, operation or use of mitigation systems Applications Refusal of registration Registration i 4 4 4 5 5 6 6 6 7 7 7 7 8 9 9 9 9 10 Regulation 25. 26. 27. Page Modification Expiry of registration Register of certificates 10 10 11 PART 4—GENERAL 28. 29. 30. 12 Details of change Withdrawal of registration Notification of modification __________________ 12 12 12 SCHEDULES 13 SCHEDULE 1—Regulations revoked 13 SCHEDULE 2—Fees for cathodic protection systems 14 ═══════════════ ENDNOTES 15 1. General Information 15 2. Table of Amendments 16 3. Explanatory Details 17 ii Version No. 001 Electricity Safety (Stray Current Corrosion) Regulations 1999 S.R. No. 50/1999 Version as at 3 May 1999 PART 1—PRELIMINARY 1. Objectives The objectives of these Regulations are to— (a) prescribe standards for the operation of cathodic protection systems and mitigation systems; (b) provide procedures for the registration of cathodic protection systems and mitigation systems; (c) protect metallic structures from damage associated with stray current corrosion and cathodic protection and mitigation systems. 2. Authorising provisions These Regulations are made under sections 155 and 157 of the Electricity Safety Act 1998. 3. Commencement These Regulations come into operation on 3 May 1999. 4. Revocation The Regulations listed in Schedule 1 are revoked. 1 Electricity Safety (Stray Current Corrosion) Regulations 1999 S.R. No. 50/1999 Part 1—Preliminary r. 5 5. Definitions In these Regulations— "Cathodic Protection Standard" means Australian/New Zealand Standard 'Cathodic protection of metals—Part 1: Pipes and cables, AS/NZS 2832.1:1998', published jointly by Standards Australia and Standards New Zealand as amended from time to time; "electrolysis drainage bond" means the path by which stray traction current from an underground or underwater metallic structure is returned to its originating source; "galvanic anode" means an electrode used to protect a structure by galvanic action; "impressed current" means direct current supplied by an external power source; "stray current" means current flowing through paths other than an intended circuit; "stray traction current" means current flowing through the ground or water as a result of the operation of any railway or tramway system by a path other than the intended circuit; "the Act" means the Electricity Safety Act 1998. 6. Prescribed systems (1) For the purposes of the definition of "cathodic protection system" in section 3 of the Act, the following systems are prescribed systems— (a) a system which uses galvanic anodes; or (b) a system which uses impressed current. 2 Electricity Safety (Stray Current Corrosion) Regulations 1999 S.R. No. 50/1999 Part 1—Preliminary r. 7 (2) For the purposes of the definition of "mitigation system" in section 3 of the Act, a system which uses electrolysis drainage bonds and associated apparatus, cable and drainage equipment is a prescribed system. 7. Existing cathodic protection systems If permission was granted for a cathodic protection system under the State Electricity Commission (Cathodic Protection) Regulations 19881 and that permission was in force immediately before commencement of these Regulations, the cathodic protection system is to be taken on that date to be registered under these Regulations until a date which is 10 years after the date on which the permission was granted. _______________ 3 Electricity Safety (Stray Current Corrosion) Regulations 1999 S.R. No. 50/1999 Part 2—Cathodic Protection Systems r. 8 PART 2—CATHODIC PROTECTION SYSTEMS 8. Design and installation of cathodic protection systems The owner of a cathodic protection system must ensure that the system is designed and installed in accordance with the Cathodic Protection Standard. Penalty: 20 penalty units. 9. Operation of cathodic protection systems For the purposes of section 93(2) of the Act a cathodic protection system must be operated in accordance with the Cathodic Protection Standard. 10. Application (1) A person may apply to the Office for registration of a cathodic protection system. (2) An application must— (a) be in writing; and (b) include the name and address of the owner and the operator of the cathodic protection system; and (c) be accompanied by— (i) a map showing the location of the proposed cathodic protection system, the metallic structure it is to protect and all metallic structures likely to be affected by the proposed system; and (ii) drawings detailing the proposed system; and (iii) the relevant prescribed fee set out in Schedule 2. 4 Electricity Safety (Stray Current Corrosion) Regulations 1999 S.R. No. 50/1999 Part 2—Cathodic Protection Systems r. 11 11. Waiver or rebate of fee The Office may waive or rebate the relevant prescribed fee in respect to a cathodic protection system if that system has been registered under these Regulations. 