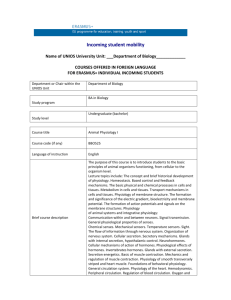
PRACTICAL CLASSES (LABS) American and Taiwan STUDENTS I
advertisement

PRACTICAL CLASSES (LABS) American and Taiwan STUDENTS I/4, and American, Taiwan and Arabic STUDENTS III/6 Spring semester LAB 1 THE CIRCULATION – PART 1 CONTROL TEST (10 QUESTIONS) OBLIGATORY THEORETICAL KNOWLEDGE: Textbook of Medical Physiology (12th Edition) – A. C. Guyton and J. E. Hall Chapters: 14-16 General functions of big and small circulation. Functions of arteries. Functions of veins. Blood flow – types, velocity. Pulse – its mechanism, features and importance in medicine. Blood pressure – types, method of investigation. Systemic blood pressure - factors determining its value. EXPERIMENTAL PART 1. Arterial pulse examination and determination of its features. 2. Venous pulse examination and determination of its feature. 3. Resting blood pressure measurement. 4. Examination of different factors impact on the size of arterial pressure and pulse. body position impact (standing, sitting, lying position) • impact of rapid position change (orthostatic test) • impact of gravity (impact of raised arm or lowered arm in the comparison with heart position) • impact of the pressure in the chest (maximal inspiration position or maximal expiration position) e-Fizjologia – computer simulations LAB 2 THE CIRCULATION – PART 2 CONTROL TEST (10 QUESTIONS) OBLIGATORY THEORETICAL KNOWLEDGE: Textbook of Medical Physiology 12th Ed. – A. C. Guyton and J. E. Hall Chapters: 16-18; pp. 177-211; Chapter 21, pp. 243-253 Local regulation of blood flow: acute, nervous, humoral, chemical. Autoregulation. Long-term (angiogenesis, development of collateral circulation). Specificity of cardiac, pulmonary, brain and renal circulation. Blood flow in skeletal muscle. Functions of capillaries. Role of lymphatic system and its importance in medicine. EXPERIMENTAL PART Films and Computer exercises (e-Fizjologia). Blood flow in vessels of frog’s foot webbing Blood flow in frog’s tongue – resting flow and influence of different substances LAB 3 RESPIRATORY PHYSIOLOGY CONTROL TEST (10 QUESTIONS) OBLIGATORY THEORETICAL KNOWLEDGE: Textbook of Medical Physiology 12th Ed. A. C. Guyton and J. E. Hall Chapters: 37 and 38; pp.465-484 and Chapters: 39-41; pp. 485513 Mechanics of breathing. Events during inspiration and expiration. The work of breathing. Lung compliance. Surface tension of alveoli and role of surfactant. Airflow and resistance within the airways. Measurement of pulmonary function. Lung volumes and capacities. Alterations of ventilatory mechanics in diseases. Neural and chemical control of respiration. Normal and abnormal patterns of breathing. Mechanisms of tissue hypoxia. Transport of oxygen and carbon dioxide in blood and tissue fluids. EXPERIMENTAL PART Measurement of peak expiratory flow using Mini-Wright Peak Flow Meter. Measurement of the main spirometric parameters during a test of “forced expiration" using Spirodoc. Simulations of restriction and airways obstruction – using Spirodoc Respiratory physical examination: • inspection of the thorax during normal respiration and during hyperventilation • palpation of the chest wall (assessment of tactile fremitus) • auscultation of the lung Influence of different factors on respiratory pattern (e-Fizjologia) LAB 4 ENDOCRINOLOGY Textbook of Medical Physiology A. C. Guyton and J. E. Hall 12th ed. Chapters 74-77, pp. 881-937 Coordination of body functions by chemical messengers. Chemical structure and synthesis of hormones. Hormone secretion, transport, and clearance from the blood. Mechanisms of action of hormones. Measurement of hormone concentrations in the blood. Pituitary gland and its relation to the hypothalamus. Thyroid metabolic hormones. Adrenocortical hormones. LAB 5 Hormones Textbook of Medical Physiology A. C. Guyton and J. E. Hall 12th ed. Chapters 78-79, pp. 939-972 Insulin, glucagon and diabetes mellitus. Insulin synthesis, chemistry and action. Effect of insulin on carbohydrate, fat and protein metabolism. Insulin secretion. Glucagon and its function. Effects of glucagon on glucose metabolism. Regulation of glucagon secretion. Diabetes Mellitus. Parathyroid hormone, calcitonin, calcium and phosphate metabolism. LAB 6 PHYSIOLOGY OF DIGESTIVE SYSTEM 1 CONTROL TEST (10 QUESTIONS) OBLIGATORY THEORETICAL KNOWLEDGE: Textbook of Medical Physiology by A.C. Guyton and J.E. Hall, 12th Edition; Chapters 62-65; pp. 753-798. 