Catchment management case studies
advertisement

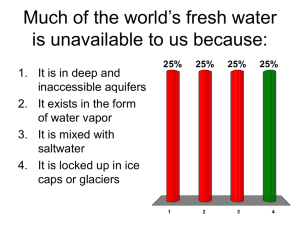
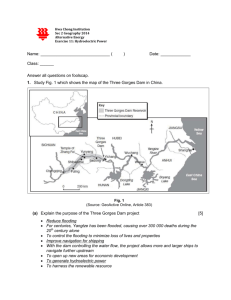
Raffles Junior College JC 1 Physical Geography Catchment Management Revision Pointers Aral Sea Arid zoneAral sea drying upships abandonedcoastline receding Causes Soviet schemeintended for the Aral to recede by diverting two rivers which fed Aral Sea. By lowering Aral Sea’s level, it would boost the two other river’s potential for hydroelectric power. River water was also removed to irrigate the desert to grow valuable crops such as cotton. Lots of water was taken from Aral for growing of cottonlimited success due to salty water. Even more water was used up in effort to flush away salt in waterlogged soil. Impacts Fishing industry declinefishes all dead due to high salinity levels Growth of salty desert/ Salt-filled soil is infertile Social impact on local people o Health problems (one baby in ten dies before its first birthday) o Water supplies polluted by chemicals washed from cotton fields upstream o Salty dust attacks human throats and lungs Responses Minimise cotton growth as it requires lots of water The 5 countries have pledged 1% GDP each to save the river Build dam for water supply Cut water supply to canal 1 River Nile Arid environment 10 riparian states with 300 million people (more than 40% of world’s population) Causes Cotton growing in Egypt and Sudanunder Britain’s control and pressure to expand growth European “grab” of the area and parts of the Nile. Britain controlled Lake Victoria, source of the Nile Building of dams for HEP and irrigation purposes High loss of water to evaporation Emperor of Ethiopia agreement with Britain (lasts up till today) not entitled to use the water Impact Egypt dominates use of the Nile (more than 2/3 of water) Aswan Dambenefits 60 million people River delta has seen change in formation Monuments are affected Response Talks for a more equitable share of water Suggestion that Egypt should reduce or stop growing of cotton (too high a level of water consumption) River Jordan 200km long Spans through several countries Desert area Politically/culturally and religiously complex area Causes 2 Building of canals for large-scale irrigation of desert Villages claim land for farmingincrease in demand for water Massive farming to increase food supply Rapid population growth due to migration Underground water being tapped at an unsustainable rate esp. by Israel Plants which water comes from are controlled by Israel. Impacts Israel has dominant control over usage and consumption of water Resort to tapping of groundwater Palestinian and Jordanian having limited access to waterneed to apply for to Israeli authorities for permission to drill for water trapped in the reservoirs Palestinians not allowed to build deep wells River is shrinking Response Water conflicts and war? Treaty for more equitable distribution of water (suggestion) River Colorado Arid desert 40 million people in 7 states Naturally high salt content made more concentrated by high temp. and rocks in irrigation areas Causes High usage (tourism and recreation) River is regulated to the maximumprovides water that irrigates farms and vineyards Ground water reserves are depleting at an alarming rate 3 Hoover Dam- Over regulates the river and builds up silt Canals for farming and irrigation of crops in California Wasteful methods of irrigation crop surplus, yet farmers are heavily subsidized for irrigation Evaporation (massive) Urbanisation and population growthincreased demand and living standards Impacts Tap on groundwater/aquifer (drying outland subsides leaving salt on soil) Conflicts (residents vs. visitors) Conflict over right of water (farmers vs. Native tribal Americans) Farming under threat Response Colorado Compactagreement between states to control river usage California has laws controlling excessive use of water in droughts Recycling of water Three Gorges Dam Yangtze is one of the world’s fastest and most dangerous riversmajor flood once every ten years 1998 Great Floodone of the worst floodsdestroyed 1/10 of China’s grain supplyenormous human costs, fighting and repairing damagethreatened to destabilize China’s economy Causes Construction of dam to prevent flooding Impacts Protect 10 million people from flooding High risk construction 4 Hydro Electric Powerinexpensive way of generating powergeneration of 18.2 million kilowatts of electricitylargest power plant in the world supplying power needed by a city four times the size of LAreduce China’s dependence on coal Inundation behind dam Volume of shipping expected to increase five-foldbetter for economy Loss of shipping passageshipping elevator and system of locks Loss of some cities/villages and its sense of community Loss of crop growing areas with fertile soil for previously self-sufficient communities Resettlement of communities in upstream areas (1.13 million), e.g. Fongdu, Fuling Loss of traditional thought, ancient temples and beautiful landscape Piling up of silt behind reservoir create huge flooding problem upstreamoccur more frequently May trigger off earthquake and landslides as the dam sits on a fault line Destruction of historical artifacts and archaeological treasures including Zhang Fei temple Species such as the Chinese river dolphin and Chinese paddlefish are near extinction Response Some strong village communities have chosen to build their new villagepulling together government compensations so they can build the village they enjoy. Management of river catchments creating conflicts of interests Management Issues Urbanization (Colorado River, Three Gorges Dam) Vegetation Changes (Aral Sea, Three Gorges Dam, Colorado River) Extraction from aquifers (River Jordan, Colorado River) Water quality (Aral Sea) Changes in river delta formation (River Nile) Sedimentation/Silting of river (Three Gorges Dam) 5 Conflict of Interests Shared water resources (All except Three Gorges Dam) Damming (Three Gorges Dam) Control of water by upstream states (River Nile & Jordan River) Pollution (Aral Sea) Cultural issues (Three Gorges Dam, River Nile) Responses to Conflict of Interests Political o Treaties (Colorado River, possible for Jordan River, River Nile, Aral Sea) o Hydrowars (possibly for River Nile & Jordan River) Economic o Economic Cooperation o Economic dominance Environmental o Joint efforts to protect the environment (Aral Sea, River Nile) o Changes to freshwater technology (Colorado River) 6