12. Notification to affected persons (1) An applicant for registration of a cathodic protection system with a total output over 250 milliamperes must notify all persons whose metallic structures are likely to be affected by stray current from that system. (2) The notice must— (a) give details in writing of the proposed system; and (b) be accompanied by two copies of a map showing the location of the proposed cathodic protection system and the metallic structure it is to protect. (3) A person who is notified under sub-regulation (1) may, within 20 business days from receipt of the notice— (a) return to the applicant one copy of the map showing the location of any metallic structure of that person which is likely to be affected by the proposed system; and (b) inform the applicant in writing that— (i) the person agrees to the proposed system; or (ii) the person objects to the proposed system and give reasons for that objection. (4) On expiry of the period referred to in subregulation (3) the applicant must advise the Office in writing of— 5 Electricity Safety (Stray Current Corrosion) Regulations 1999 S.R. No. 50/1999 Part 2—Cathodic Protection Systems r. 13 (a) any objection made under sub-regulation (3)(b); and (b) any additional metallic structure identified by a person under sub-regulation (3) that is likely to be affected by the proposed system; and (c) correction required to the map given to the Office under regulation 10(2)(c). 13. Further information The Office may require any other information relating to the application that it considers necessary from the applicant. 14. Certificate of registration (1) If the Office is satisfied with a cathodic protection system, the Office may register the system and grant a certificate of registration for the system to the owner of the system. (2) Registration under this Part expires— (a) 10 years after the date it is granted; or (b) when it is withdrawn under these Regulations— whichever occurs first. 15. Refusal of registration The Office may refuse to register a cathodic protection system until testing or modifications have been carried out on the system to the satisfaction of the Office if the Office has reason to believe that any metallic structure, other than the one to which the system is or will be connected, may have its electrical potential with respect to earth changed due to the operation of the system. 6 Electricity Safety (Stray Current Corrosion) Regulations 1999 S.R. No. 50/1999 Part 2—Cathodic Protection Systems r. 16 16. Register of certificates (1) The Office must keep a register of cathodic protection systems. (2) The register must contain the names and addresses of the owner and the operator of registered cathodic protection systems and particulars of each system. 17. Notice of operation A person who is the operator of a registered cathodic protection system must give the Office at least 5 business days notice of intention to commence operation of the system. 18. Provision for testing (1) The owner of any cathodic protection system which uses impressed current must make provision for the insertion of a time switch to enable the power supply to be interrupted for test purposes. Penalty: 20 penalty units. (2) The owner of any cathodic protection system which does not use impressed current must make provision for the circuit between any anode of the system and the metallic structures to be protected to be readily disconnected for test purposes. Penalty: 20 penalty units. 19. Audit by the operator (1) An operator of a registered cathodic protection system must inspect and record the operating current of the system annually. (2) The operator must ensure that the record is available for inspection at all reasonable times by the Office and persons whose metallic structures are affected or likely to be affected by that cathodic protection system. 7 Electricity Safety (Stray Current Corrosion) Regulations 1999 S.R. No. 50/1999 Part 2—Cathodic Protection Systems r. 20 (3) This regulation does not apply to cathodic protection systems using galvanic anodes with a total output up to and including 250 milliamperes. 20. Exemption from requirements The Office may exempt an applicant for registration of a cathodic protection system from the requirement of regulations 10(2)(c)(i), 10(2)(c)(ii) and 12. _______________ 8 Electricity Safety (Stray Current Corrosion) Regulations 1999 S.R. No. 50/1999 Part 3—Mitigation Systems r. 21 PART 3—MITIGATION SYSTEMS 21. Installation, operation or use of mitigation systems A person must not install, operate or use a mitigation system unless the system is registered by the Office and the person has been granted a certificate of registration for that mitigation system. Penalty: 20 penalty units. 22. Applications (1) A person may apply to the Office for registration of a mitigation system. (2) An application must— (a) be in writing; and (b) include the name and address of each person whose metallic structure is connected or is to be connected to the mitigation system; and (c) be accompanied by— (i) a map showing the location of each metallic structure to be connected to the mitigation system; and (ii) evidence of the effects on the metallic structures of the leakage of stray traction current. (3) The Office may require any information about the application and the mitigation system that it considers necessary from the applicant. 23. Refusal of registration The Office may refuse to register a mitigation system until testing or modifications have been carried out on the system to the satisfaction of the Office if the Office has reason to believe that any metallic structure, other than the one to which the 9 Electricity Safety (Stray Current Corrosion) Regulations 1999 S.R. No. 50/1999 Part 3—Mitigation Systems r. 24 system is or will be connected, may have its electrical potential with respect to earth changed due to the operation of the system. 