The World of Plants – What you need to know
advertisement

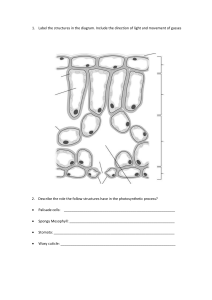
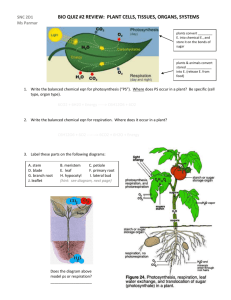
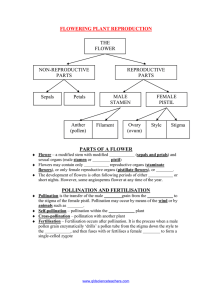
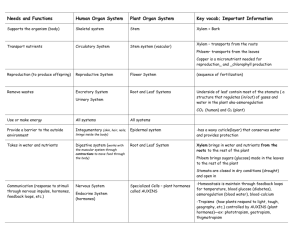
The World of Plants – What you need to know The numbers refer to pages in ‘Leckie & Leckie Success Guide’ Introducing plants (p18-19) G Give four examples of advantages of their being a wide variety of plants C Explain possible results of a reduction in the variety of plants G Describe three specialised plant uses (raw materials, food, medicine) C Describe a plant production process e.g. malting barley C Describe two potential uses of plants e.g. new medicines, new food sources Growing plants (p20-25) G Describe the function of the seed coat, embryo and food store in a seed G Describe the effect of temperature, water availability and oxygen on germination C Explain how percentage germination of seeds varies over a range of temperatures G Describe the functions of the parts of a flower (sepal, petal, stamen, anther, stigma, ovary, nectary) C State and explain the differences between wind and insect pollinated flowers G State the meanings of pollination and fertilisation G Describe the difference between self pollination and cross pollination C Describe the growth of the pollen tube and fusion of the sex cells G Describe fruit formation after fertilisation C Describe one example of each of the three dispersal mechanisms (wind, animals – internal, animals – external) G Describe artificial propagation by cuttings and grafting C Explain the advantages to man of artificial propagation C State that a clone is a genetically identical group of plants produced from a single parent G Describe asexual reproduction by runners and tubers C Describe the advantages of both sexual and asexual reproduction to plants Making food (p26-31) G Explain the need for transport systems in plants C Describe the structure of xylem and phloem tissue C Explain how xylem cells provide support to the plant G Describe the pathway of movement of water, minerals and food in the xylem and phloem G State that plants take in carbon dioxide from the air through stomata can open and close C Describe the structure and function of the different parts of a leaf (cuticle, epidermis, palisade mesophyll, spongy mesophyll) G State that water vapour is lost through open stomata G State that green plants make their own food which is stored as starch C State that the product of photosynthesis may be converted to structural or storage carbohydrates, or used as an energy source G State that green plants use chlorophyll to convert light energy to chemical energy G Give a word equation for photosynthesis, and identify the raw materials and products C Explain what is meant by a limiting factor, and describe the main limiting factors in photosynthesis