Igneous Rocks
advertisement

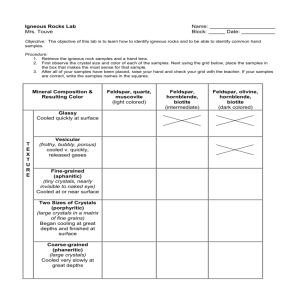
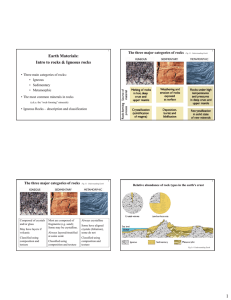
Igneous Rocks A rock is a group of minerals bound together in some way. Igneous rocks are formed by the cooling and hardening of molten rocks. a) Intrusive (plutonic) - form below the Earth’s surface b) Extrusive (volcanic) – form above the Earth’s surface Texture refers to the size of the crystals in an igneous rock I Intrusive (plutonic) Igneous Rocks Magma is molten rock underneath the Earth’s surface. Intrusive igneous rocks cool slowly deep within the earth and produces large crystals Intrusive igneous rocks will result in a very coarse (pegmatite) or coarse (phaneritic) texture (ex. granite) II Extrusive (volcanic) Igneous Rocks Lava is molten rock that pours out onto the Earth’s surface. Volcanic rocks lack distinct mineral grains due to rapid cooling of lava at the Earth’s surface Extrusive igneous rocks will result in fine (aphanitic) texture (ex. basalt) If the cooling is instantaneous a glassy texture may form (ex. obsidian) If gas bubbles are trapped as the lava rapidly cools a vesicular texture may occur (pumice) III Porphyritic rocks contains two stages of cooling. cools first at great depth forming large crystals still surrounded by magma it is then rushed to the surface and the remaining liquid around it cools quickly forming fine-grained crystals VI Common Igneous Rocks Granite- quartz, orthoclase feldspar, and at least one other mineral; light-colored; coarse-grained; makes up continents; felsic Ryolite- fine-grained granite; felsic Obsidian- volcanic glass; rapid cooling; pyroclastic; felsic Pumice- sponge-like because of escaping air bubbles during cooling; felsic Basalt- fine-grained; dark-colored; makes up the ocean floor; mafic Gabbro- coarse-grained basalt; mafic Diabase- grain size inbetween basalt and gabbro; mafic Basalt glass- mafic obsidian Scoria- mafic pumice