1. General principles of gastrointestinal function. (motility, nervous control and blood circulation, propulsion and mixing of food in the alimentary tract) 2. Secretory functions of the alimentary tract. 3. Digestion and absorption in the gastrointestinal tract. (processes in oral cavity, characteristics and activity of oesophagus, functions of stomach, role of duodenum and other parts of small intestine, functions of large intestine, especially of colon) EXPERIMENTAL PART: Films and computer simulations (e-Fizjologia) LAB 7 PHYSIOLOGY OF DIGESTIVE SYSTEM 2 CONTROL TEST (10 QUESTIONS) OBLIGATORY THEORETICAL KNOWLEDGE: Textbook of Medical Physiology by A.C. Guyton and J.E. Hall, 12th Edition; Chapters 66, pp. 799-805; Chapter 70, 837-842. 1. Physiology of gastrointestinal disorders. 2. Digestive and non-digestive role of pancreas. 3. Digestive and non-digestive role of liver (vascular functions, secretory functions, metabolic functions, other functions). EXPERIMENTAL PART: 1) Endoscopic examination of digestive system – film 2) Methods of digestive system examination. a) Gallstones and acute cholecystitis, b) Achalasia, c) Zollinger-Ellison Syndrome, d) Lactose intolerance, e) Vibrio Cholerae infection. LAB 8 PHYSIOLOGY OF KIDNEY PART 1 CONTROL TEST (10 QUESTIONS) OBLIGATORY THEORETICAL KNOWLEDGE: Textbook of Medical Physiology by A.C. Guyton and J.E. Hall, 12th Edition;Chapters 25 and 26, pp. 285-322. 1. Functional anatomy of kidney. nephron (structure, number and types), components of the nephron, renal blood flow differences between blood flow of cortex and medulla, features of particular types of renal vessels in comparison with peripheral vessels, functional localization of glomeruli 2. Principles of nephron functioning. plasma filtration in the glomerulus, selective reabsorption in tubules, tubular secretion, urine secretion 3. Plasma filtration in glomeruli. structure and feature of filtration membrane, net filtration pressure, amount and composition of glomerular filtrate 4. Regulation of GFR (glomerular filtration rate) and RBF (renal blood flow). autoregulation of GFR and RBF, nervous system control, humoral regulation, the role of mesangial cells EXPERIMENTAL PART: Films and computer simulations (e-Fizjologia) LAB 9 PHYSIOLOGY OF KIDNEY PART 2 CONTROL TEST (10 QUESTIONS) OBLIGATORY THEORETICAL KNOWLEDGE: Textbook of Medical Physiology by A.C. Guyton and J.E. Hall, 12th Edition;Chapters 27-29, pp. 323-378; Chapter 31, pp. 397-410 1. Processing glomerular filtrate in tubules. structure of reabsorption membrane, net reabsorption pressure, mechanism of crossing particular elements through the wall of tubules, the differences in absorption ability of the particular parts of the nephron, maximal transport and tubular load of different substances, tubular secretion of H+ and K+, amount and volume of urine. 2. Tubular reabsorption regulation. glomerulotubular balance, hormonal regulation - the significance of ADH, aldosterone, angiotensin II, ANP, parathyroid hormones; blood pressure impact - pressure-diuresis and pressure-natriuresis, nervous system impact 3. Renal mechanisms of blood osmolarity regulation and Mechanisms of urine secretion. the role of hypothalamus, water removal with urine - mechanism of urine dilution, maximal water diuresis, mechanism of urine concentration, countercurrent multiplier, countercurrent exchangers, obligatory urine volume 4. Renal clearance and its clinical significance. inulin clearance and endogenic creatinine clearance and the size of glomerular filtration, PAH clearance and the size of the red blood flow, osmotic clearance and free water clearance and kidney ability to concentrate and dilute urine 5. Endocrinologic functions of kidney. LAB 10 ARTERIAL BLOOD PRESSURE & KIDNEYS: Role of the kidneys in regulation of arterial pressure CONTROL TEST (10 QUESTIONS) OBLIGATORY THEORETICAL KNOWLEDGE: Textbook of Medical Physiology by A. C. Guyton and J. E. Hall, 12th Edition Chapter 19, pp 213-228; Chapter 29, pp 361-378 1.The baroreceptor feedback mechanism and arterial pressure 2.Effect of arterial natriuretic factor (ANF) on pressure 3.Role of antidiuretic hormon (ADH) 4.The renin – angiotensin system 5. Role of aldosteron on the control of blood volume 6.Types of hypertension EXPERIMENTAL PART: Films and computer simulations (e-Fizjologia) Essential hypertension – a short presentation LAB 11 ACID-BASE BALANCE CONTROL TEST (10 QUESTIONS) OBLIGATORY THEORETICAL KNOWLEDGE: Textbook of Medical Physiology by A. C. Guyton and J. E. Hall, 12th Edition Chapter 30, pp 379-396. 