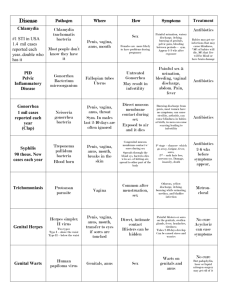
Disease

Disease
Vaginitis
In men -
Balanitis
Pathogen Where How Symptoms Treatment
Chlamydia gardnerella herpes, candidiasis herpes, trichomonas mycoplasma
Caused by virus monilia
Vagina, penis, anus, throat
Usually sex, but can be transferred without sex
Moist items containing organism
Pain, discharge, secretes a white liquid, irritation, redness, itching, odor, secretion thickens during cycle
Antibiotics, other drugs depending on cause
Pubic Lice
(crabs)
Pediculosis pubis
Pubic hair
Sex, bedding, toilets, clothing
Itching, rash, pinhead-sized blood spots on underwear
Medical lotion and shampoos
Trichomoniasis Protozoan parasite
Vagina
Common after menstruation, sex
Odorous, yellow discharge, itching, burning while urinating, urethra, and bladder infection
Metroncloral
Scabies
Gonorrhea
1 mil cases reported each year
(Clap)
Parasitic mite that burrows under the skin
Skin contact
Attach their eggs to hair shafts
Sex, but sometimes no sex, clothing, bedding must be washed and dried in heat
Itching in the genital area
Feeds off blood vessels of the skin
Neisseria gonorrhea bacteria
Medical lotion and shampoos
Penis, vagina, anus, throat
Sym. In males last 2-10 days are often ignored
Direct mucous membrane contact during sex
Exposed to air and it dies
Burning discharge from penis, most women have no symptoms, can cause sterility, arthritis, can cause blindness in babies at birth, in men can cause scarring leading to infertility
Antibiotics
Genital Warts
Human papiloma virus
Genitals, anus
PID
Pelvic
Inflammatory
Disease
Gonorrhea
Bacterium microorganism
Fallopian tubes
Uterus
Sex
Untreated
Gonorrhea
May result in infertility
Warts on genitals and anus
No cure
But podophylin, laser or liquid nitrogen surgery may get rid of it
Painful sex & urination, bleeding, vaginal discharge, abdom. Pain, fever
Antibiotics
Disease
Hepatitis A
Pathogen
Hepatitis A virus
Where
Mouth
How Symptoms
Treatment
Anal- oral sex, contaminated water
Flu-like symptoms, dark urine, abdominal pain, jaundice
No Cure
Hepatitis B
Hepatitis B virus
Penis, vagina, anus, mouth, skin breaks, blood
Non-Gonococal
Urethrits
(NGU)
Chlamydia
#1 std in USA
3-10 mil cases reported each year
Chlamydia ureaplasma mycoplasma trichomonas
Chlamydia trachomatis bacteria
Most people don’t know they have it
Penis, vagina, anus, throat
Penis, vagina, anus, mouth
Saliva, sex, blood, needles, etc.
Direct mucous membrane contact during sex
Flu-like symptoms, dark urine, abdominal pain, jaundice
Men – watery or milky discharge from penis
Women – burning urination
No Cure
Antibiotics
& other drugs depending on causes
Sex
Females are more likely to have problems during pregnancy
Painful urination, watery discharge, itching, burning of genitals, pelvic pain, bleeding between periods--- sym.
Appear 1-3 wks after exposure
Antibiotics
Babies may get eye infections that may cause blindness,
*50% of babies will die, 50% that live will be blind or have brain damage
Genital Herpes
Herpes simplex
II virus
Two types:
Type I – above the waist
Type II – below the waist
Penis, vagina, anus, mouth, transfer to eyes if sores are touched
Direct, intimate contact
Blisters can be hidden
Painful blisters or sores on the genitals, swollen glands, fever, headaches, tiredness
Takes 2-10 days develop
Can be caused stress and worries
No cure
Acyclovir can ease symptoms
Syphilis
90 thous. New cases each year
Treponema pallidum bacteria
Blood born
Penis, vagina, anus, mouth, breaks in the skin
Congenital mucous membrane contact w/ sores during sex
Spreads through the blood sys, bacteria dies w/in sec. of hitting air, spread to other part of the body
1 st stage – chancre- which go away, fatigue, fever, sores,
2 nd – rash hair loss, nervous sys. Damage, insanity, death
Antibiotics
2-6 wks before symptoms appear,
AIDS
HIV – human immunodeficiency
Virus
Penis, vagina, anus, mouth, blood, mucous membrane
Sex, sharing needles, mother to baby, transfusions
Skin rashes, diarrhea, fever, weight loss, dry cough, swollen glands, loss of appetite, opportunistic infections, death
No cure
STD –cup activity
AIDS Test
Match the following term with the definition.
1.Lymophocyates F
2.Antibodies D
3. HIV
4. AIDS
J
E
A. a test to determine the presence of antibodies for HIV
B. disorder that destroys the
brain tissue
C. helps fight infection
D. proteins that destroy or neutralizes pathogens in your
5. Western blot I
6. ELISA A
7. AIDS dementia B body
E. a fatal communicable disease
caused by HIV
F. a white blood cell that destroys invading pathogens
G. a gradual deterioration of all
body functions
8. Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia H H. an opportunistic infection associated with AIDS
9. Mycobacterium avium intracellular G I. A test that is very specific in
10. T helper cells C identification of HIV antibodies
J. virus that attacks the body’s
immune system
Complete the following.
11.
What does AIDS stand for?
Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome
12.
What does HIV stand for?
Human Immuneodeficiency Virus
13.
What does ELISA stand for?
Enzyme Linked Immuno Sorbent Assay
14.
Name two ways to contract HIV.
Needles, blood, sex, mom to baby
15.
Name two major types of lymphocytes.
B & T
True or False
16.
HIV can be transmitted through casual contact.
-F
17.
Taking unhealthy risks will increase your chances of contracting
HIV.
-T
18.
It only takes 6 months for HIV to show up .-F
19.
There is a cure for HIV and AIDS.
-F
20.
Symptoms such as a fever, body aches, rashes, and the inability to fight infections are some signs of HIV.
-T