24. Registration (1) If the Office is satisfied with a mitigation system, the Office may register the system and grant a certificate of registration to each person whose metallic structure is or is to be connected to the system. (2) A certificate of registration may be granted on any conditions (including conditions as to testing) as the Office thinks fit. 25. Modification (1) Any person may apply to the Office to modify a registered mitigation system to permit a metallic structure to be connected to or removed from the system. (2) Regulations 22 and 23 apply to an application under sub-regulation (1) as if it were an application for registration of the system. (3) If the Office is satisfied that the modification should be made to the mitigation system, it may register the modification to the system and issue a new certificate of registration to all persons who are the owners of metallic structures connected or to be connected to the system. 26. Expiry of registration (1) Subject to sub-regulation (2) registration under this Part expires— (a) 10 years after the date it is granted; or (b) if the system is modified, 10 years after the date that the latest modification is registered under regulation 25. 10 Electricity Safety (Stray Current Corrosion) Regulations 1999 S.R. No. 50/1999 Part 3—Mitigation Systems r. 27 (2) If a registration is withdrawn under these Regulations, the registration expires. 27. Register of certificates (1) The Office must keep a register of mitigation systems. (2) The register must contain details of all registered systems and certificate holders including the names and addresses of all persons owning metallic structures connected to a mitigation system and particulars of each connection. _______________ 11 Electricity Safety (Stray Current Corrosion) Regulations 1999 S.R. No. 50/1999 Part 4—General r. 28 PART 4—GENERAL 28. Details of change A certificate holder must give the Office details of a change of name or address within 20 business days of the change occurring. 29. Withdrawal of registration (1) The Office may withdraw the registration of a cathodic protection system or a mitigation system if a person to whom a notice is given under sections 95 or 96 of the Act fails to comply with the directions in that notice. (2) The Office must notify a certificate holder in writing 10 business days before it withdraws the registration. 30. Notification of modification If a person— (a) changes or becomes aware of any change in the operation of a cathodic protection system or a mitigation system that is likely to damage any metallic structure; or (b) removes a cathodic protection system altogether— that person must notify the Office verbally within 4 business days and in writing within 10 business days. Penalty: 20 penalty units. __________________ 12 Electricity Safety (Stray Current Corrosion) Regulations 1999 S.R. No. 50/1999 Sch. 1 SCHEDULES SCHEDULE 1 REGULATIONS REVOKED S.R. No. Regulations Title 207/1988 State Electricity Commission (Cathodic Protection) Regulations 1988 251/1993 State Electricity Commission (Cathodic Protection) (Amendment) Regulations 1993 _______________ 13 Electricity Safety (Stray Current Corrosion) Regulations 1999 S.R. No. 50/1999 Sch. 2 SCHEDULE 2 Fees FEES FOR CATHODIC PROTECTION SYSTEMS Examination of cathodic protection system with a total output up to and including 250 milliamperes $125 Examination of cathodic protection system with a total output over 250 milliamperes and up to and including 2 amperes $250 Examination of cathodic protection system with a total output over 2 amperes $500 ═══════════════ 14 Electricity Safety (Stray Current Corrosion) Regulations 1999 S.R. No. 50/1999 Endnotes ENDNOTES 1. General Information The Electricity Safety (Stray Current Corrosion) Regulations 1999, S.R. No. 50/1999 were made on 28 April 1999 by the Governor in Council under sections 155 and 157 of the Electricity Safety Act 1998, No. 25/1998 and came into operation on 3 May 1999: regulation 3. The Electricity Safety (Stray Current Corrosion) Regulations 1999 will sunset 10 years after the day of making on 28 April 2009 (see section 5 of the Subordinate Legislation Act 1994). 15 Electricity Safety (Stray Current Corrosion) Regulations 1999 S.R. No. 50/1999 Endnotes 2. Table of Amendments There are no amendments made to the Electricity Safety (Stray Current Corrosion) Regulations 1999 by statutory rules, subordinate instruments and Acts. 16 Electricity Safety (Stray Current Corrosion) Regulations 1999 S.R. No. 50/1999 Endnotes 3. Explanatory Details 1 Reg 7: S.R. No. 207/1988. —— Table of Applied, Adopted or Incorporated Matter Required by Subordinate Legislation Regulations 1994 Note that the following table of applied, adopted or incorporated matter is included in accordance with the requirements of regulation 6 of the Subordinate Legislation Regulations 1994. Statutory Rule Provision Title of applied, adopted or incorporated document Matter in applied, adopted or incorporated document Regulation 8 and 9 Australian/New Zealand Standard 'Cathodic protection of metals—Part 1: Pipes and cables, AS/NZS 2832.1:1998', published jointly by Standards Australia and Standards New Zealand, as amended from time to time Whole 17