1.Acid-base homeostasis 2.Buffers – their types and role 3.Effect of plasma proteins on pH 4.Acids and bases in the human body come from many sources. 5.Metabolic acidosis and alkalosis 6.Physiology of treatment in acidosis and alkalosis EXPERIMENTAL PART: Computer exercices (e-Fizjologia) Causes of the respiratory acidosis and alkalosis Causes of the metabolic acidosis and alkalosis Lab 12 Backlog – in case of missed quizes (if absence is excused) or lacking points to take FINAL Exam LECTURES FOR American and Taiwan STUDENTS I/4, and American, Taiwan and Arabic STUDENTS III/6 Spring semester LECTURE 1 CIRCULATION The circulation. Overview of the circulation. Medical physics of pressure, flow, and resistance. Vascular distensibility and functions of the arterial and venous systems. The microcirculation and the lymphatic system. Capillary fluid exchange. Interstitial fluid. Lymph flow LECTURE 2 REGULATION OF CIRCULATION Local and humoral control of blood flow by the tissues. Nervous regulation of the circulation. Rapid control of arterial pressure. Reflex control of arterial pressure. LECTURE 3 RESPIRATORY PHYSIOLOGY Respiration. Mechanics of pulmonary respiration. Pleural pressure. Compliance of the lungs. Surfactant. Work of breathing. Alveolar ventilation. Pulmonary circulation. Gas exchange. Transport of oxygen and carbon dioxide in the blood. Regulation of respiration. Respiratory centre. Reflex and Chemical control of respiration. LECTURE 4 HORMONES Endocrine glands and their hormones. Types of hormones. Storage and secretion of hormones. Mechanisms of action. Pituitary hormones and their control by hypothalamus. The thyroid hormones. Adrenocortical hormones. Hormonal function of the male and the female. LECTURE 5 GASTROINTESTINAL TRACT Gastrointestinal function. Smooth muscle. Types of smooth muscles. Mechanism of Contraction. Effect of hormones on smooth muscle. Enteric nervous system. Types of movements in the gastrointestinal tract. Gastrointestinal bloody supply. Ingestion of food. Mastication. Swallowing. Functions of the stomach. Emptying of the stomach. Movements of the small intestine. Movements of the colon. Defecation. LECTURE 6 DIGESTION Secretory functions of the alimentary tract. Role of salivary glands. The function of the liver and pancreas. Absorption of nutrients and water. LECTURE 7 PHYSIOLOGY OF THE KIDNEY part 1 The kidneys. Basic functions in homeostasis. Physiologic anatomy of the kidney. The nephron. Glomerular filtration. Composition of the glomerular filtrate. Glomerular filtration rate. Renal blood flow. Control of glomerular filtration. The juxtaglomerular complex. LECTURE 8 PHYSIOLOGY OF THE KIDNEY part 2 Mechanisms of reabsorption in renal tubules. Reabsoption of water and ions. Control of tubular reabsorption. Active secretion. Transport maximum. Excretion of dilute and concentrated urine. LECTURE 9 ARTERIAL BLOOD PRESSURE REGULATION Renal regulation of arterial pressure. Control of blood volume. Effects of nervous, hormonal, humoral factors on the blood volume. Quantitation of pressure diuresis and arterial pressure control. Control of extracellular fluid volume. Control of the extracellular concentrations of ions. Integrated system for pressure regulation in human body. LECTURE 10 ACID-BASE BALANCE REGULATION Regulation of acid-base balance. pH of body fluids. Function of acid-base buffers. Respiratory regulation of acid-base balance. Renal mechanisms in acid-base balance. Rapidity of acidbase regulation by kidney. Clinical aspects of acid-base balance: the acids and bases definitions, types of acidosis and alkalosis and their effects on the human body.